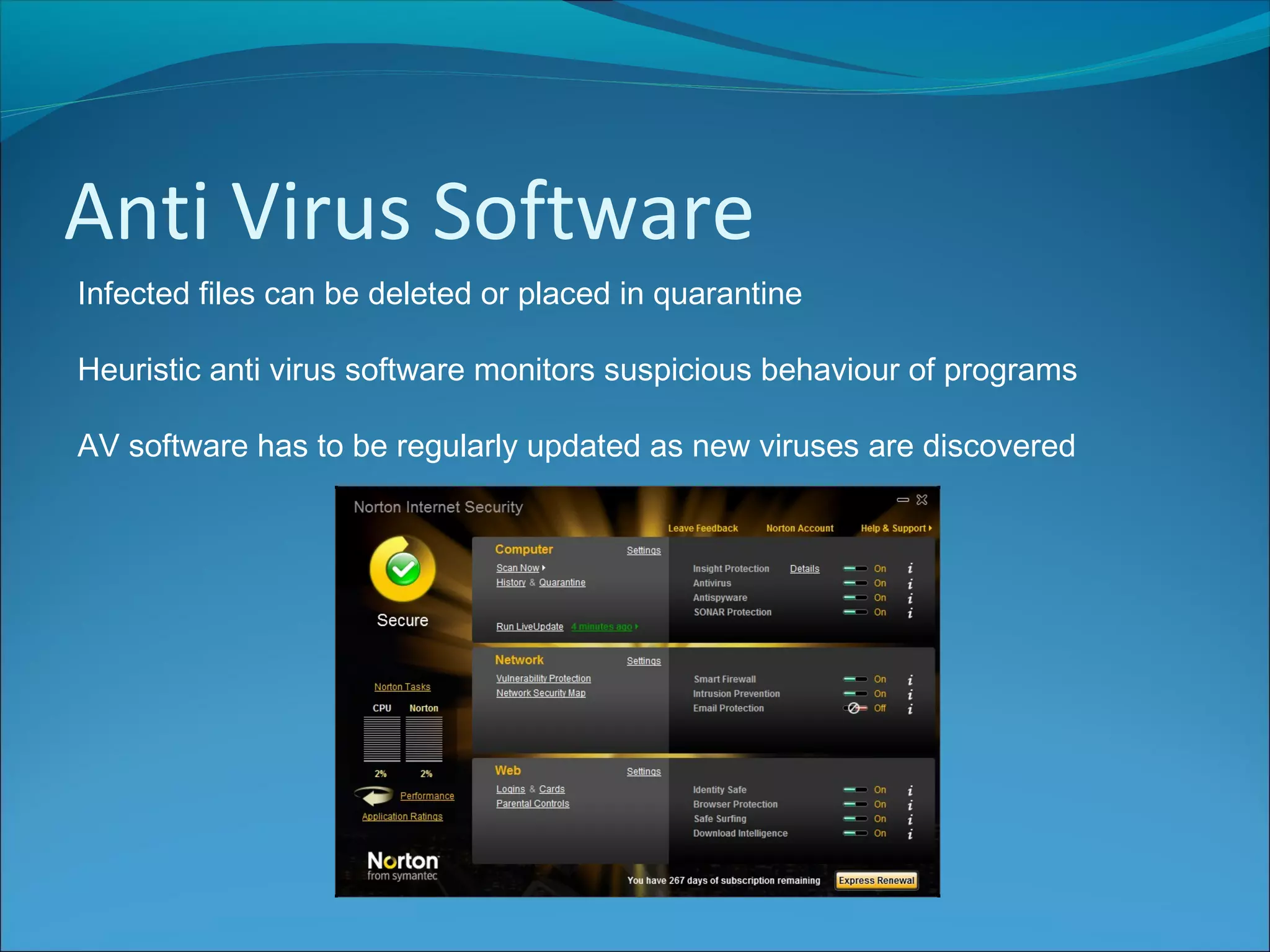
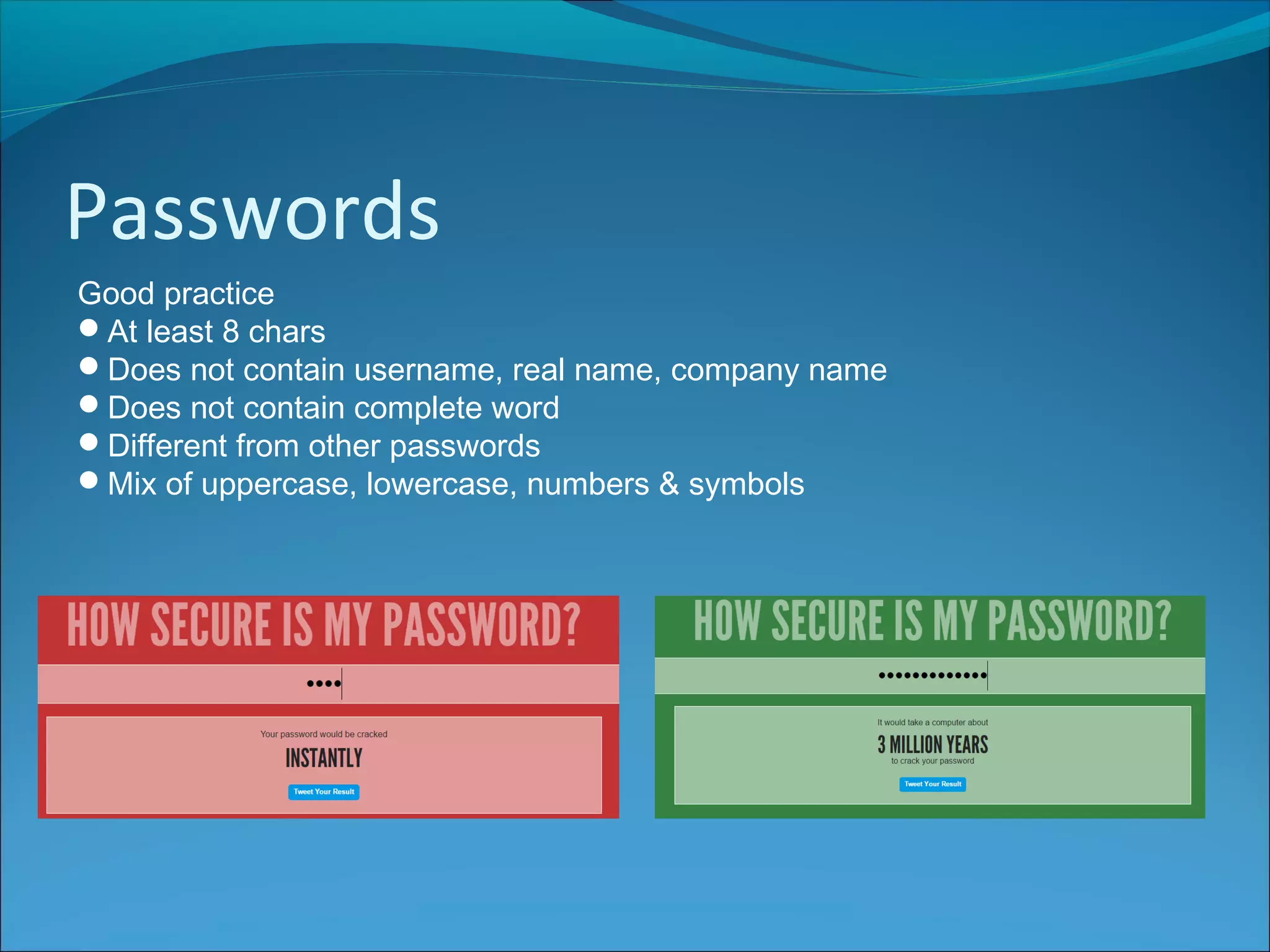
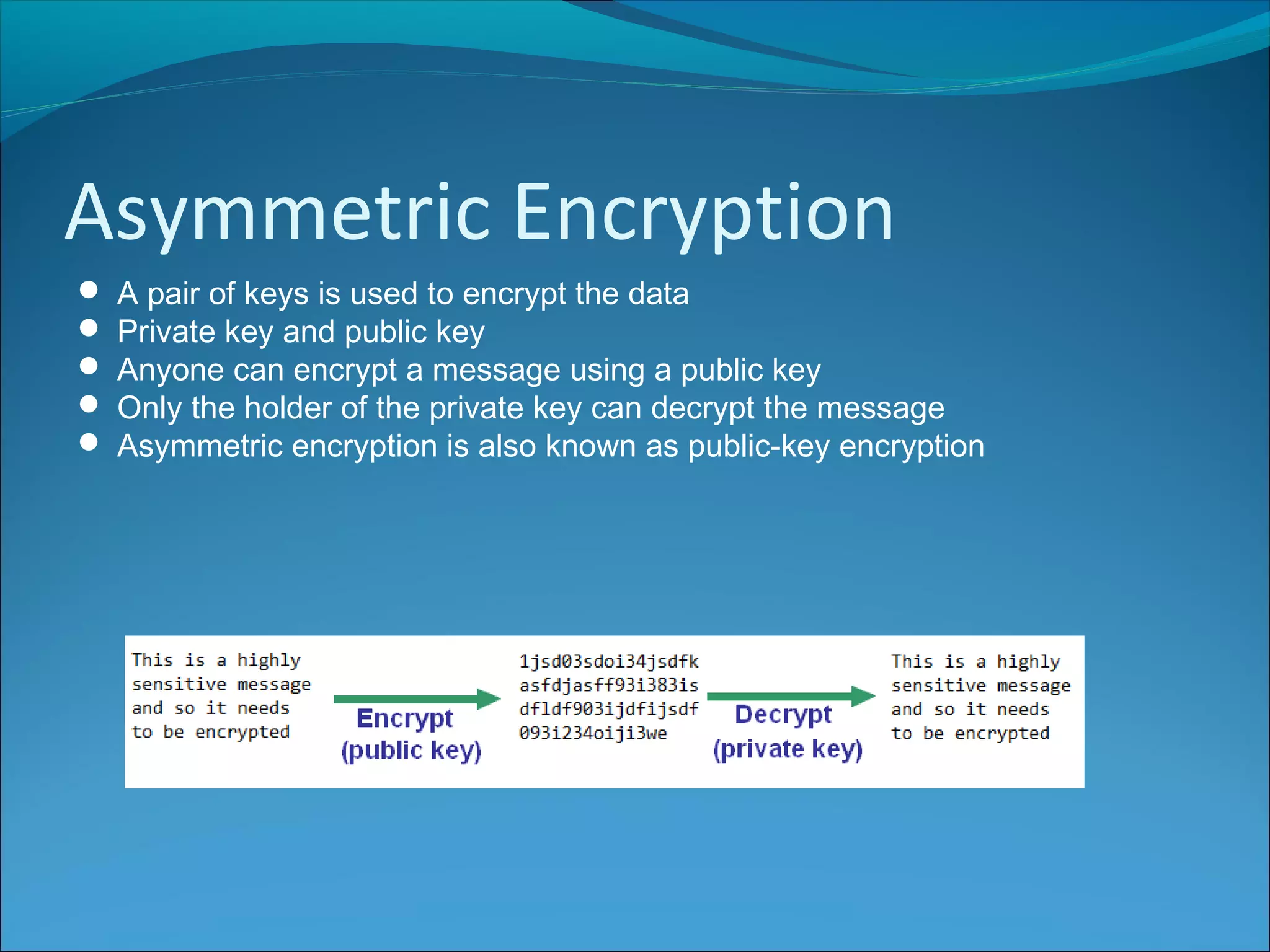
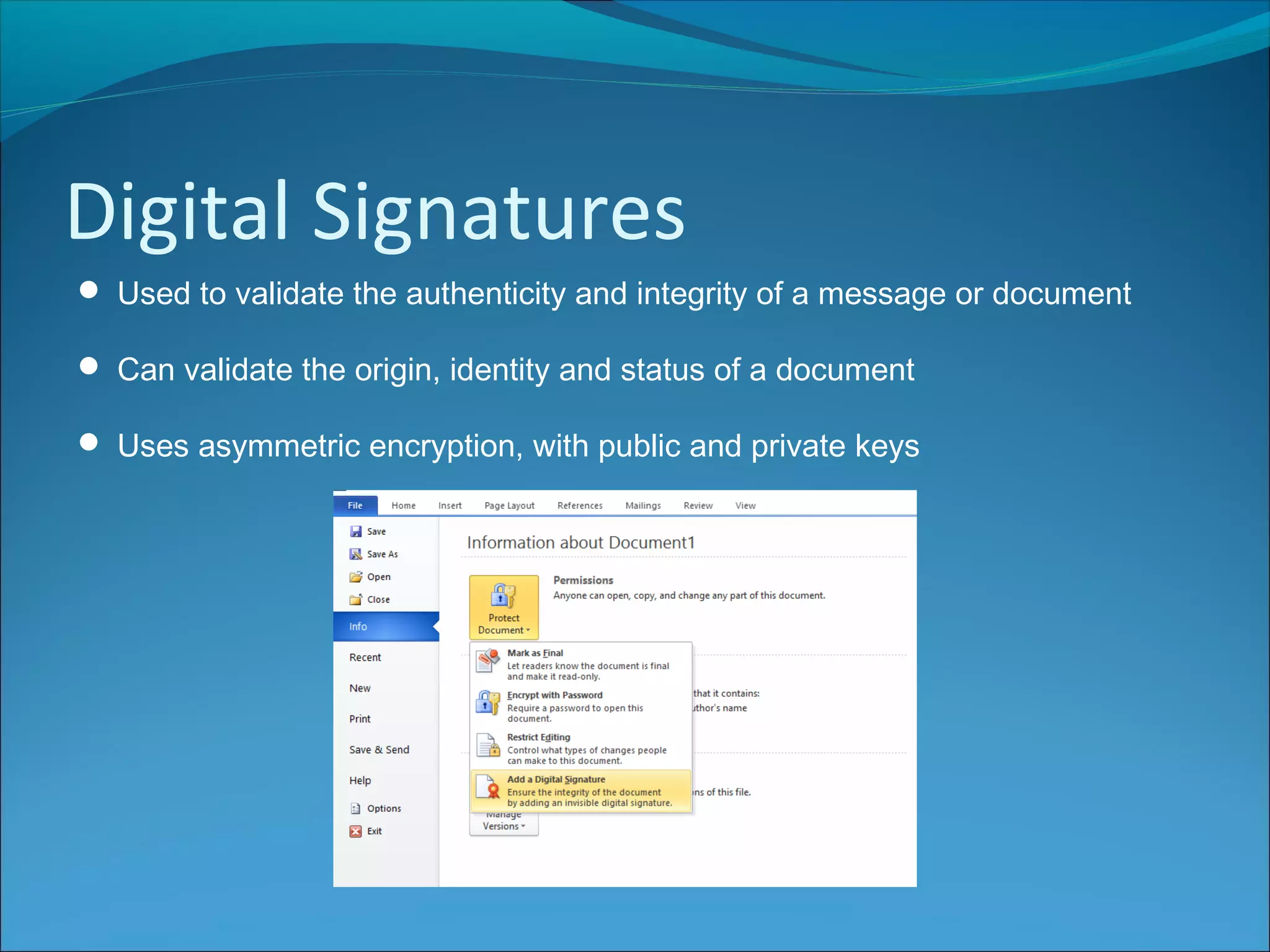
