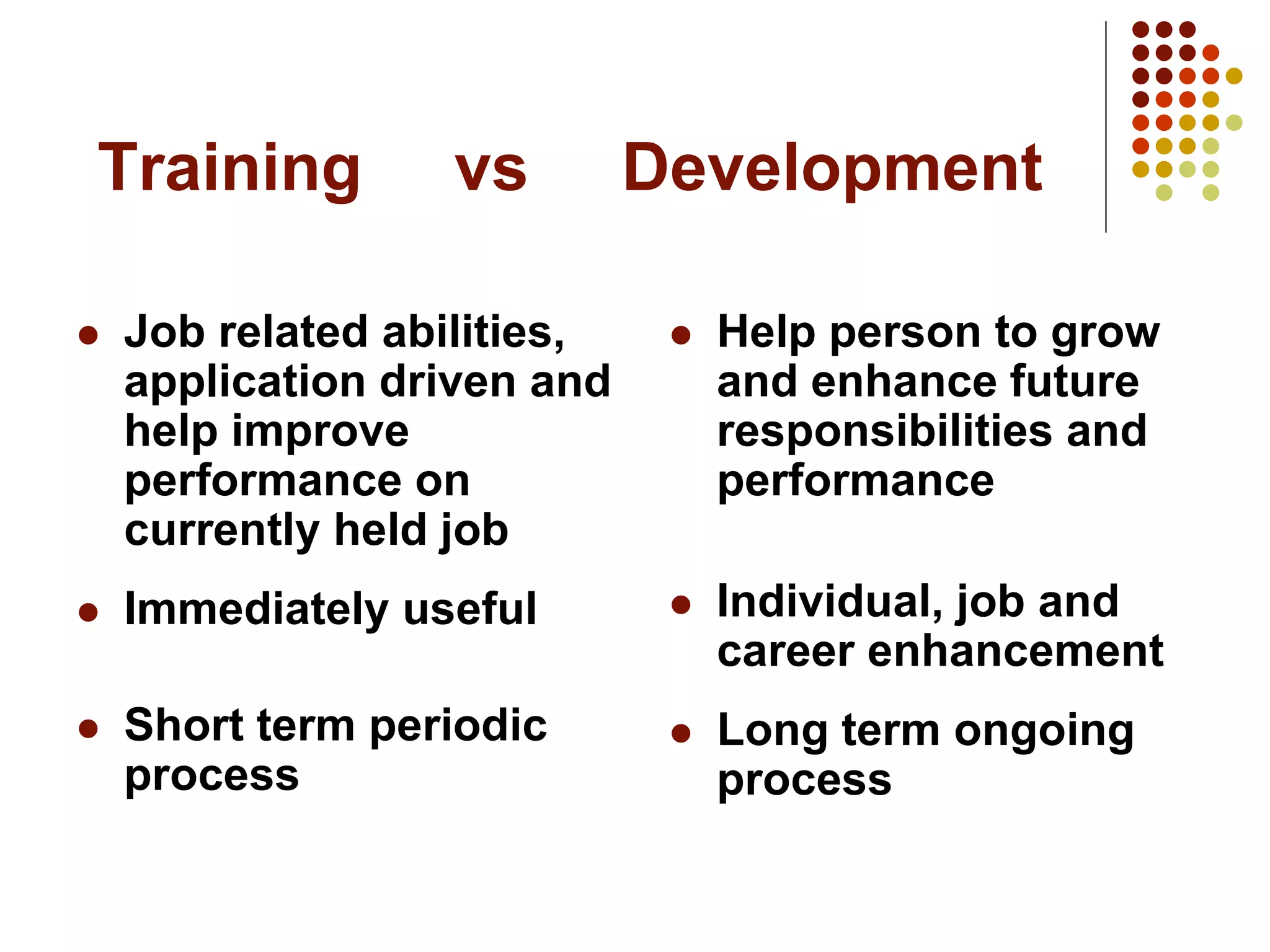
This document discusses employee training and development. It outlines key challenges that training addresses like competing in the market, improving quality and customer service, reducing costs, enhancing productivity, and adapting to new technologies. It differentiates between training, which improves current job performance, and development, which enhances future roles and responsibilities.
