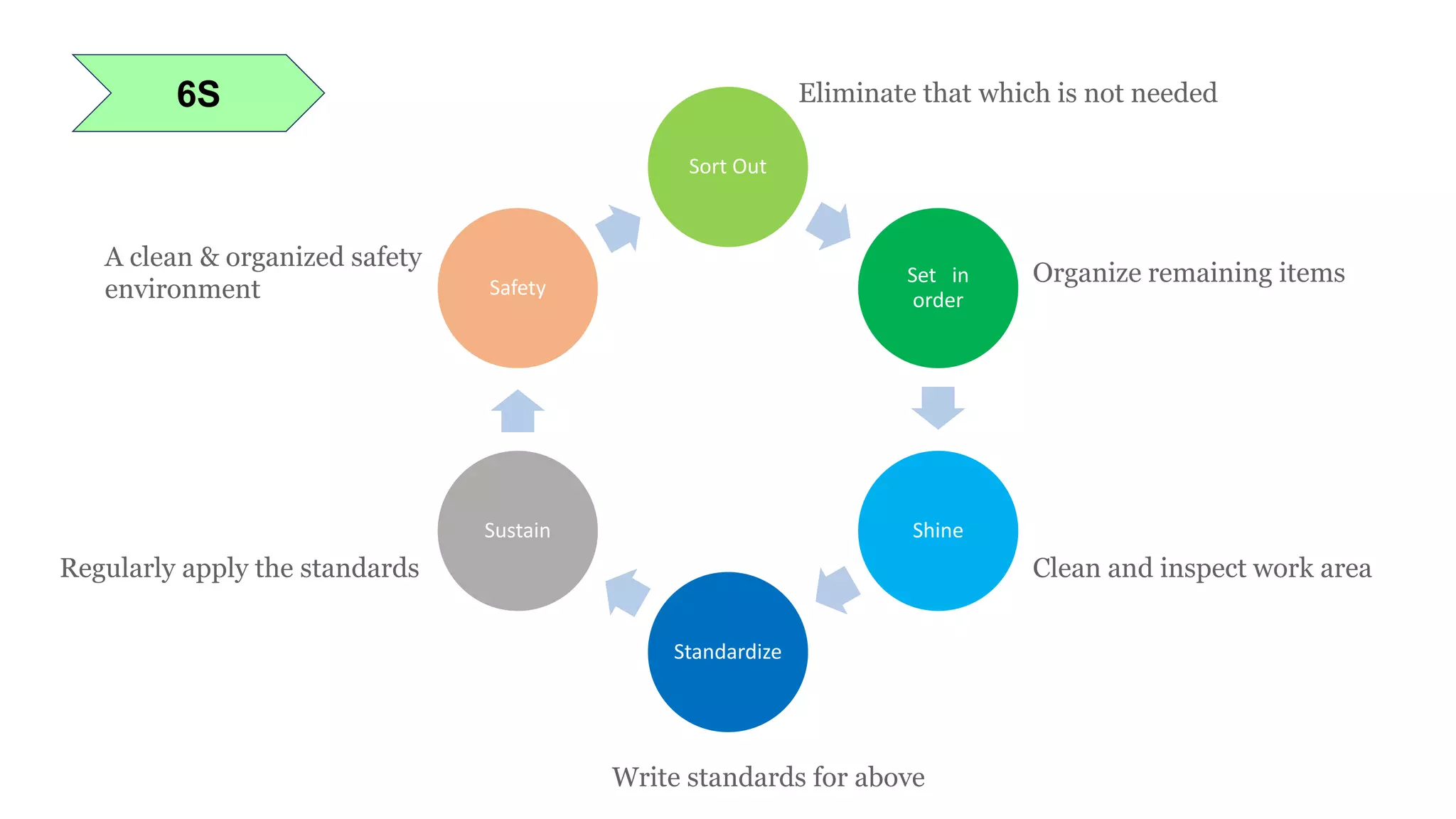
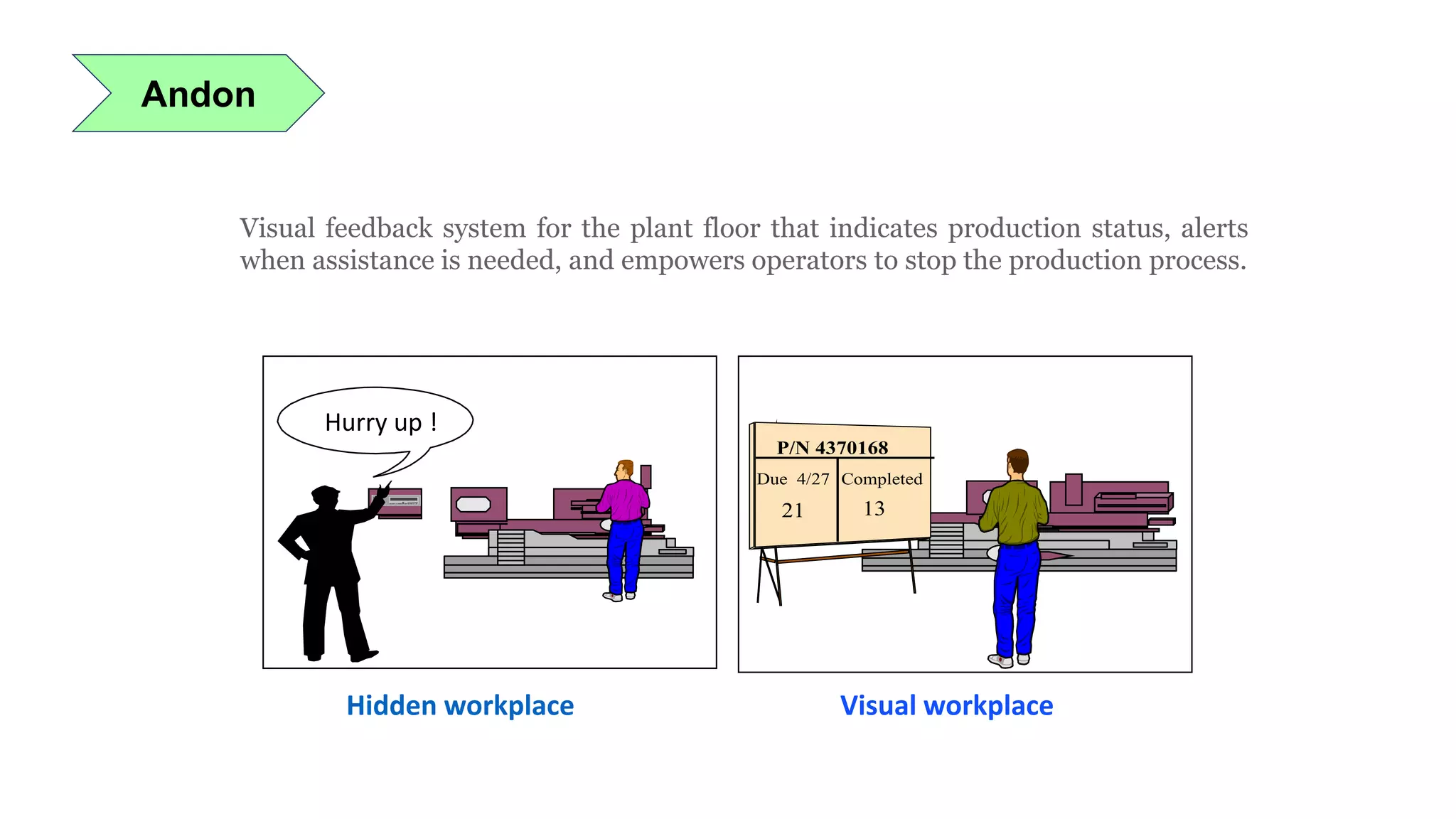
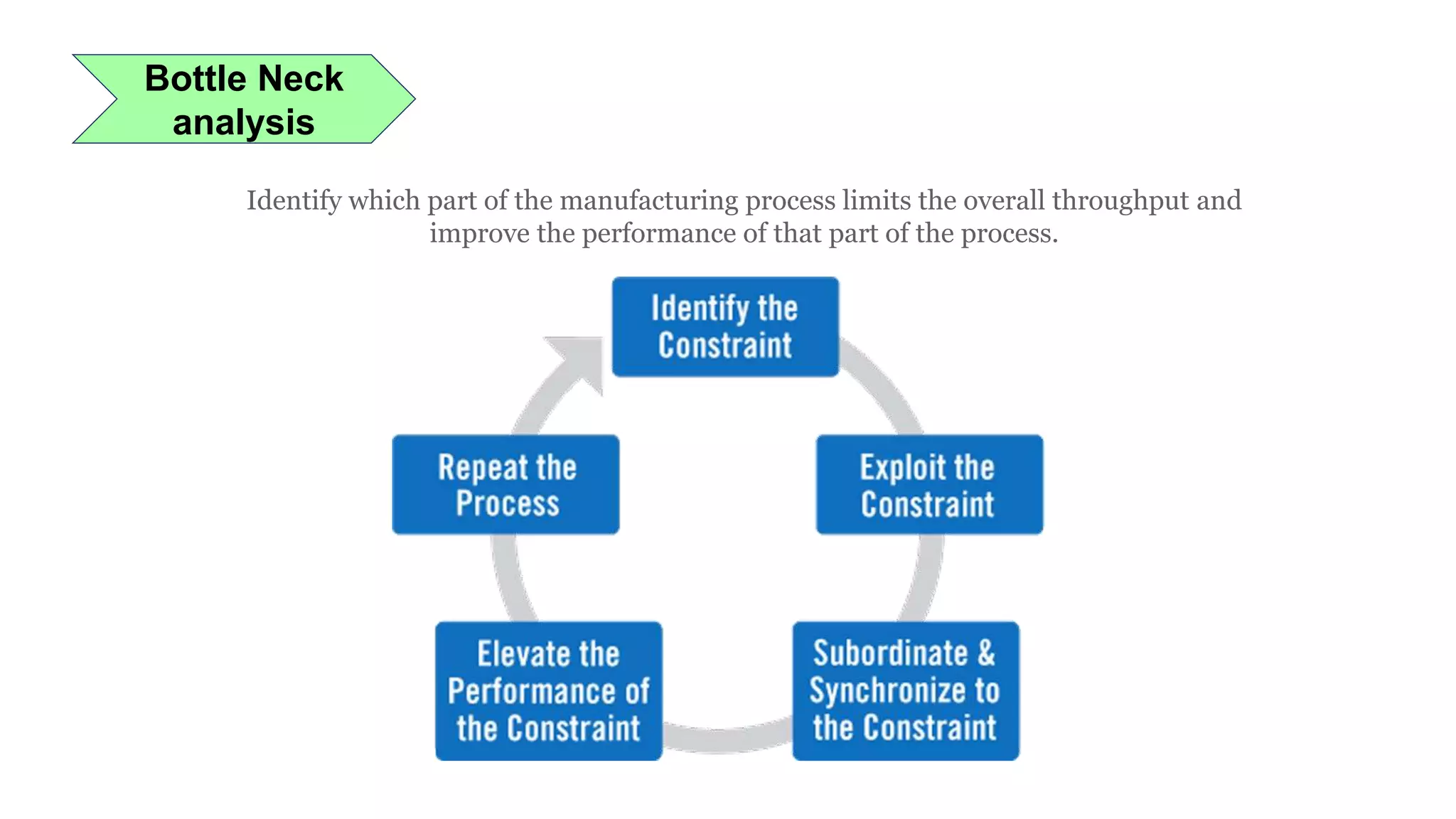
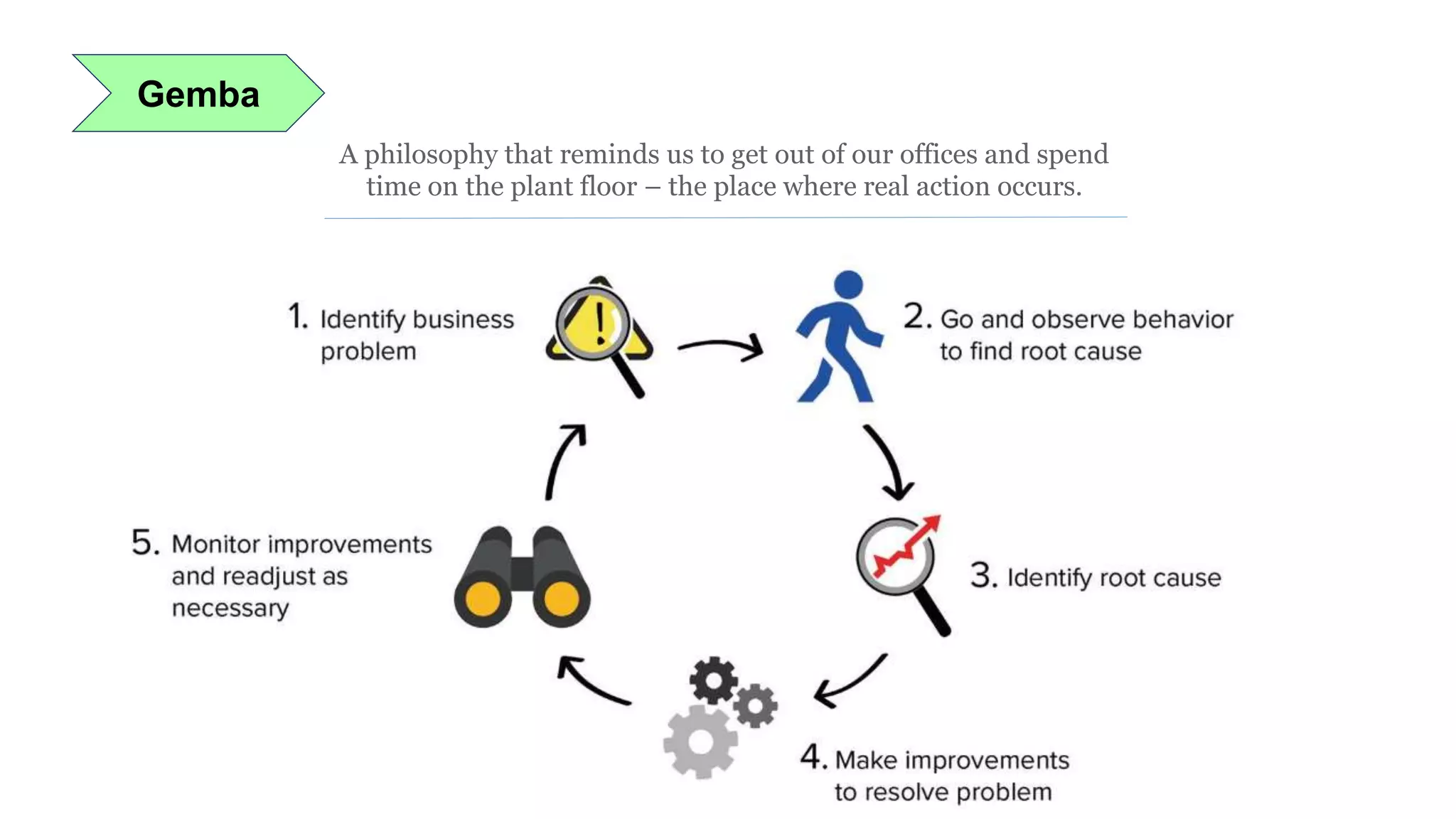
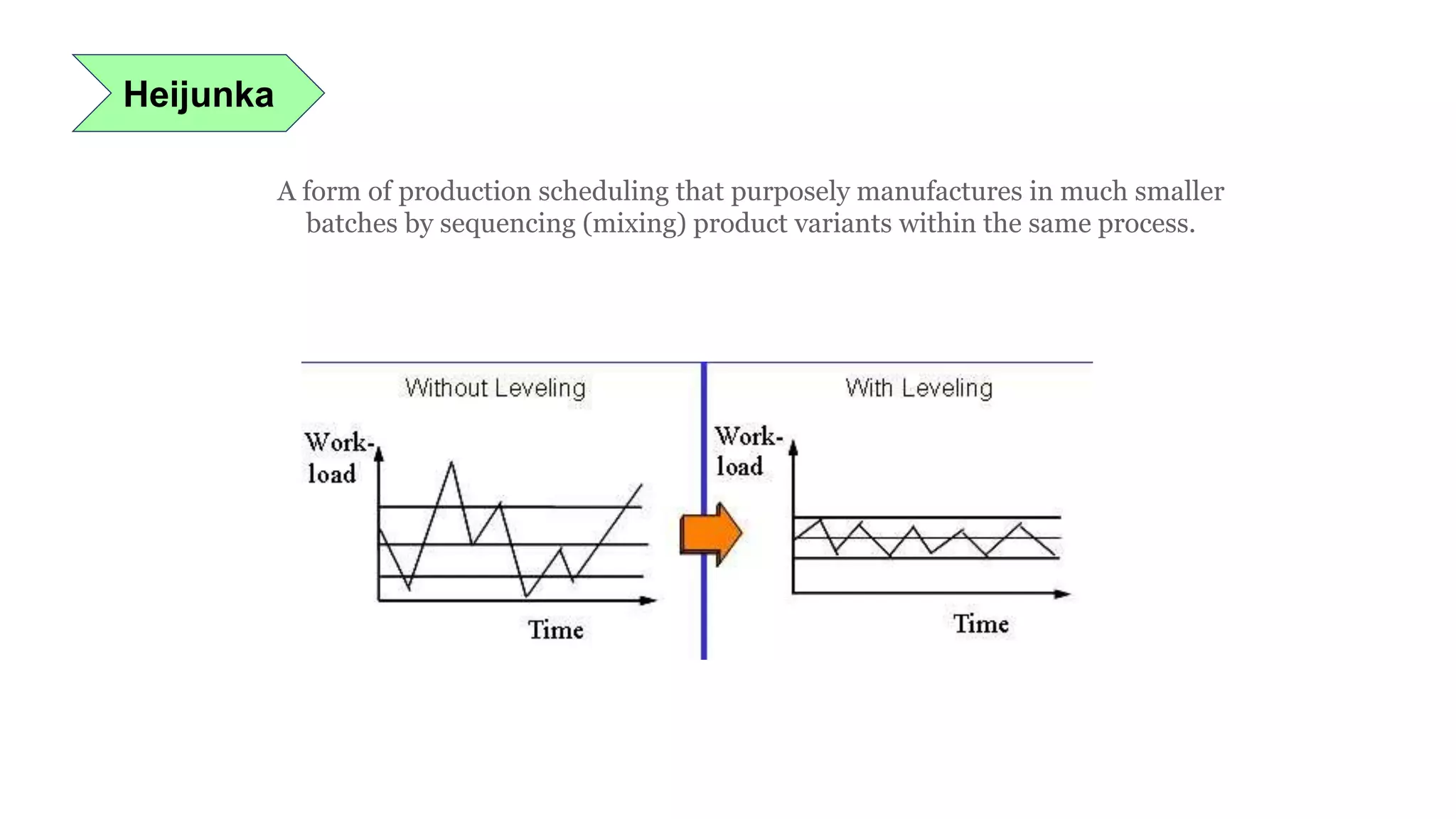