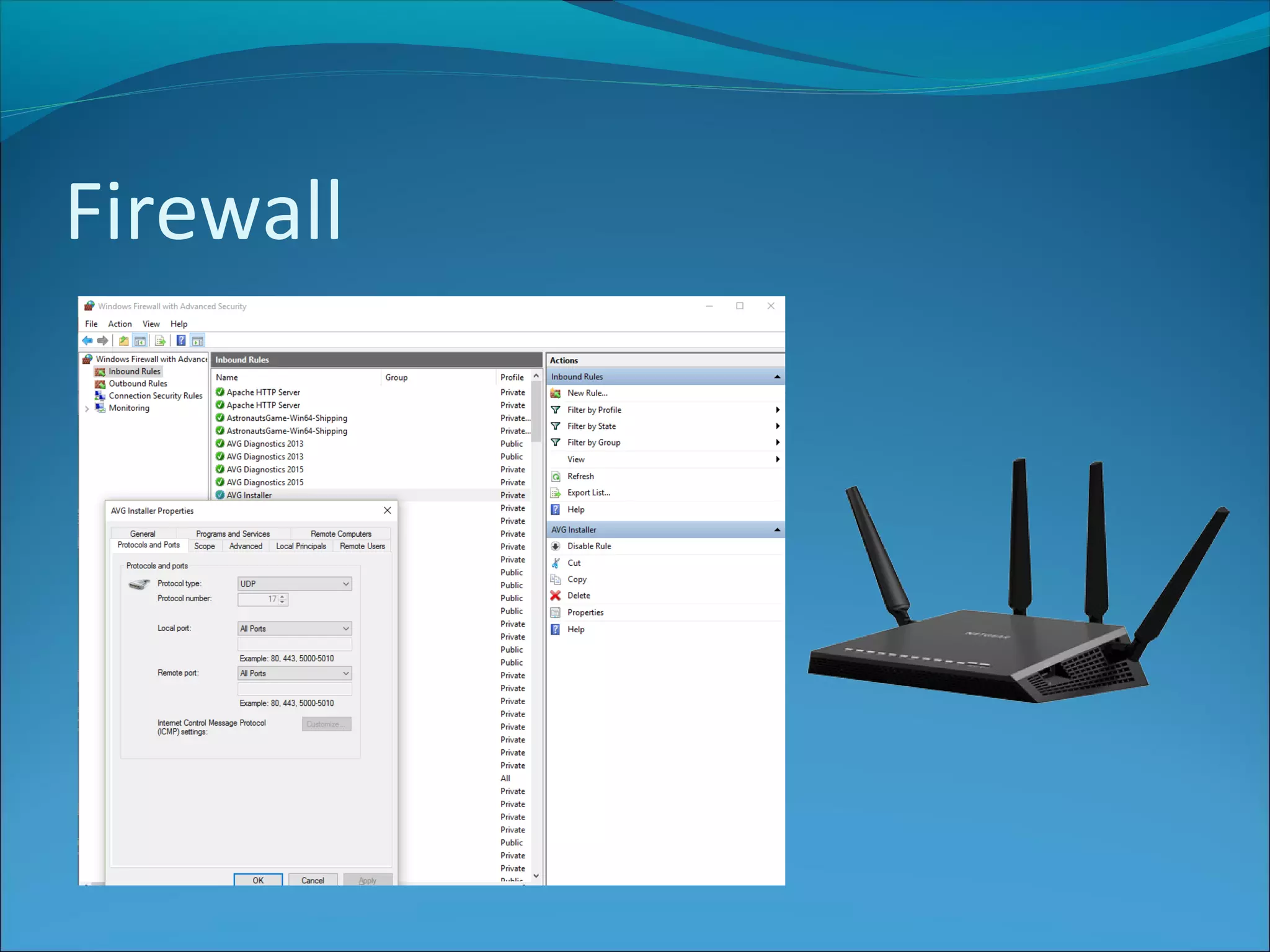
Anti-virus software scans files to identify viruses by matching signatures of previously discovered viruses. It offers real-time protection and scheduled scans, and can delete or quarantine infected files. Passwords are commonly used with usernames to authenticate users, and should be at least 8 characters long without including personal details. Biometrics authenticate users using unique biological traits like fingerprints, iris patterns, or facial recognition. Encryption converts data into an unreadable format, while decryption reverses the process, and different encryption methods include symmetric, asymmetric, and digital signatures.