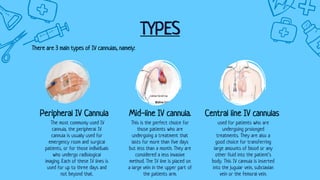
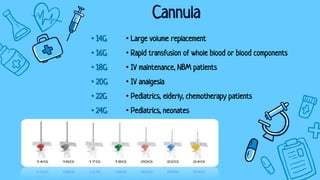
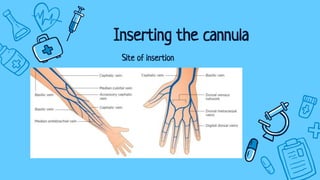
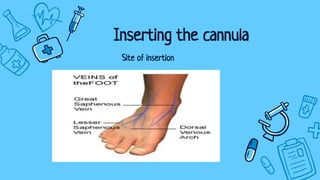
There are three main types of intravenous cannulation: peripheral IV cannula, central line IV cannula, and mid-line IV cannula. IV cannulation is indicated for blood sampling, fluid/medication administration, hemodynamic monitoring, and transfusion of blood or blood products. Contraindications include sites near infection, edematous areas, and areas with bleeding/clotting disorders. The procedure involves preparing equipment and the patient, finding a suitable vein, inserting the cannula, securing it with a dressing, and documenting. Potential complications are infiltration, infection, phlebitis, and thrombophlebitis, which can be prevented through proper technique, regular site inspection, and early troubleshooting.