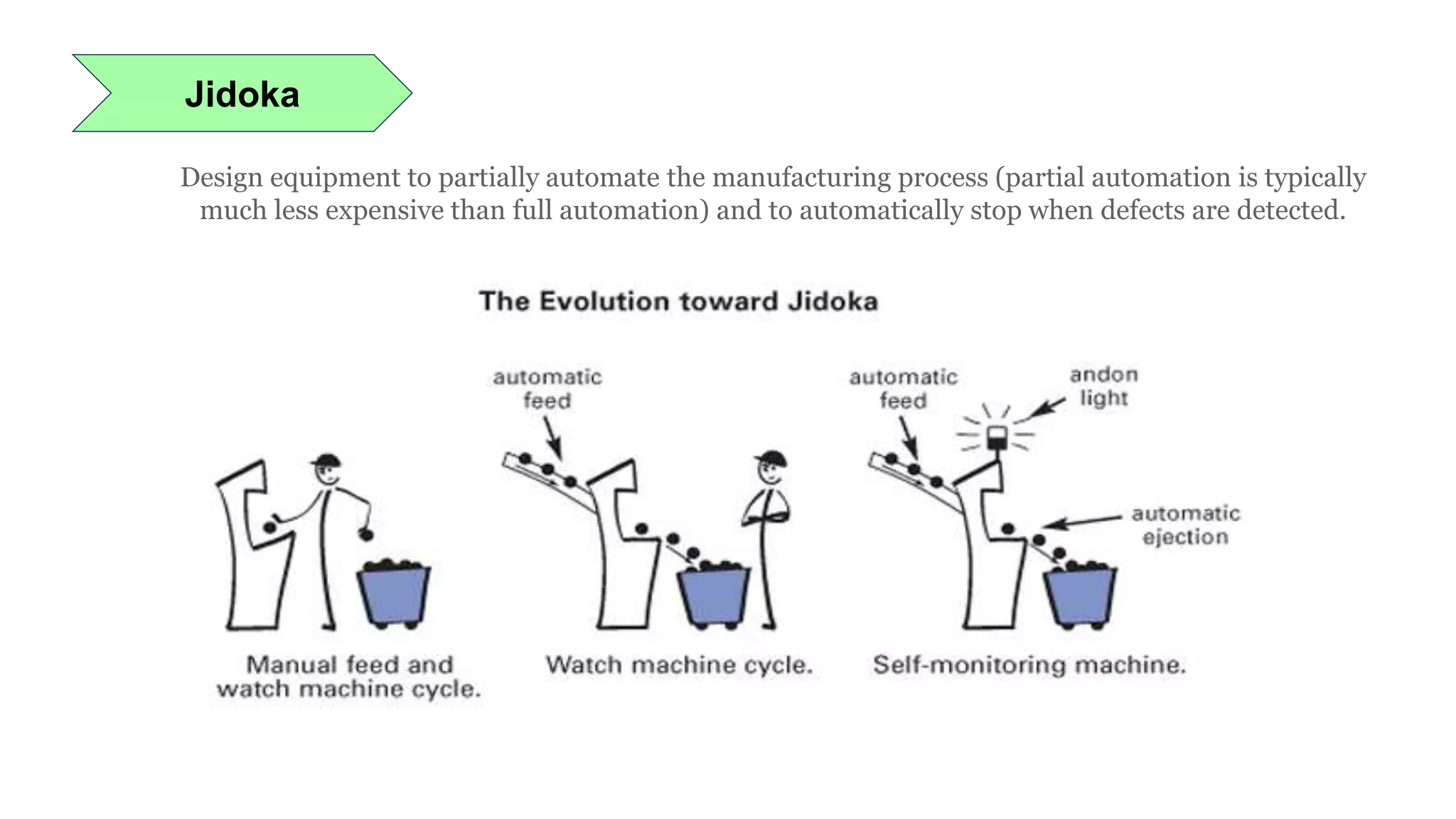
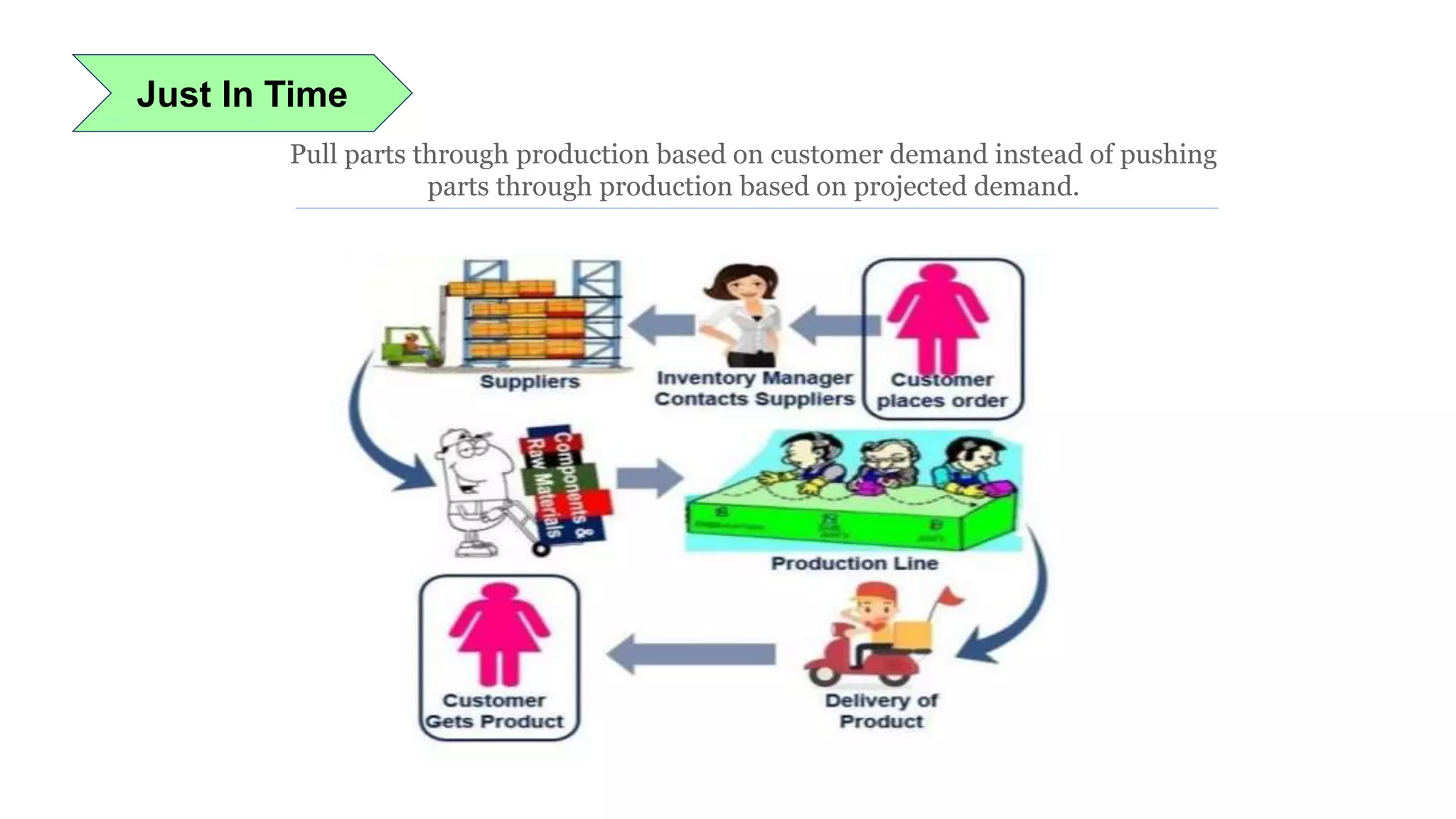
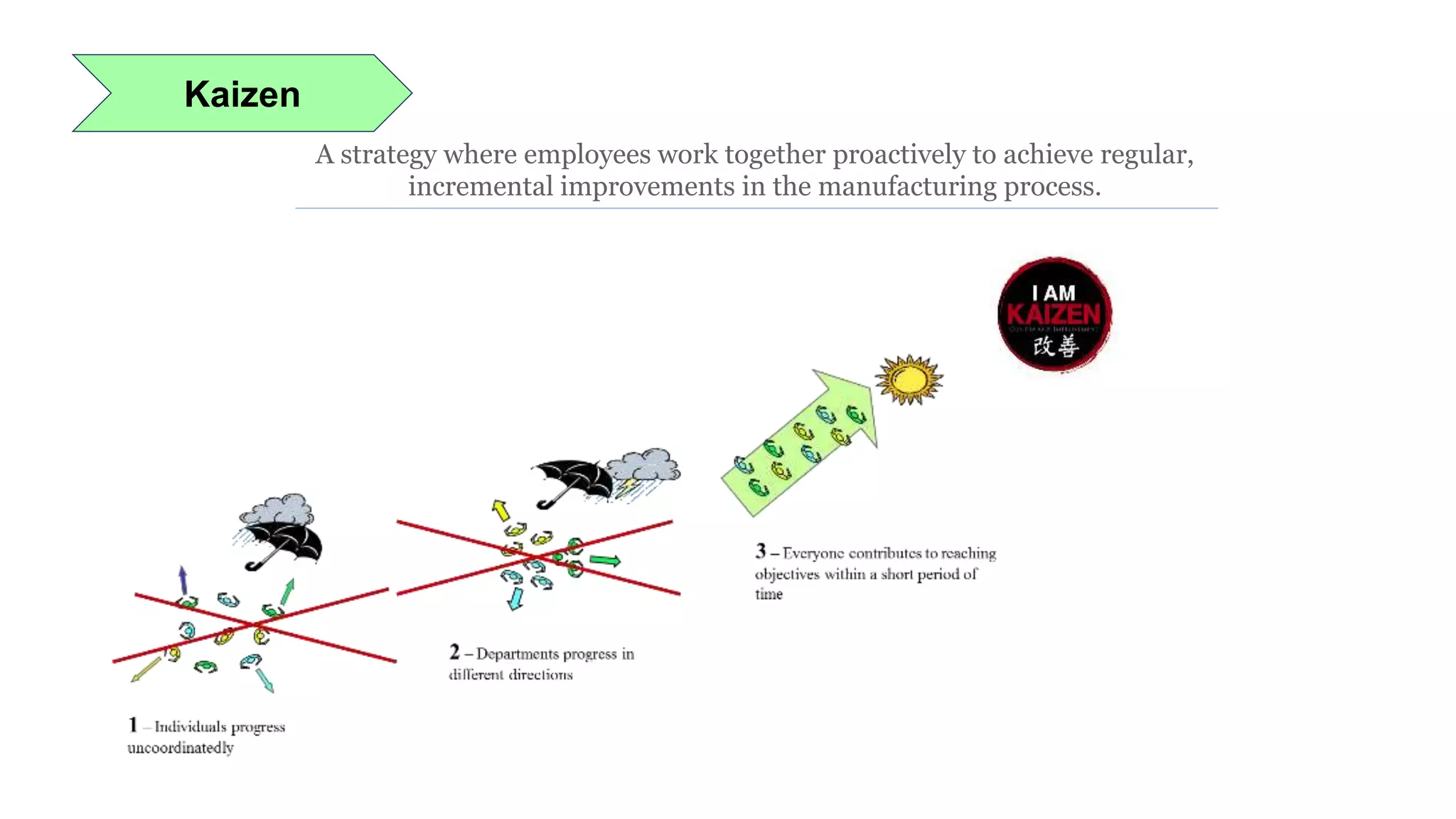
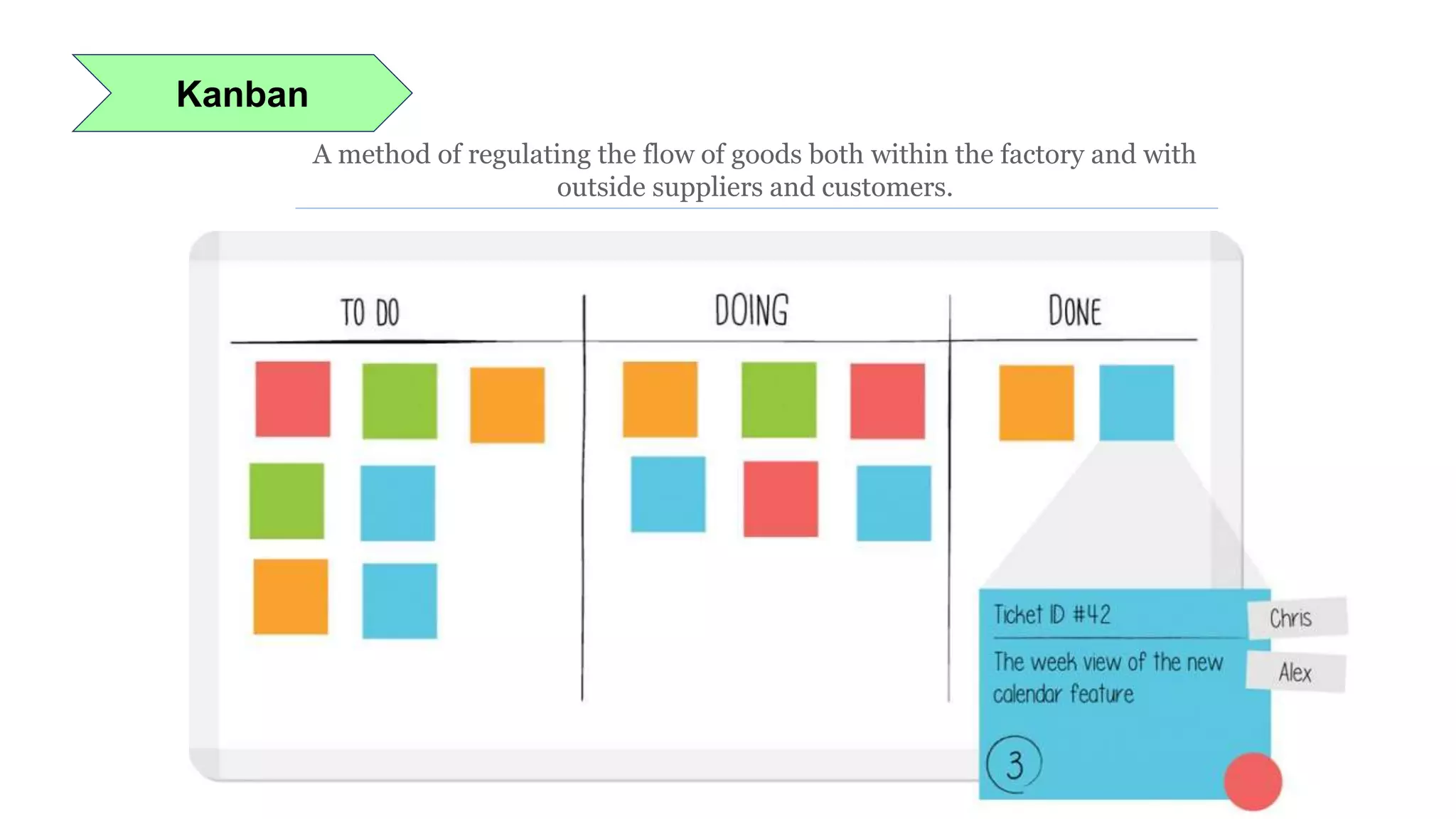
