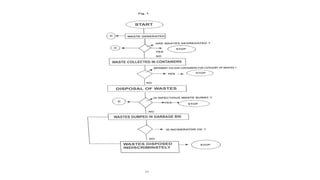
The document outlines various infection control measures including prevention of airborne contamination, safe handling of food and medical instruments, and the use of universal precautions to minimize the risk of nosocomial infections. It details transmission-based precautions for patients with highly infectious diseases and emphasizes the importance of proper waste management and environmental cleaning. Specific guidelines for isolation procedures and personal protective equipment (PPE) are also included to safeguard both patients and healthcare workers.