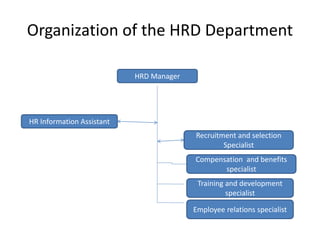
Human Resource Development (HRD) and Human Resource Management (HRM) both focus on developing employees but with different aims. HRD aims to develop employees' full potential and improve organizational performance through opportunities like training and mentoring. HRM aims to improve productivity and focuses on issues like compensation and hiring. Both are influenced by factors like business strategies, legislation, and social change. While HRM views employees as costs, HRD believes all employees have potential that can be developed to benefit both the employee and organization.