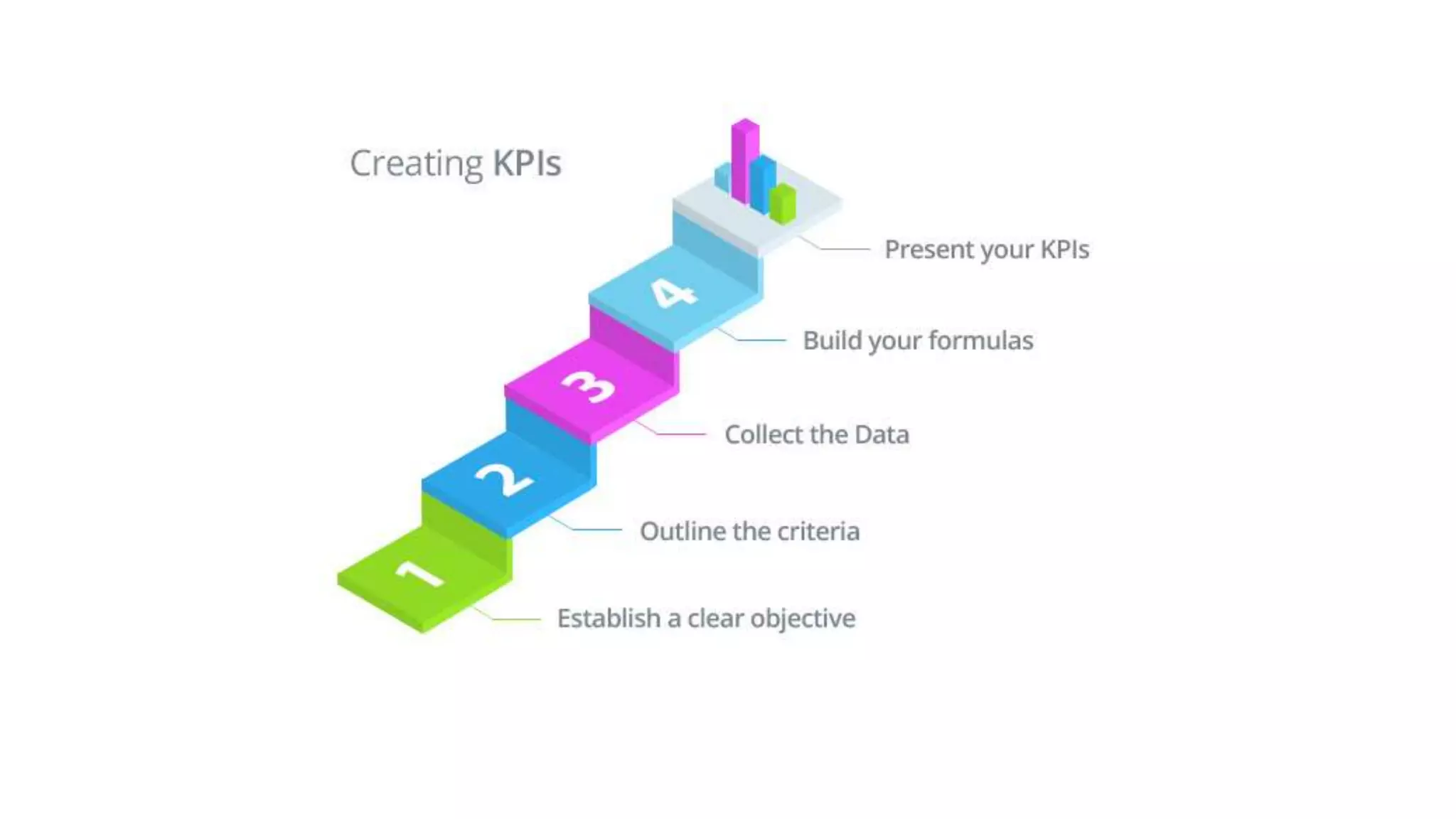
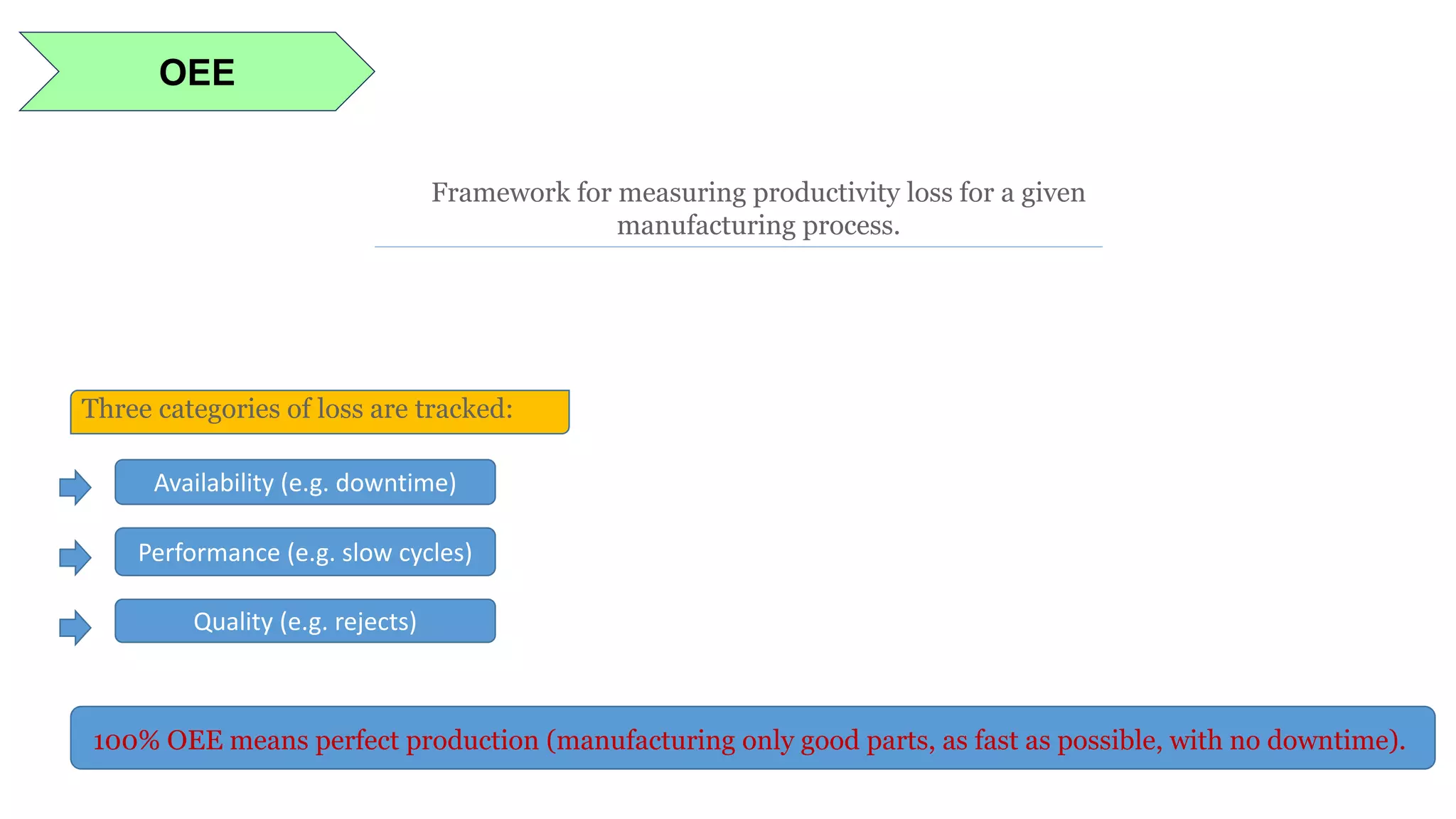
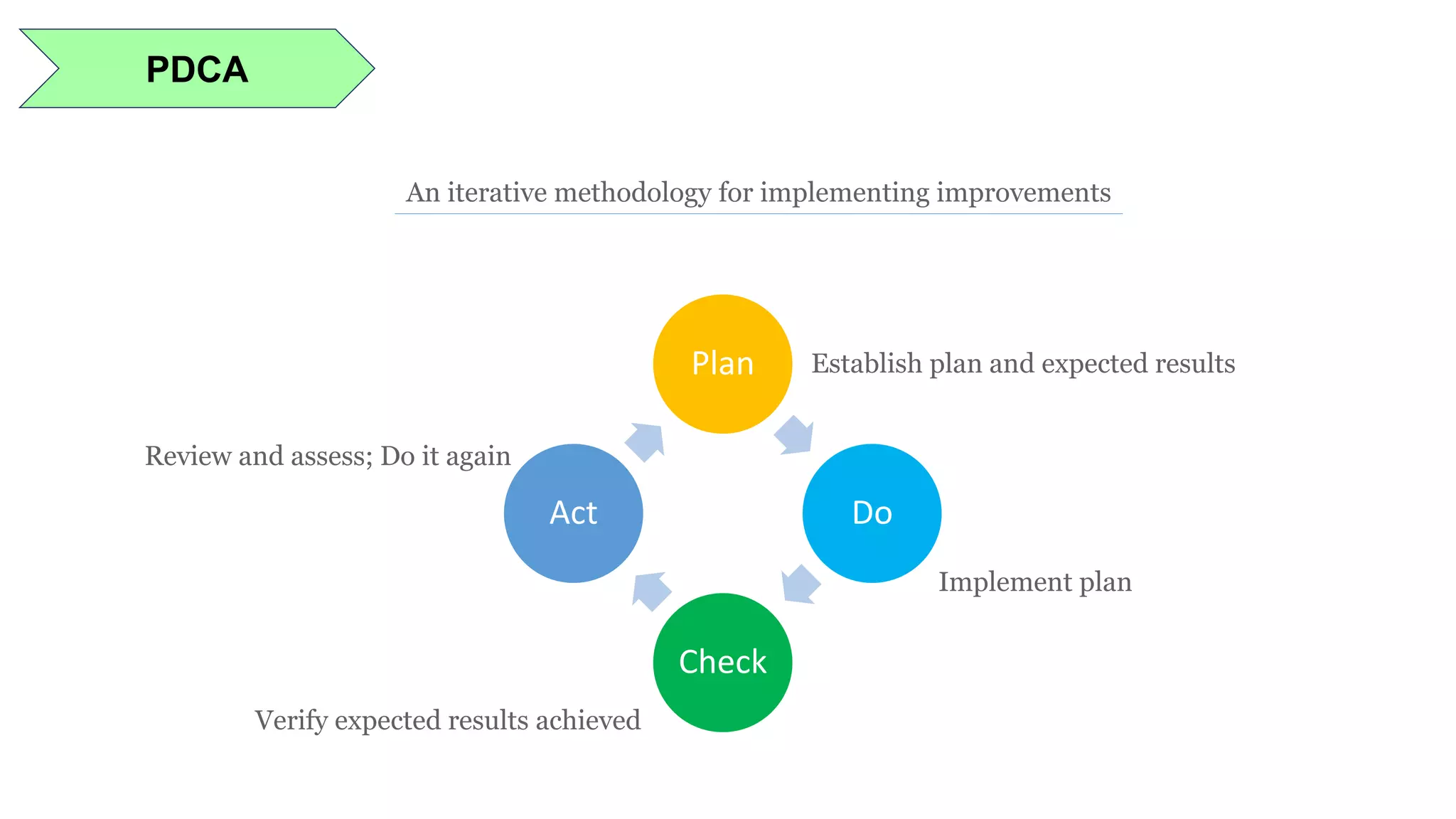
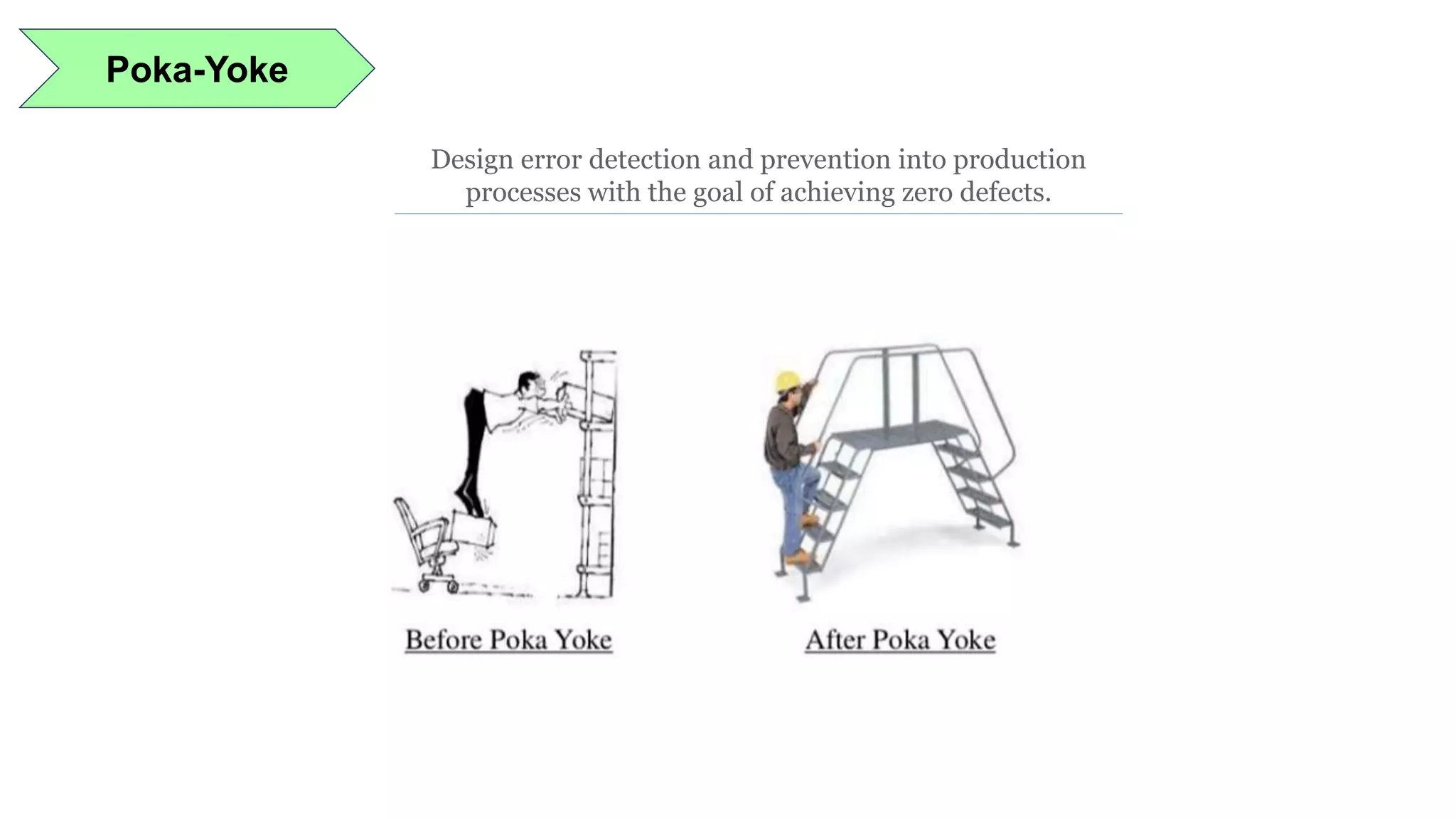
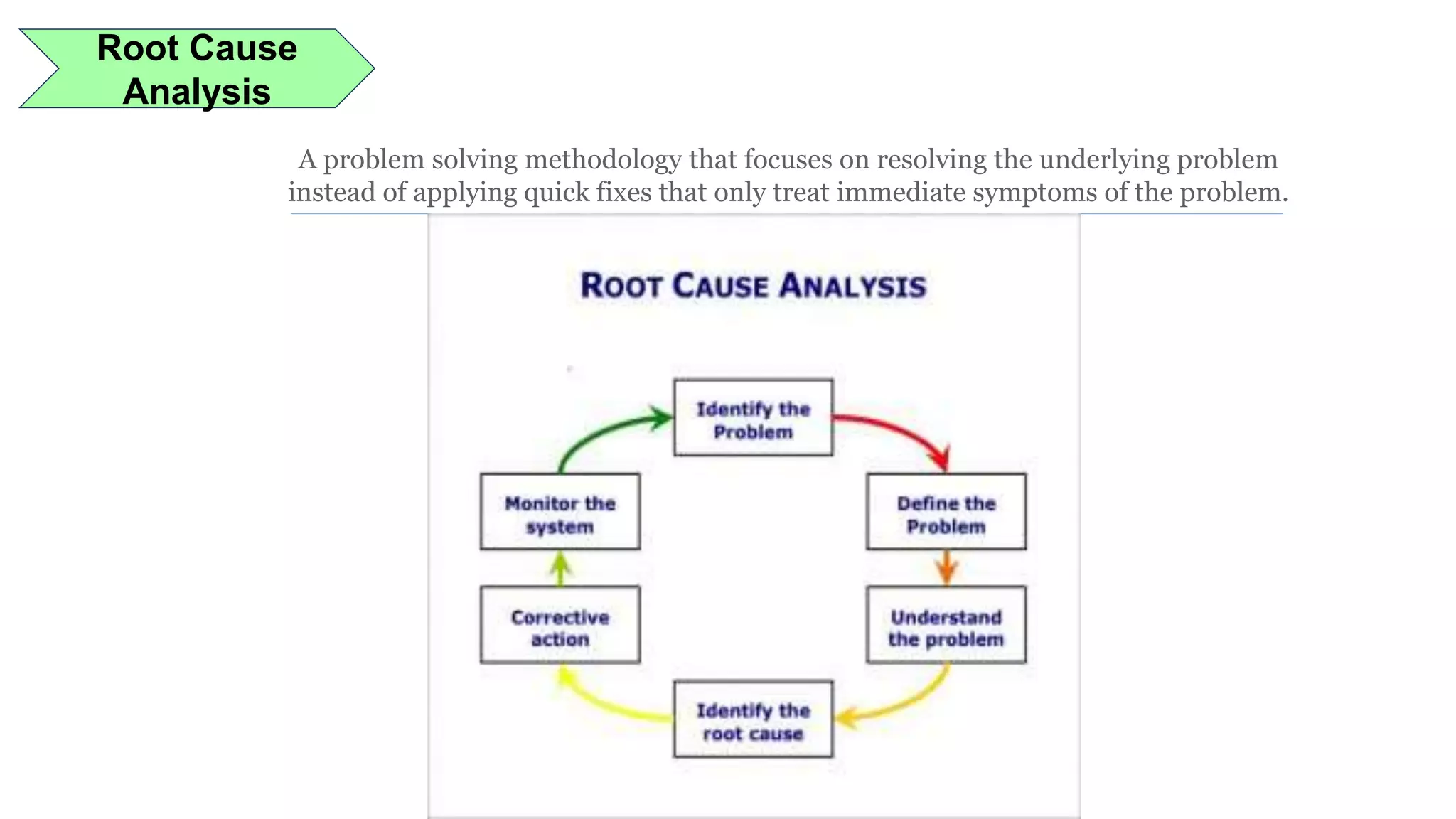
