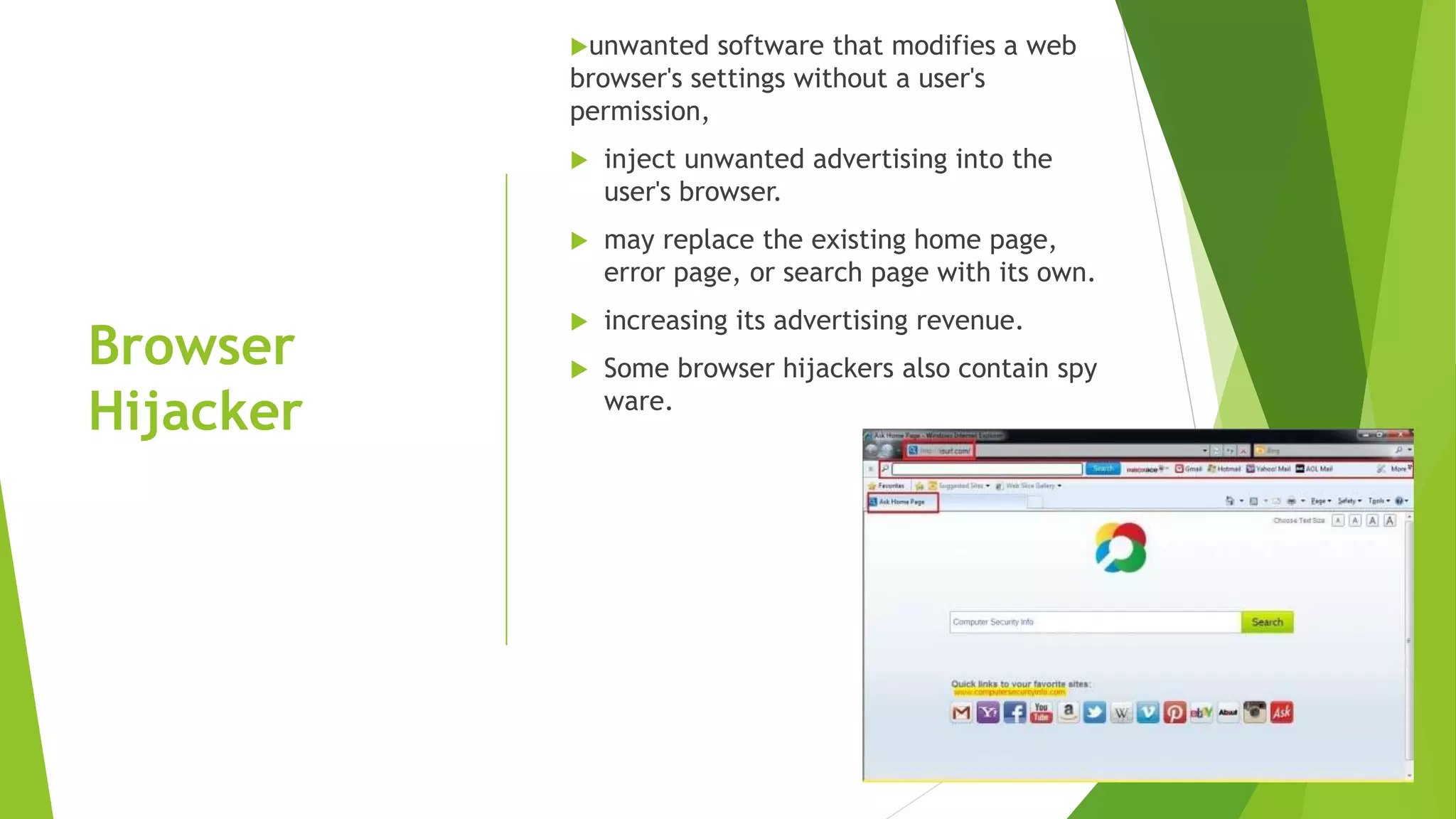
