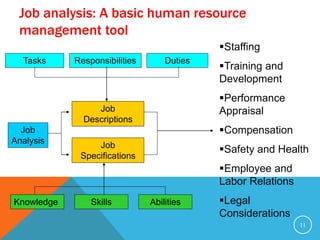
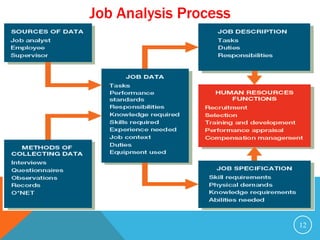
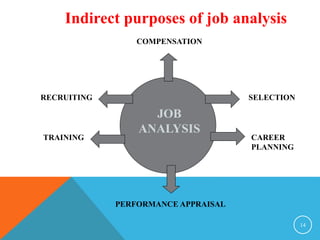
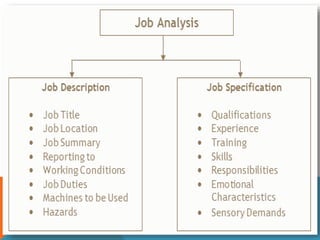
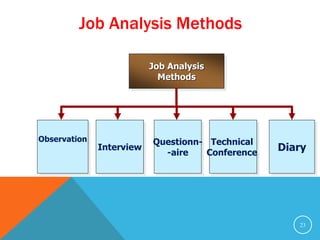
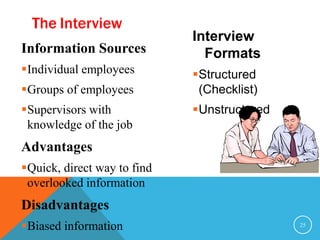
This document discusses job analysis. It begins by defining job analysis as a systematic exploration of the activities within a job to document its duties, responsibilities, and conditions. It then covers key aspects of job analysis including its hierarchy of information, components, process, and purposes. The purposes include generating job descriptions, specifications, and evaluations. Various methods for conducting job analysis are also outlined such as observation, interviews, questionnaires, and diaries.