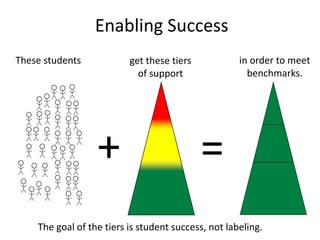
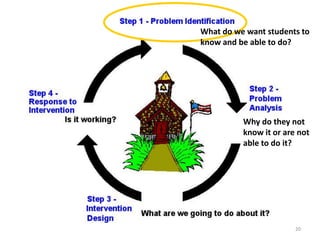
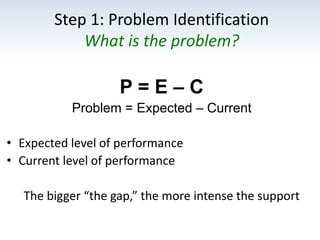
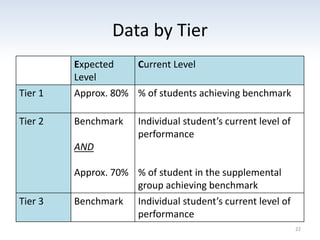
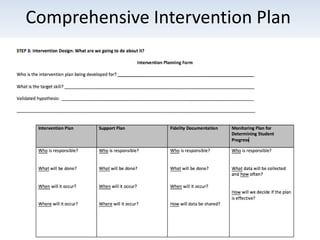
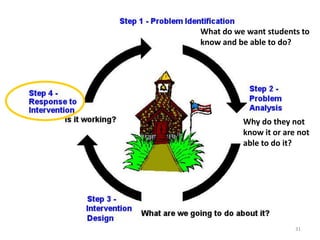
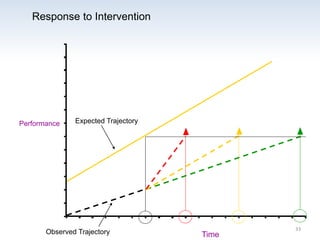
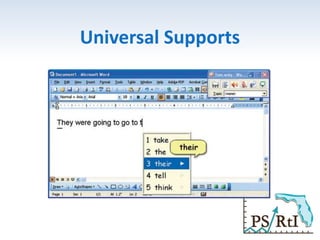
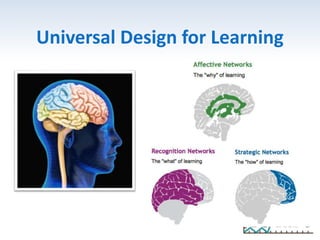
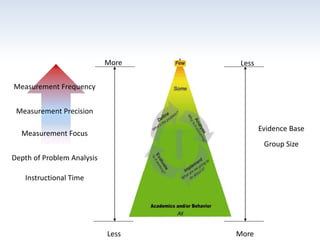
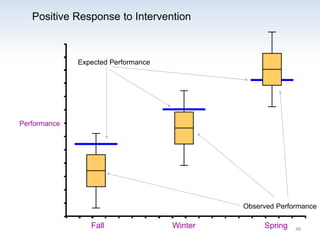
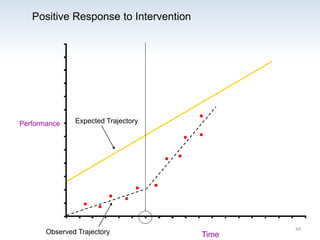
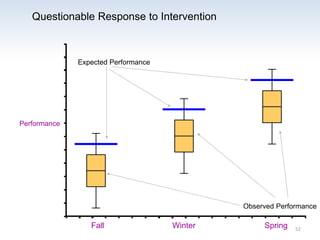
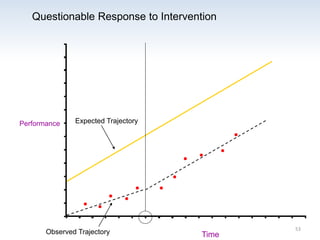
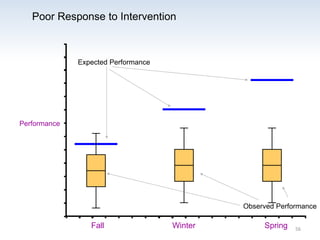
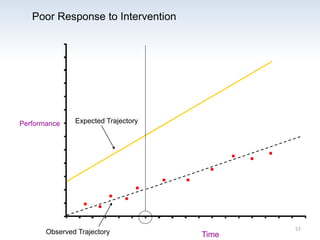
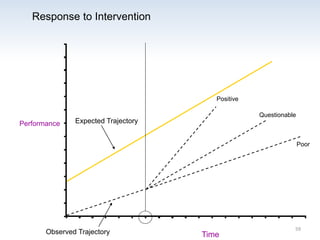
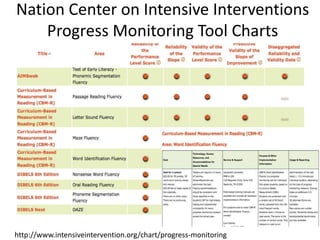
The document outlines the importance of a standards-based curriculum designed to meet the needs of all students, emphasizing a flexible and aligned approach to teaching and learning. It highlights a systematic cycle of assessment, intervention, and documentation to ensure mastery of standards, along with tiered instructional models tailored for varying levels of student support. It also addresses the significance of Individualized Education Programs (IEPs) aligned with state standards to facilitate access to general education for students with disabilities.