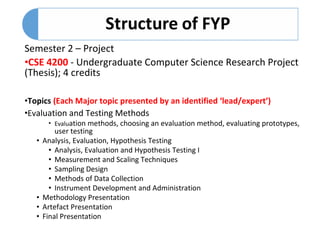
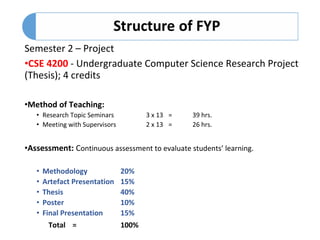
The document outlines the history and evolution of a computer science research project course, transitioning from a one-semester to a two-semester structure to allow for better development and assessment of research proposals and thesis work. It details the management philosophy, methodologies, and assessment mechanisms, emphasizing transparency, group-based management, and multiple levels of supervision. Key learning outcomes and course components are also described for both semesters, highlighting the continuous assessment approach and the importance of student experience and research ethics.