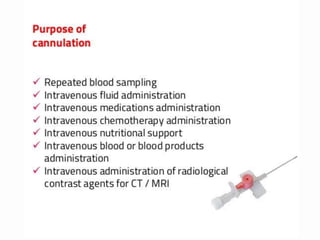
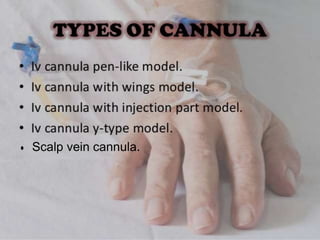
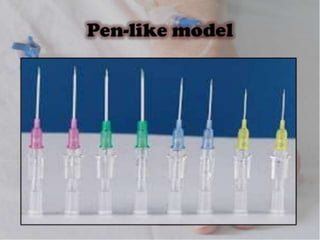
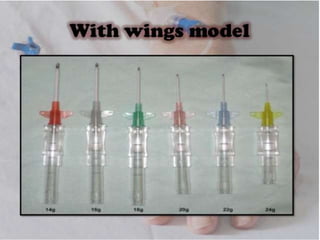
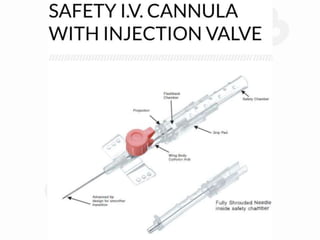
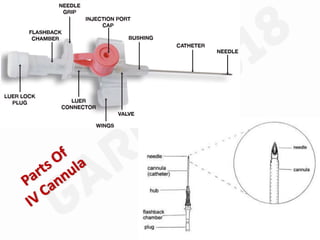
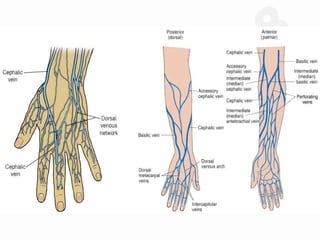
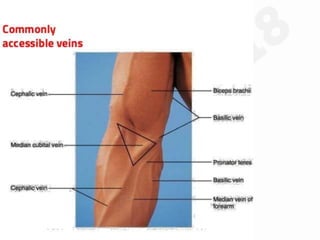
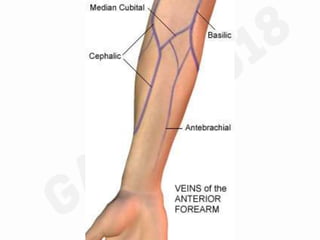
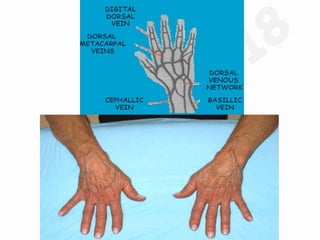
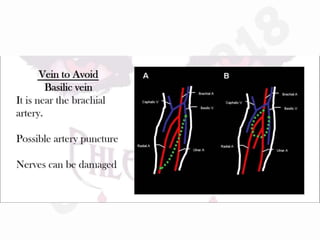
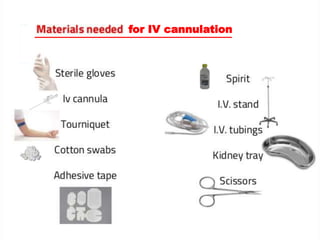
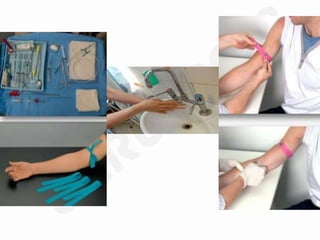
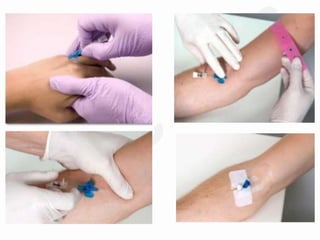
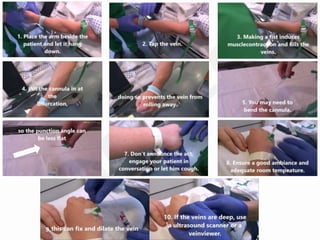
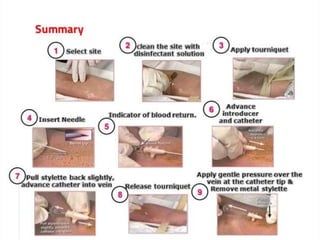
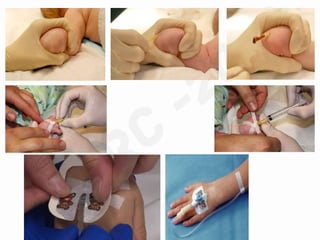
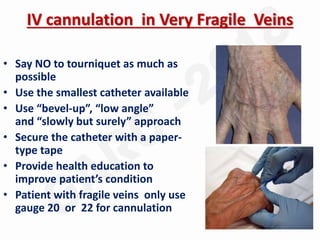
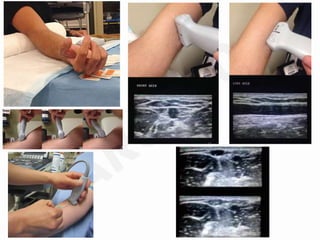
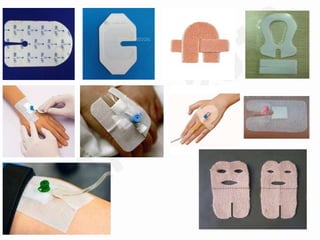
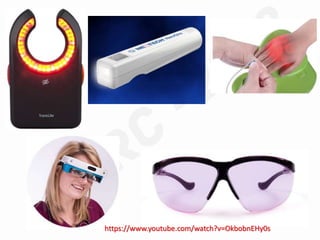
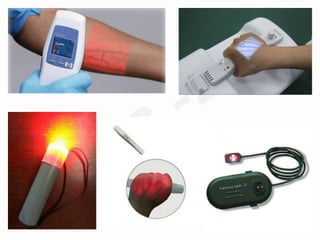
