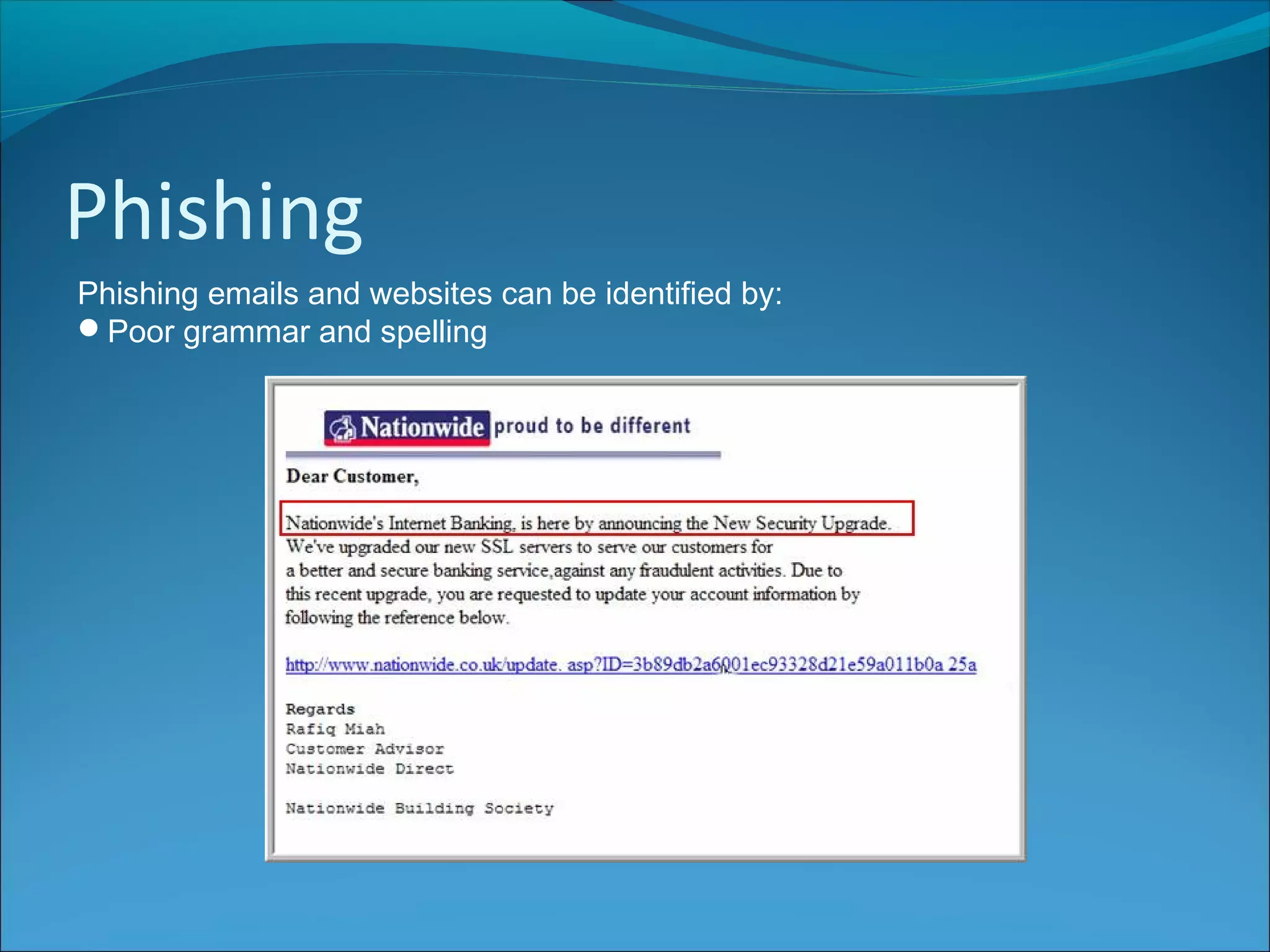
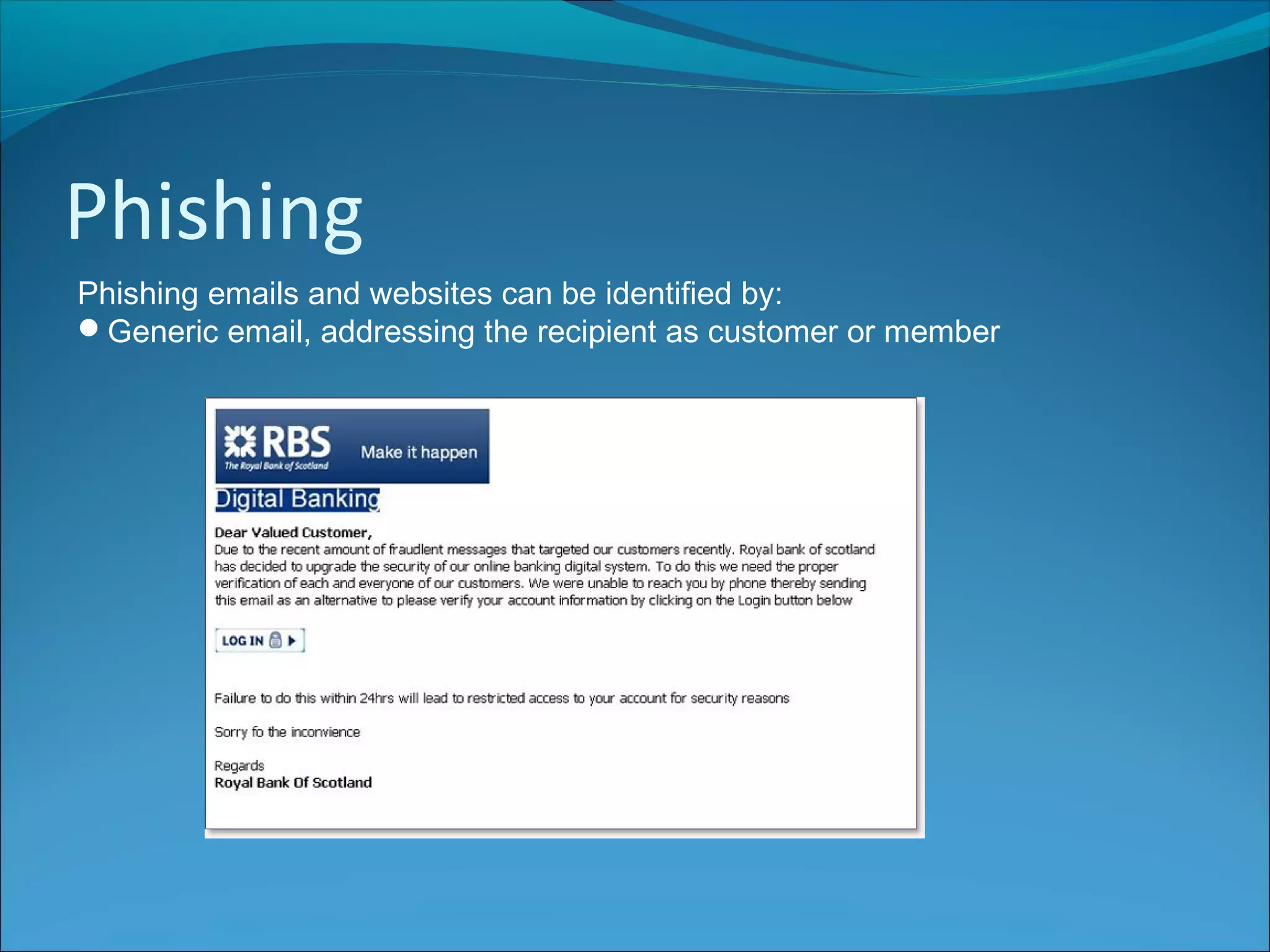
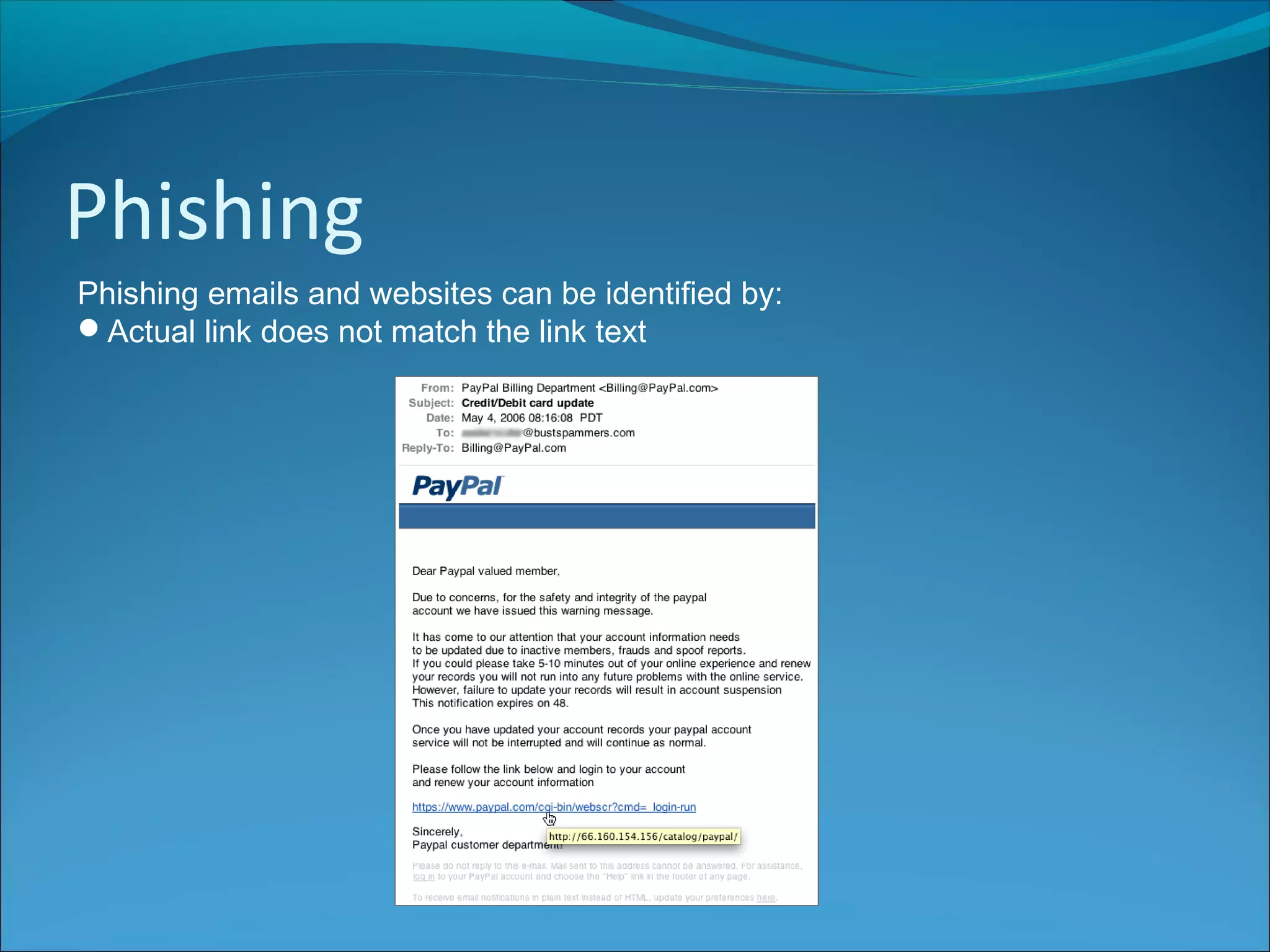
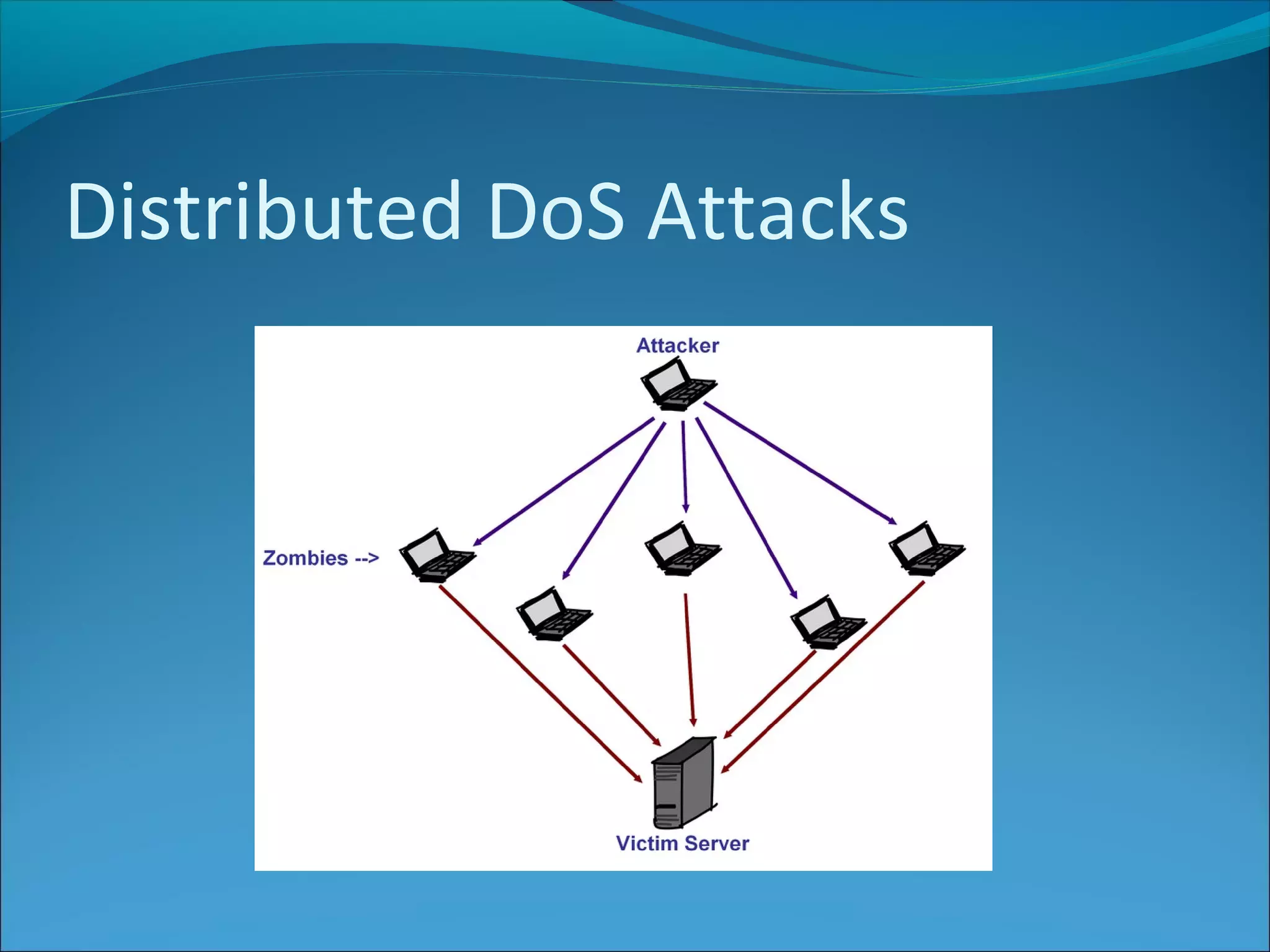
The document discusses various types of online fraud and identity theft, including goods not being delivered after payment, purchases made with stolen credit cards, loan and money transfer scams, and dating or holiday fraud. It also describes identity theft as using someone's personal information to impersonate them, and defines true name fraud and account takeover. The document then provides tips for protecting against online threats like avoiding sharing personal details or responding to suspicious emails, as well as maintaining antivirus software. It goes on to define spyware, keylogging, phishing, and denial of service attacks, explaining how to identify and mitigate these risks.