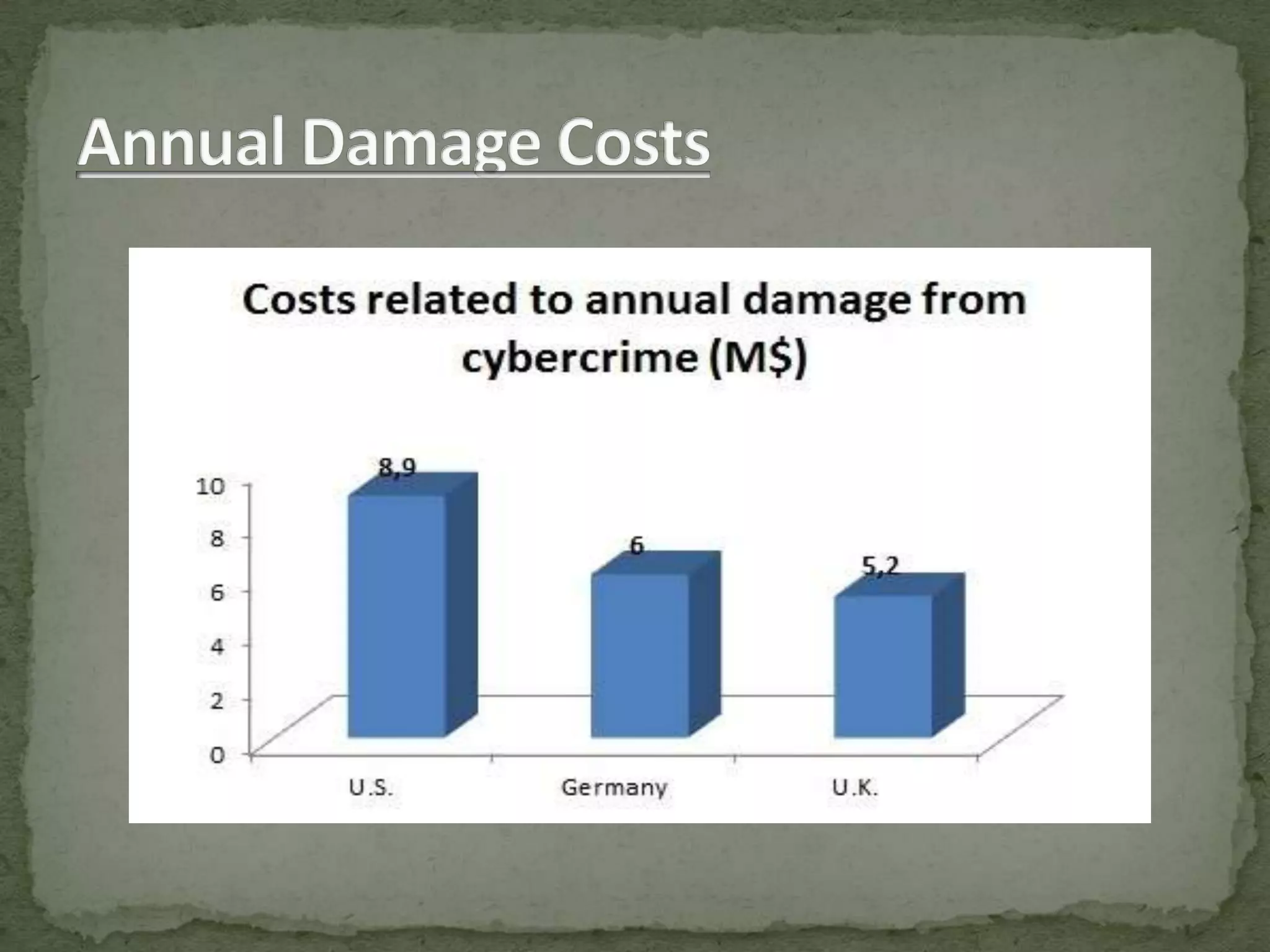
This document discusses various types of hacking including black hat hacking, data theft, and cyber attacks. It provides examples of common attacks such as SQL injection, DDoS attacks, social engineering, malware/viruses, and password cracking. The document also outlines skills required for ethical hacking to prevent attacks, and measures that can be taken including firewalls, antivirus software, strong passwords, and monitoring online activities. Statistics show cyber crimes are increasing globally and cost billions per year. Education and employing more security experts are suggested to improve prevention of cyber attacks.