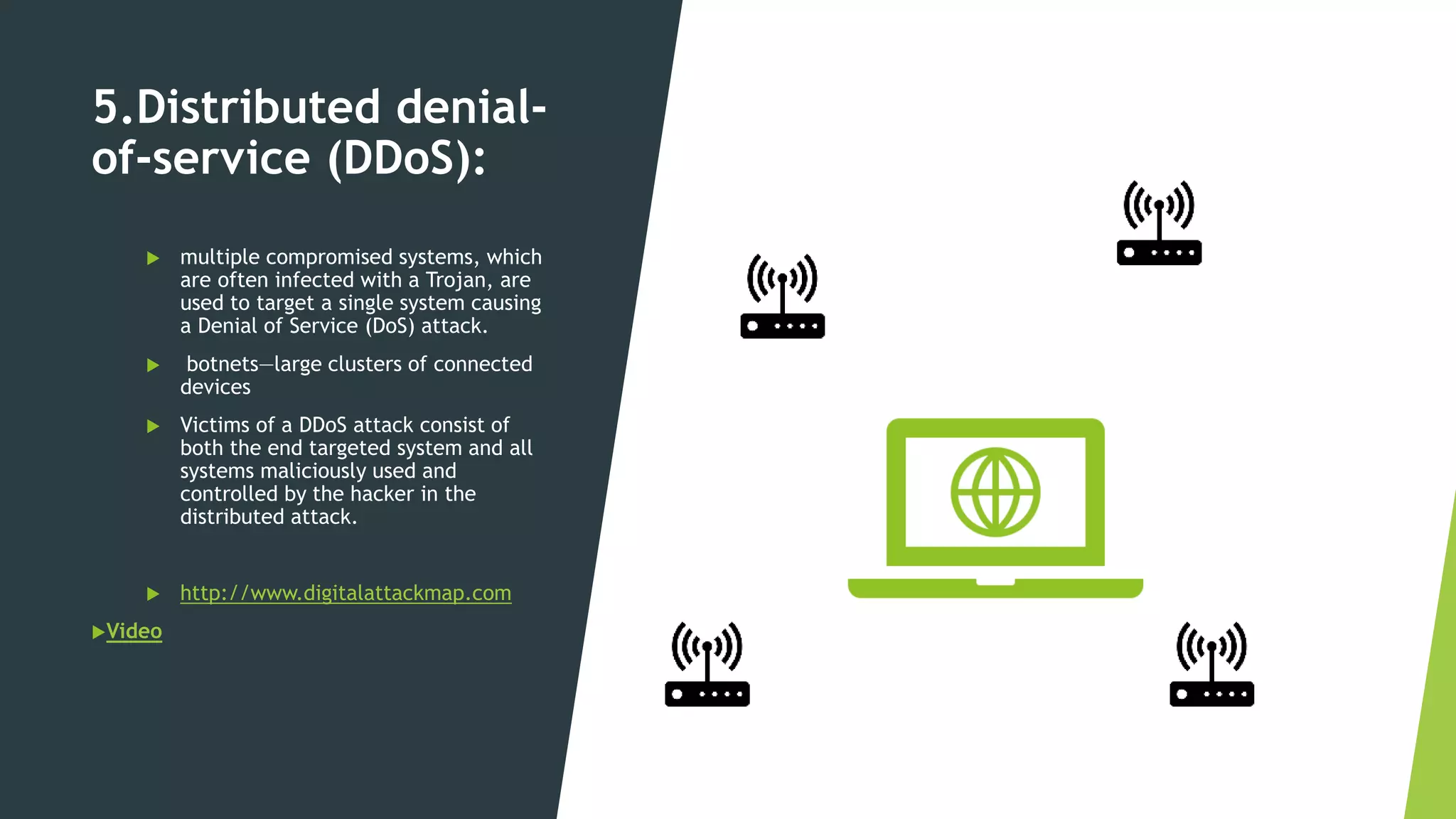
