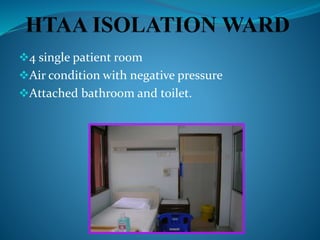
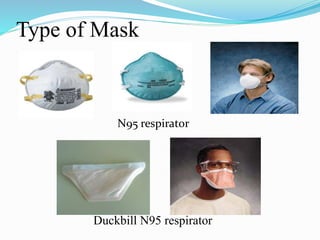
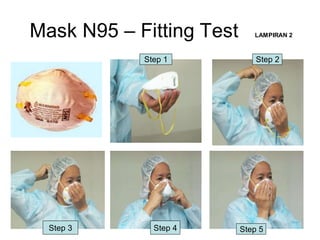
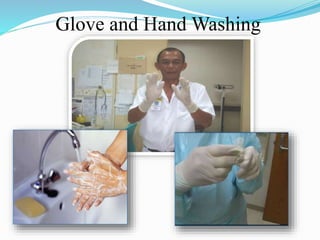
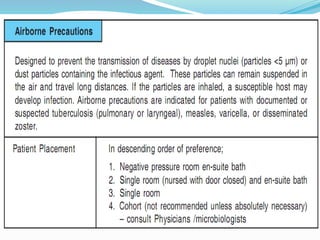
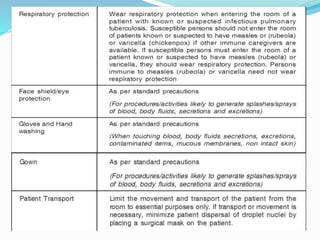
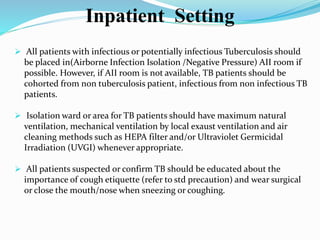
This document discusses cough etiquette and respiratory hygiene to prevent the spread of respiratory infections in healthcare settings. It recommends that individuals with respiratory symptoms cover their mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing, and dispose of tissues properly. Healthcare facilities should promote these practices and make resources like masks and hand hygiene supplies available. Proper patient placement, respiratory protection for healthcare workers, and other infection control measures are needed to manage patients with infectious respiratory illnesses like tuberculosis.