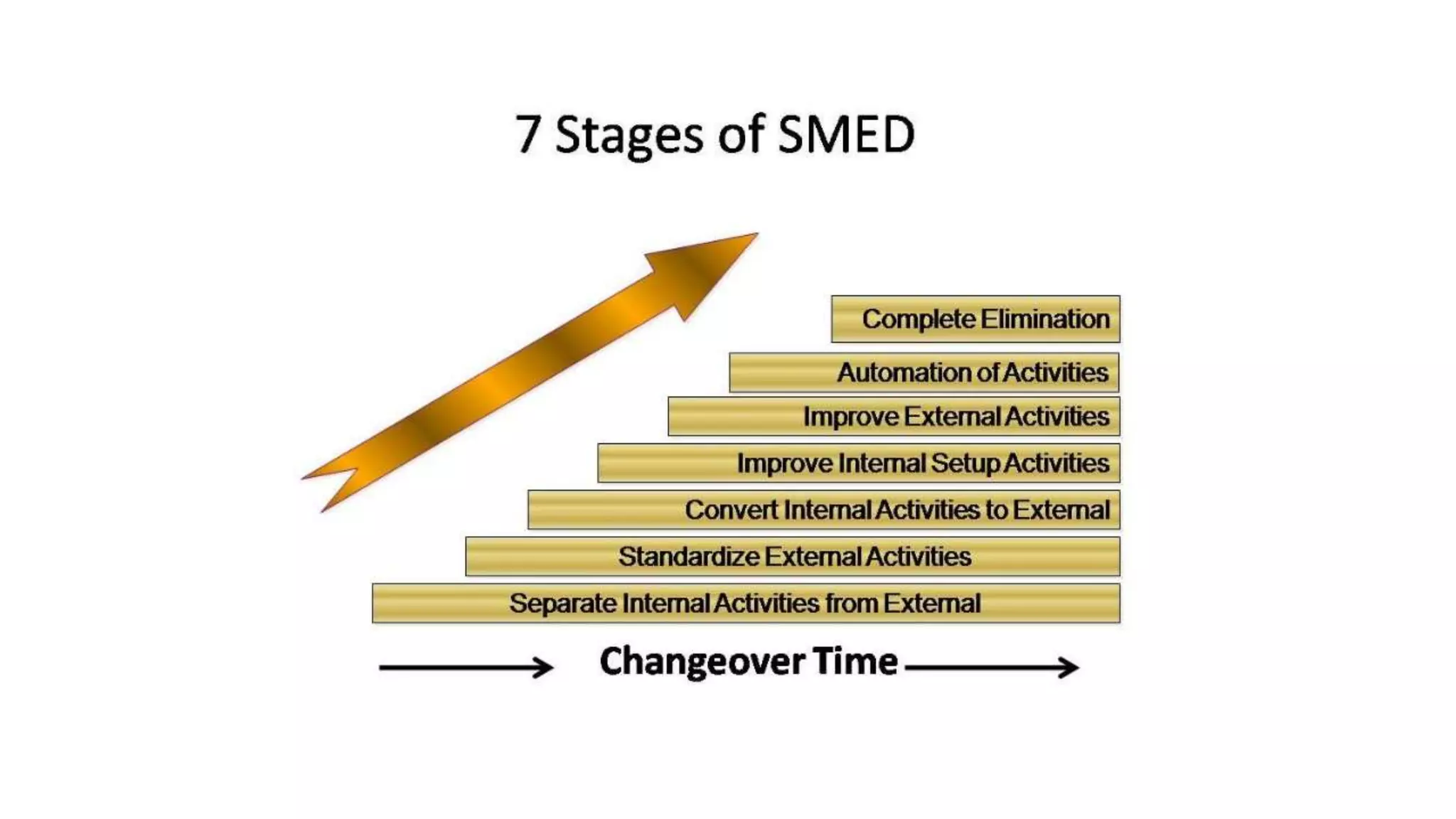
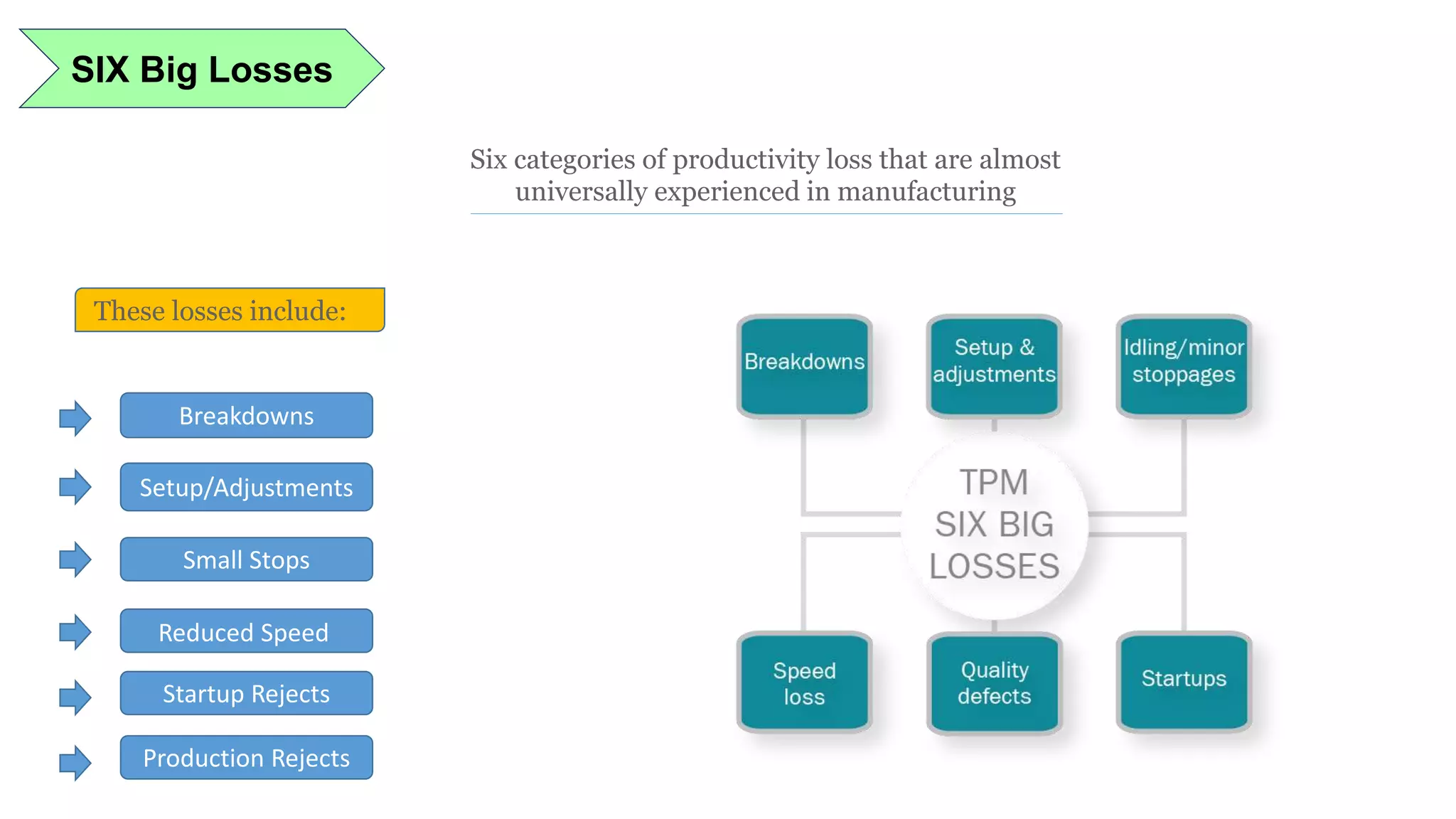
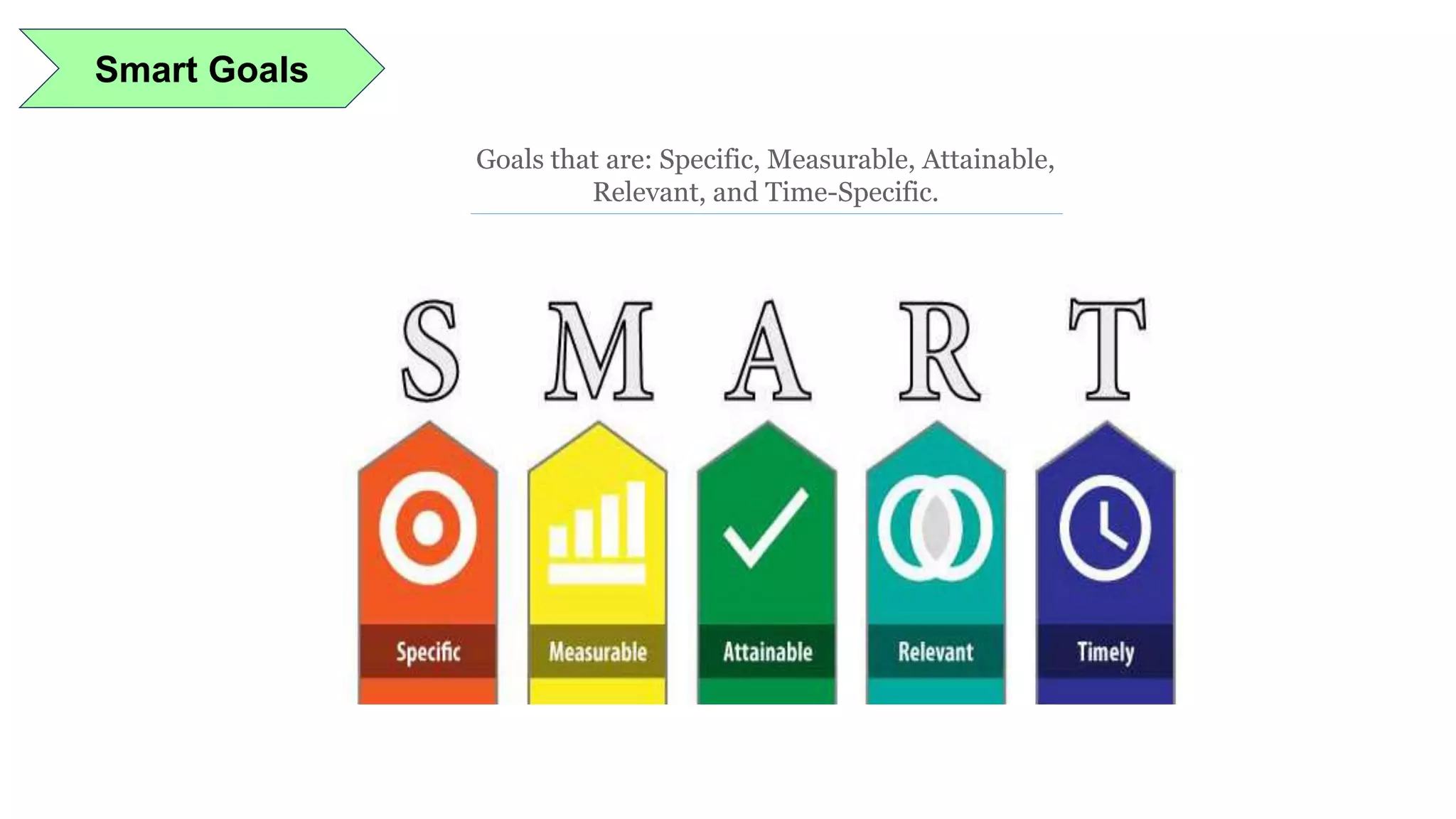
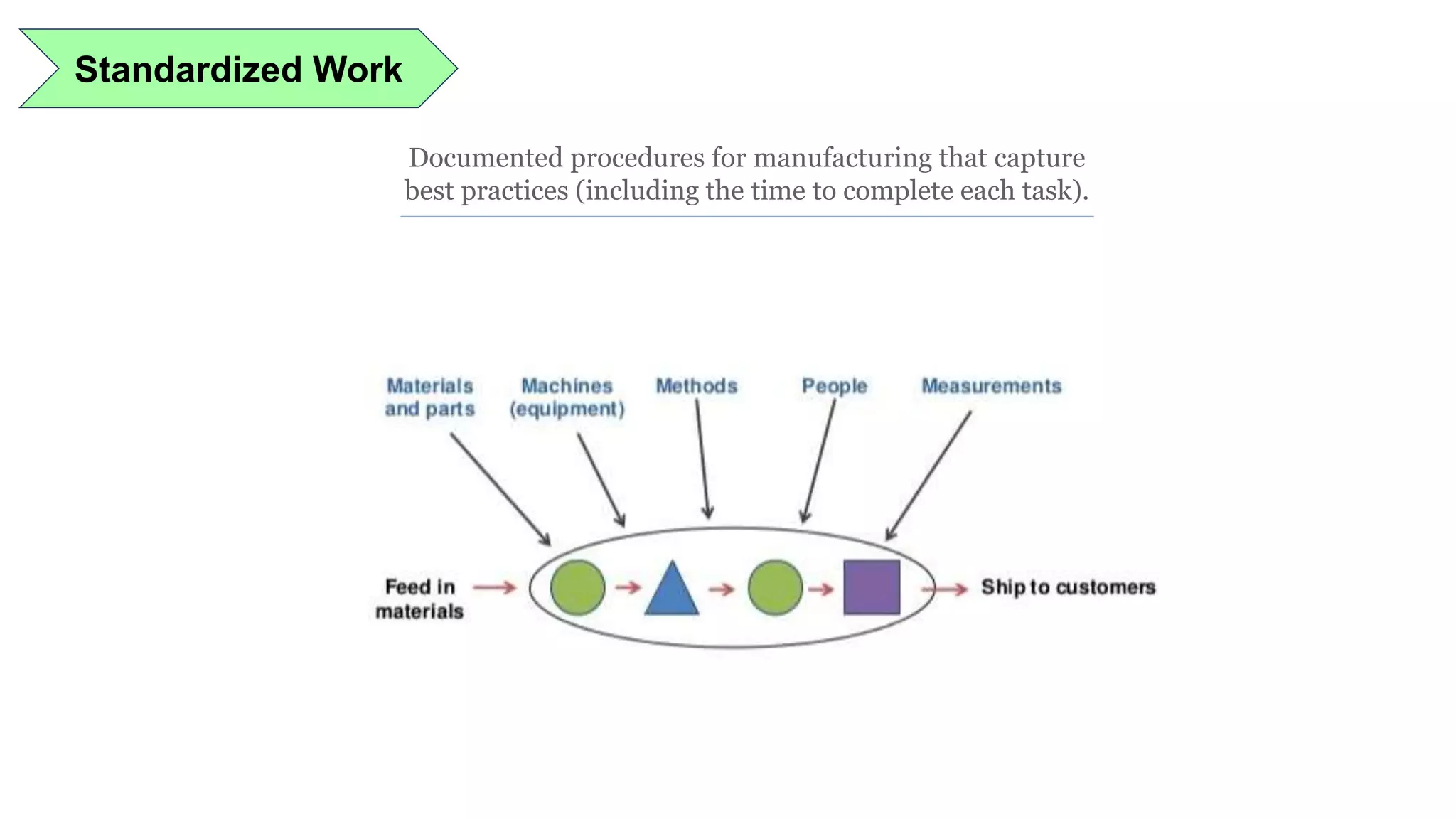
