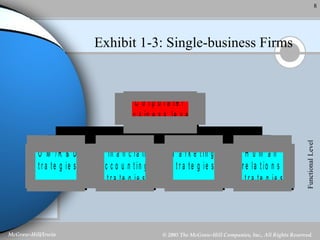
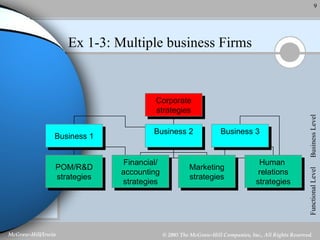
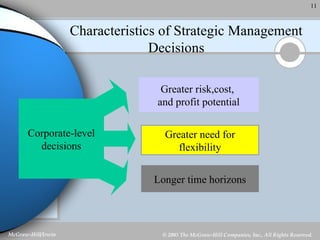
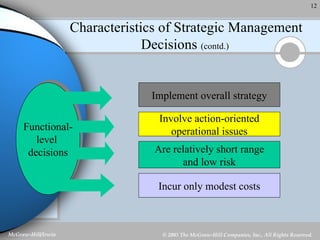
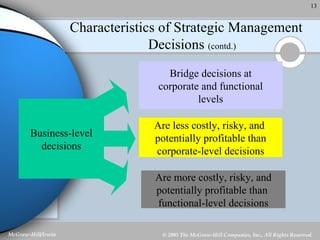
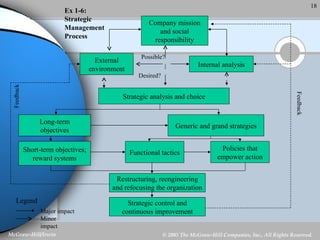
Strategic management involves analyzing a company's internal strengths and weaknesses as well as external opportunities and threats. Key steps include formulating a mission and objectives, assessing the environment, identifying strategies, and implementing and evaluating plans. Strategic decisions require top management input and large resources, and can impact the long-term prosperity of a firm. Strategies exist at the corporate, business unit, and functional levels. Formality and the roles of managers in strategic management depend on factors like organization size and culture.