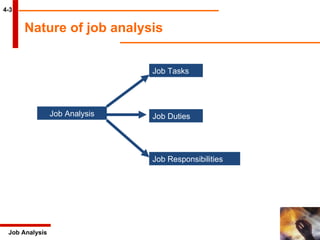
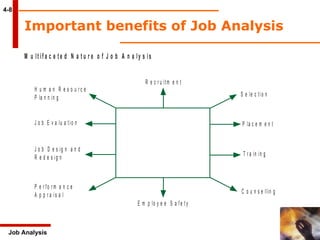
The document discusses job analysis which is defined as a systematic process of gathering information about jobs. It describes the key aspects of conducting job analysis including collecting data through questionnaires, interviews, and other methods. The main outcomes of job analysis are job descriptions which outline what employees do, and job specifications which define the necessary skills and qualifications.