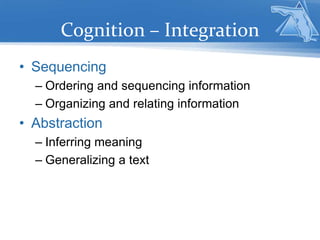
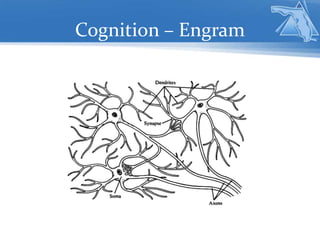
The document provides guidelines for unpacking academic standards by identifying skills and knowledge components, and addresses the importance of cognitive processes in learning. It emphasizes the use of various instructional scaffolds and technology tools to support different cognitive aspects such as input, integration, memory, and output. Additionally, it encourages reflective practices among educators to enhance instructional strategies and improve student engagement.