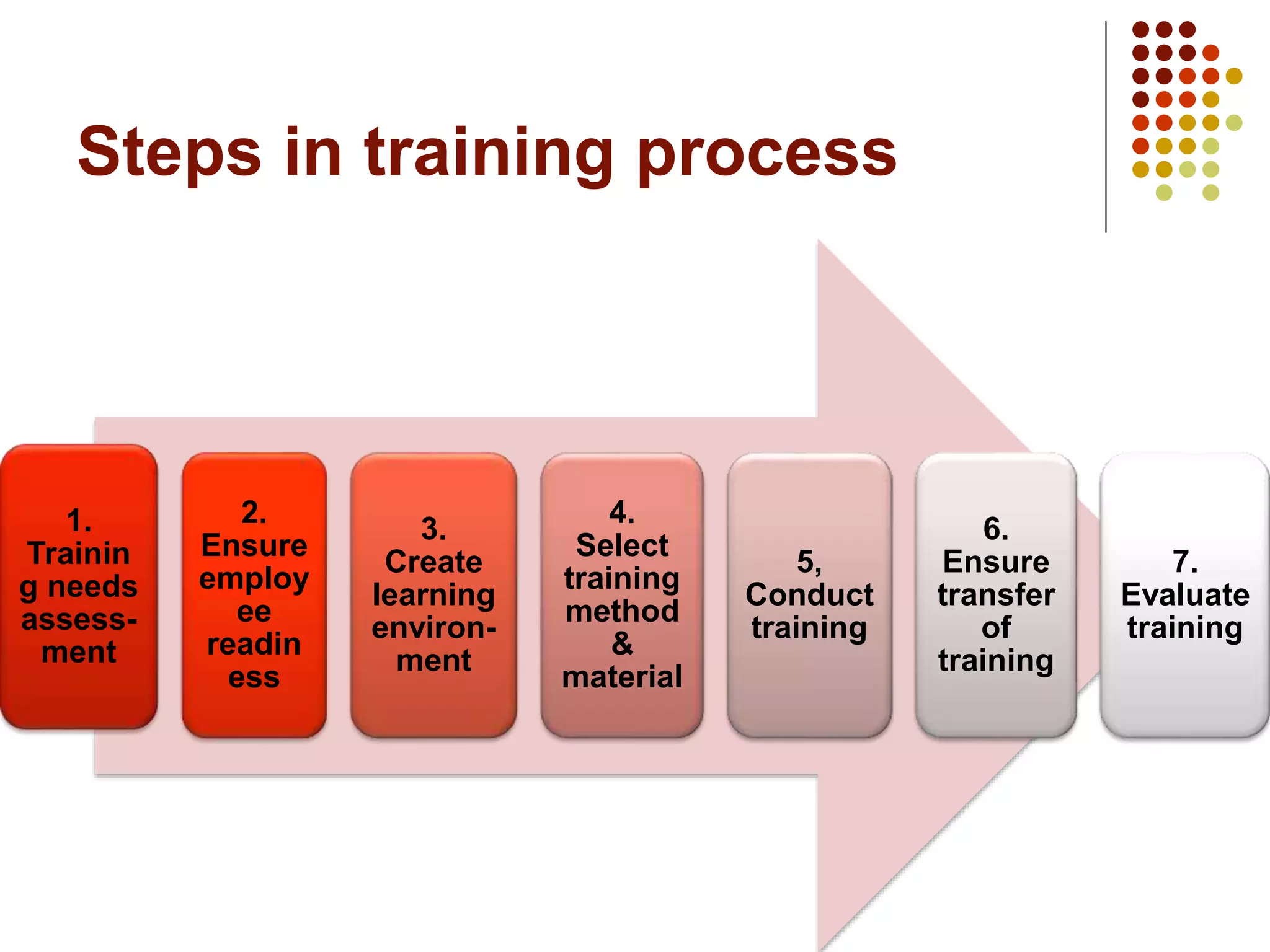
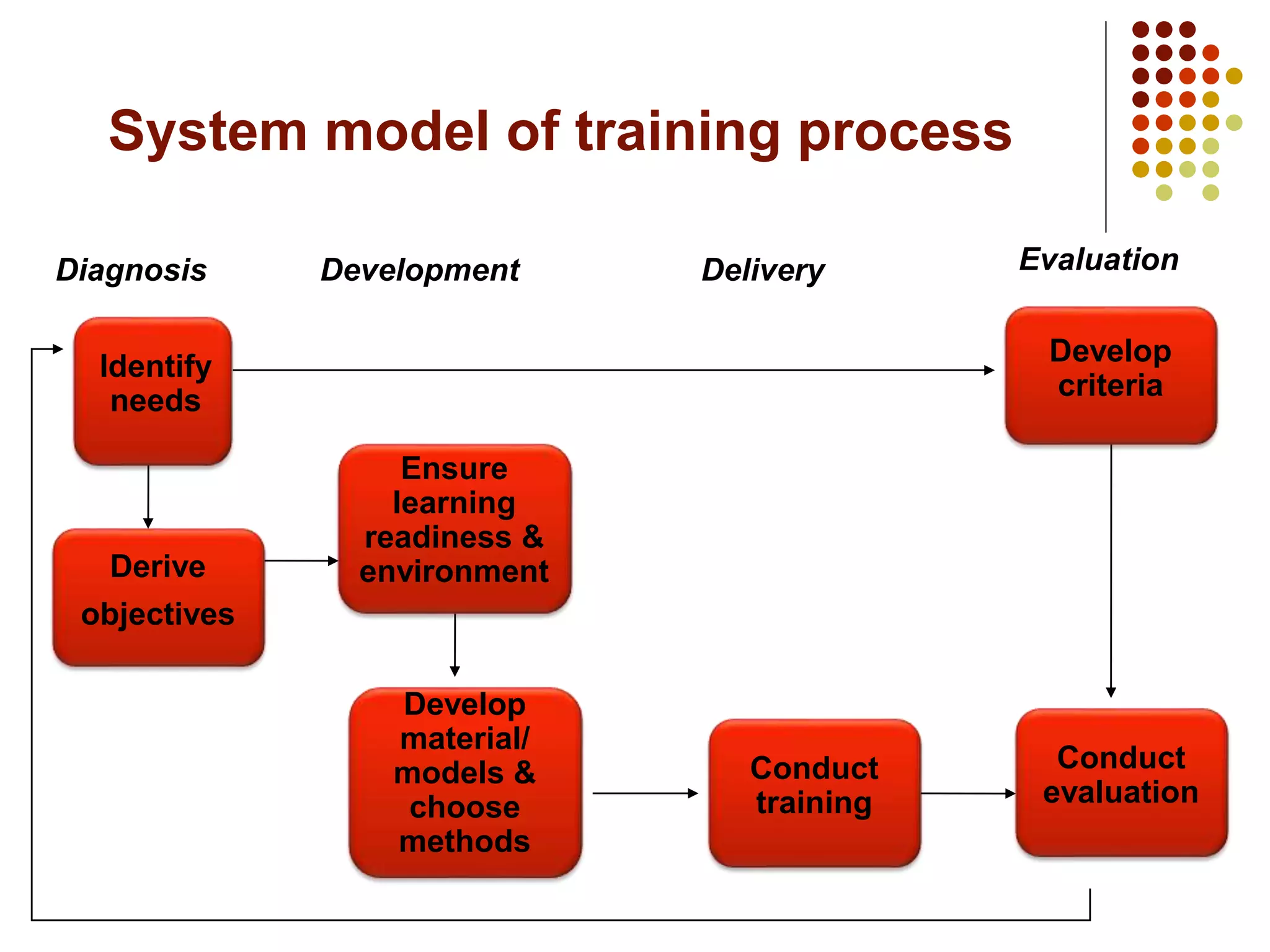
The document details the training process, including assessing needs, ensuring employee readiness, creating a learning environment, selecting methods and materials, conducting training, transferring learning, and evaluating the impact. It provides examples of training needs assessment, factors for an effective learning environment, different training methods like lectures and on-the-job training, and Kirkpatrick's model for evaluating training at different levels.