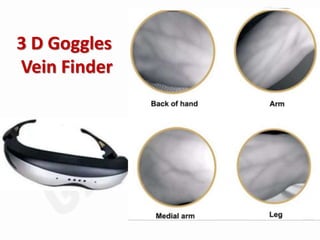
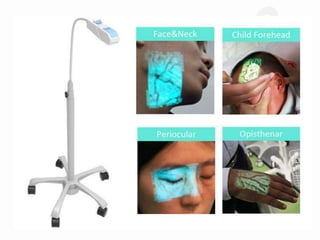
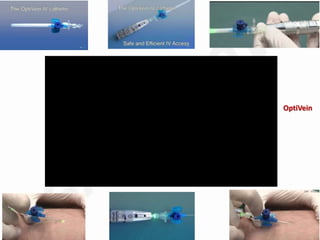
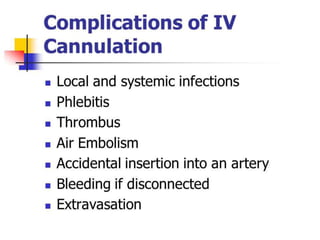
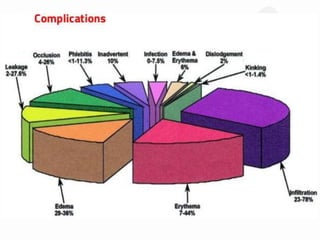
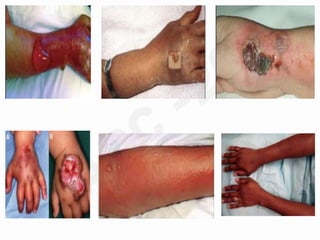
IV cannulation is a technique used to access veins to administer fluids or medications. It involves inserting a cannula into a vein. The document discusses various tips for successful IV cannulation including vein selection, making veins more visible, catheter insertion technique, securing IV lines, and special considerations for different patient populations. Potential complications of IV cannulation are also mentioned such as damage to surrounding tissues if "fishing" for veins. New technologies to help with cannulation like ultrasound guidance, vein finders, local anesthetics, and robotic systems are also reviewed.