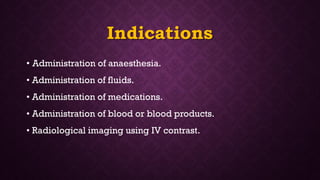
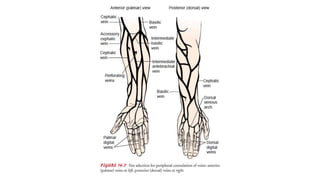
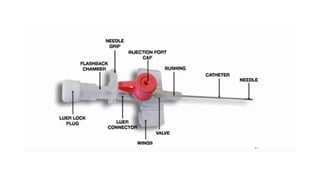
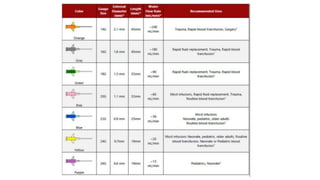
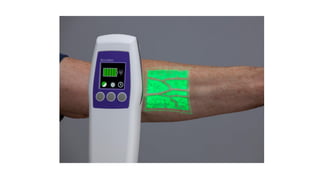
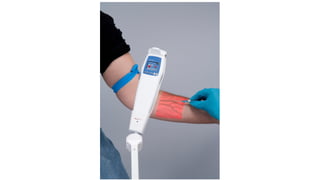
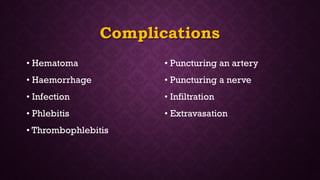
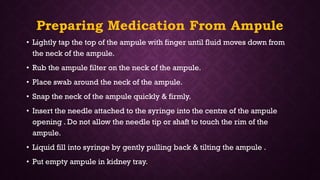
Intravenous cannulation involves inserting a flexible tube into the body to administer fluids, medications, or blood products. The procedure requires careful selection of vein sites, proper sterilization, and awareness of complications such as infection or hematoma. New methods, like the Accuvein device, assist in difficult venous access, particularly for challenging patient demographics.