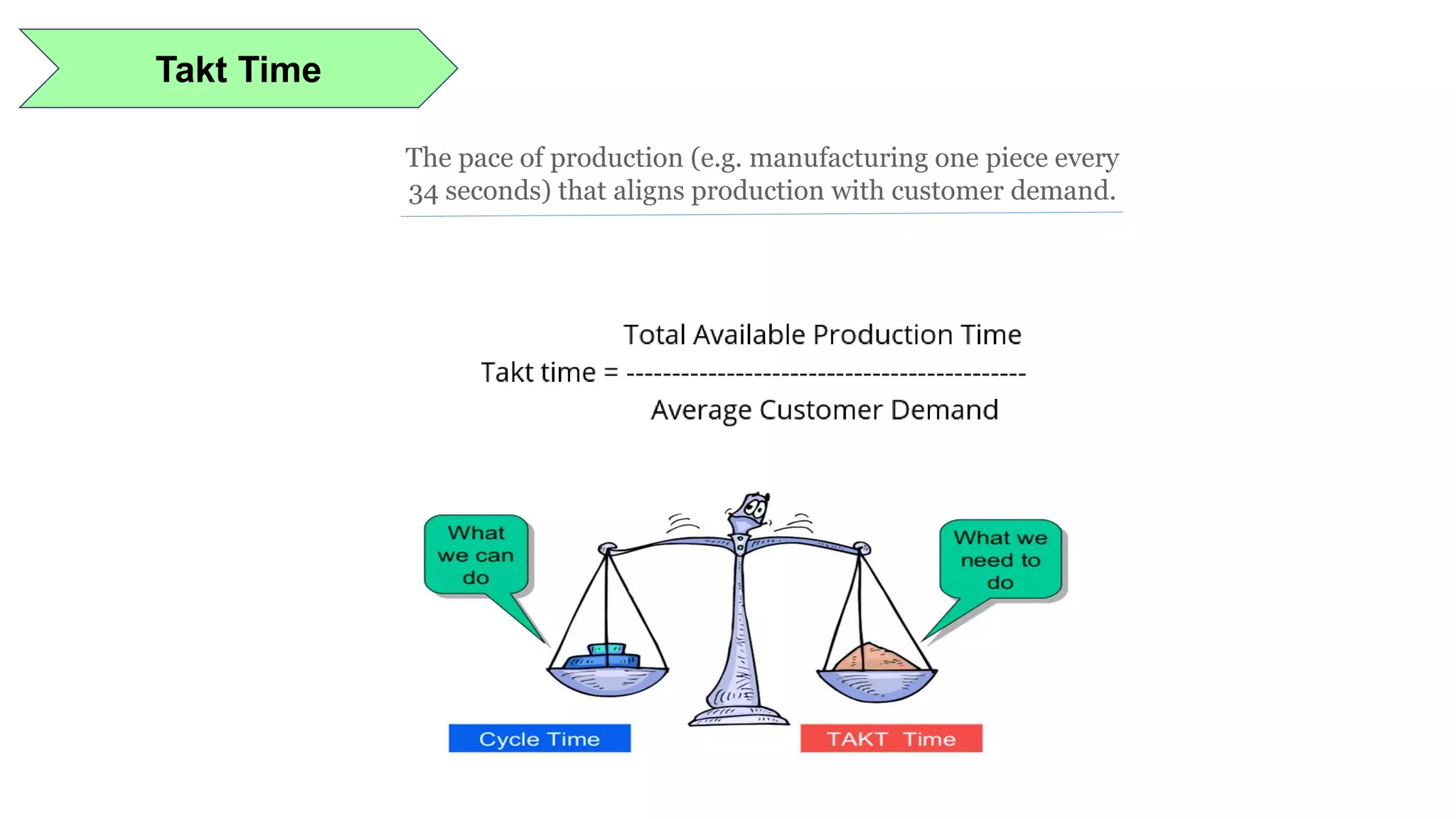
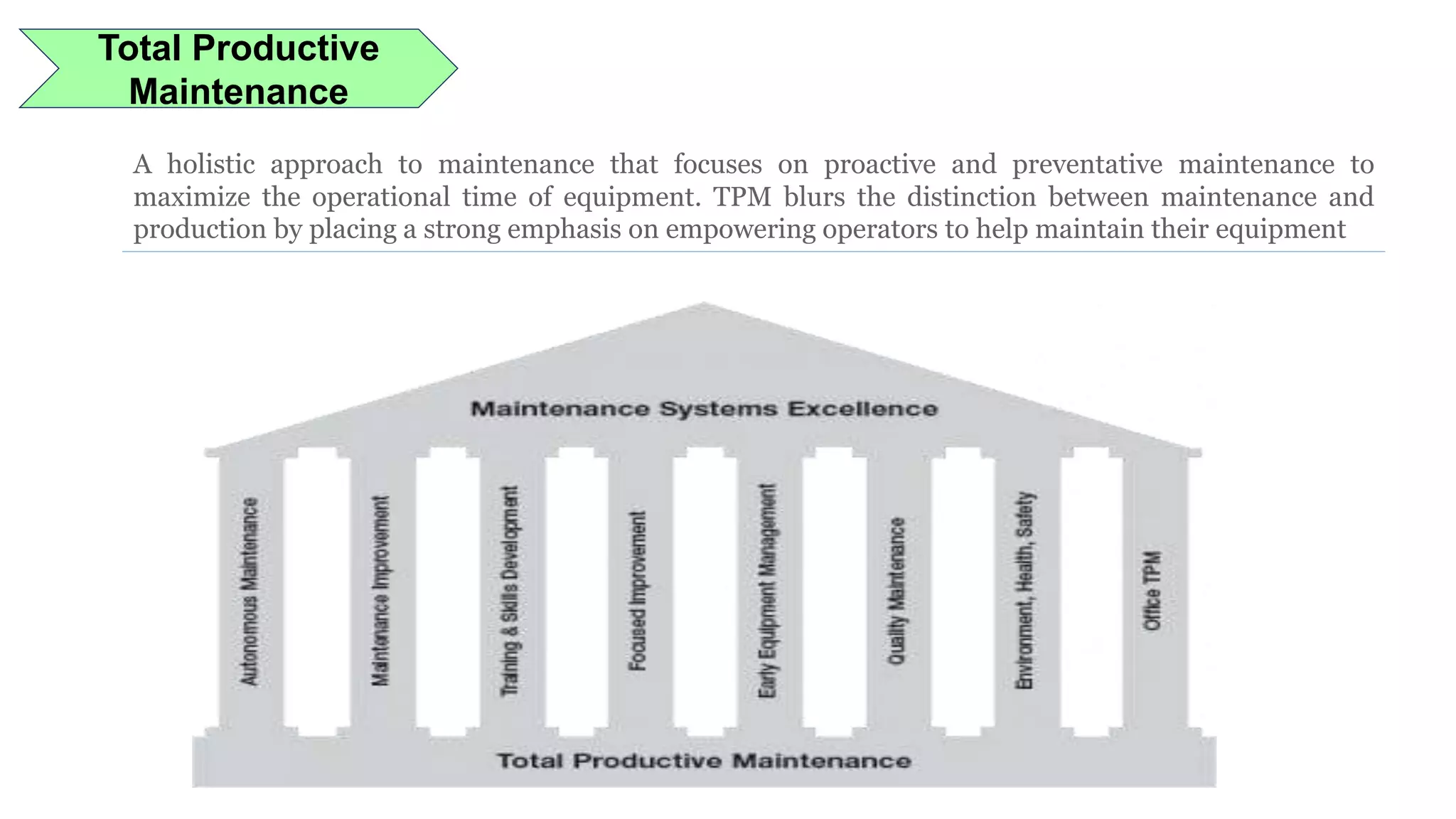
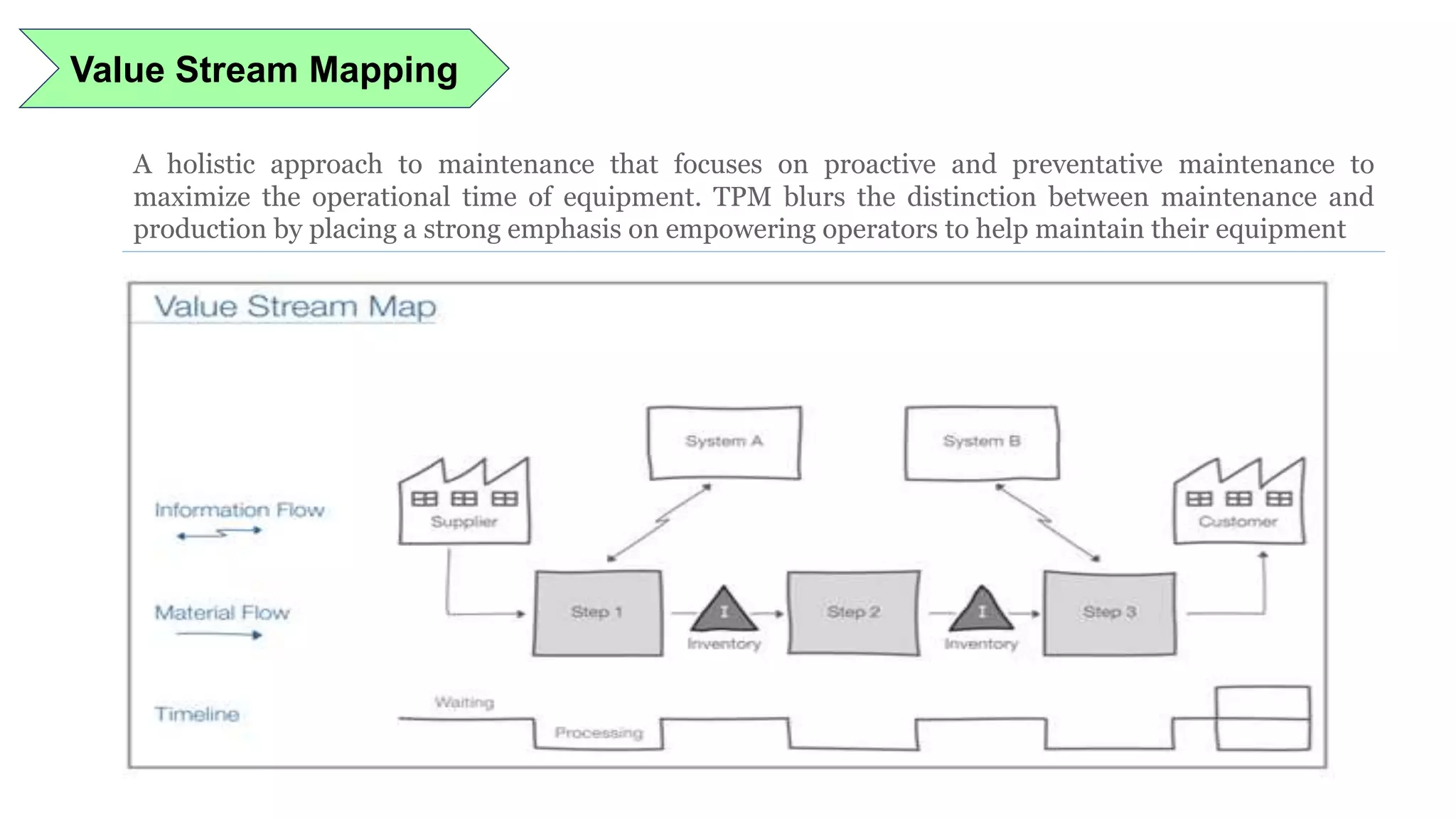
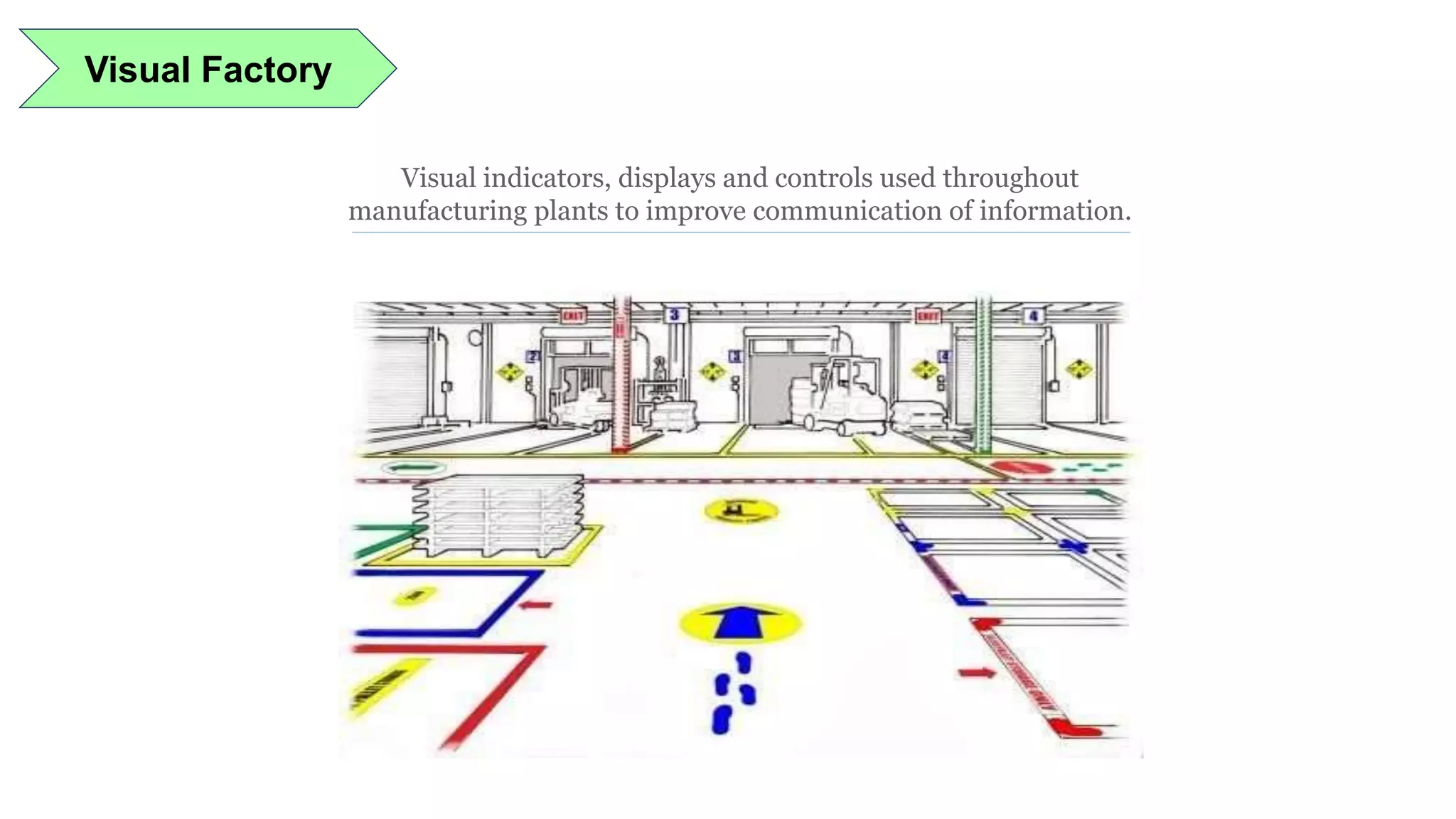
Lean manufacturing is a process that focuses on minimizing waste and maximizing productivity. It utilizes various tools such as 5S, andon systems, bottleneck analysis, continuous flow, gemba walks, heijunka leveling, and just-in-time production to improve efficiency and quality. Some key aspects of lean include identifying and eliminating muda (waste), using tools like value stream mapping and standard work, and implementing a culture of continuous improvement through kaizen events and PDCA cycles. The overall goal is to optimize operations and align production with customer demand.