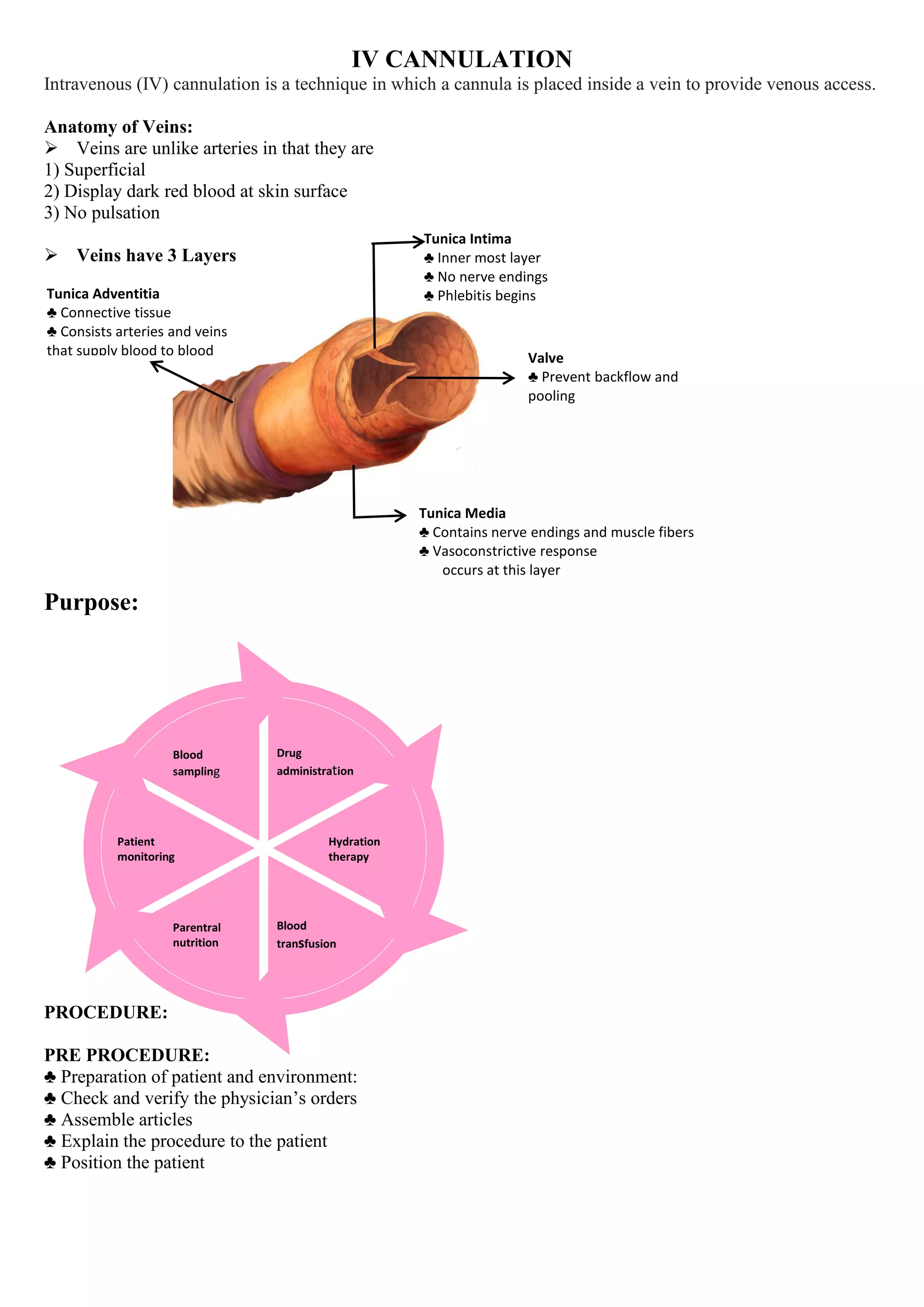
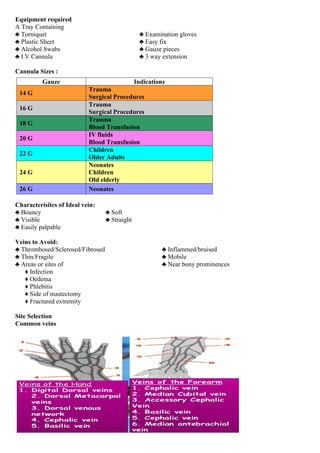
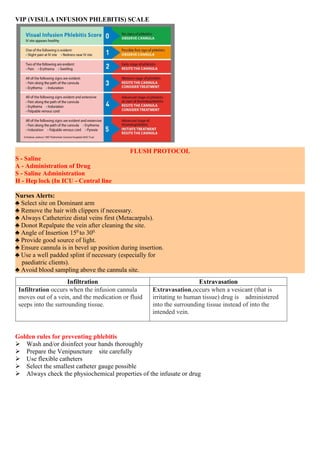
IV cannulation involves inserting a cannula into a vein to provide venous access for purposes like drug administration, hydration therapy, blood transfusion, and patient monitoring. Veins have three layers and are unlike arteries in that they are superficial, display dark red blood, and have no pulsation. The ideal vein for cannulation is bouncy, soft, visible, straight, and easily palpable. Complications can include infection, infiltration where fluid leaks into surrounding tissue, and phlebitis which is inflammation of the vein. Proper technique and regular inspection of the site are important to prevent complications.