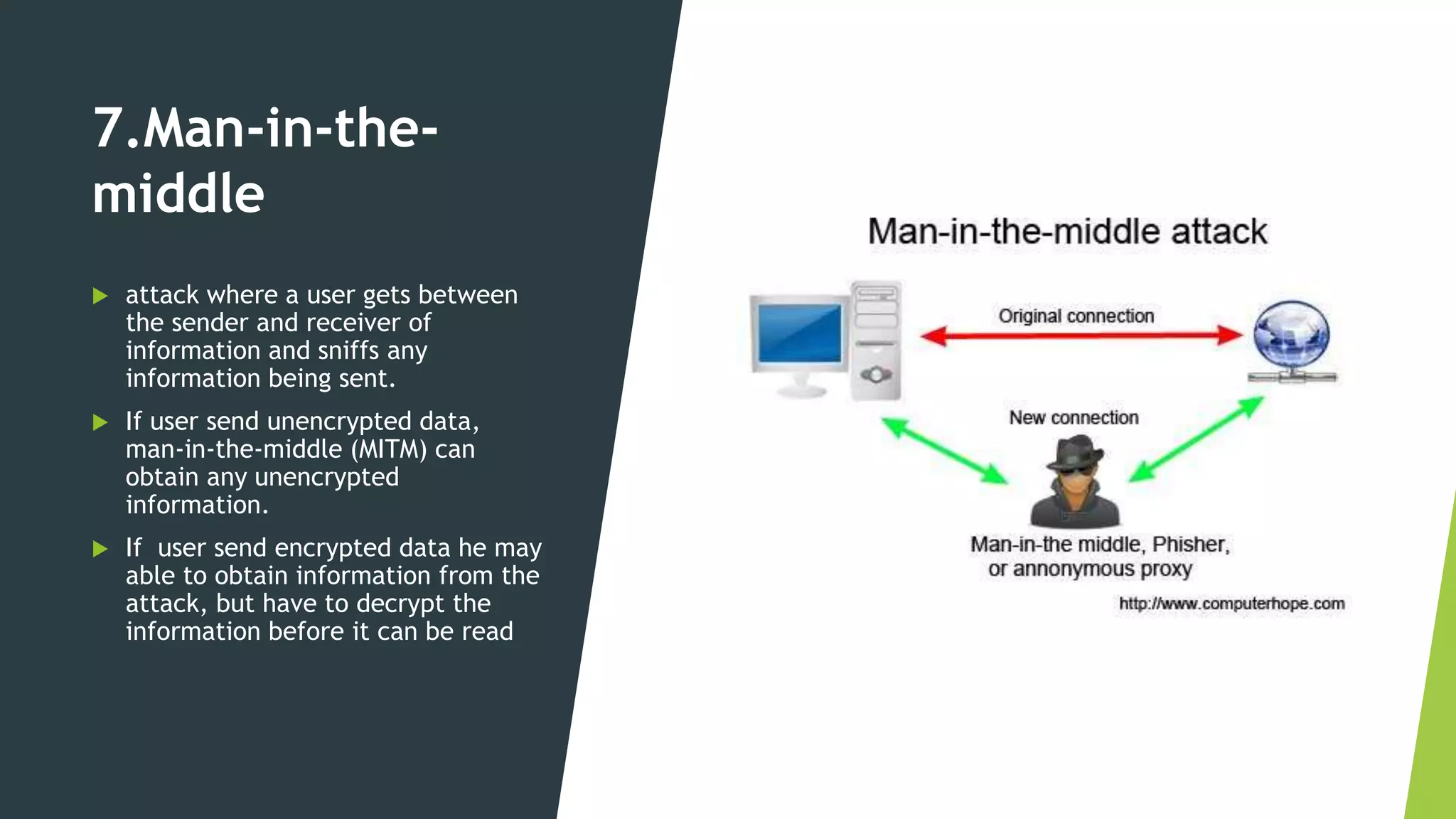
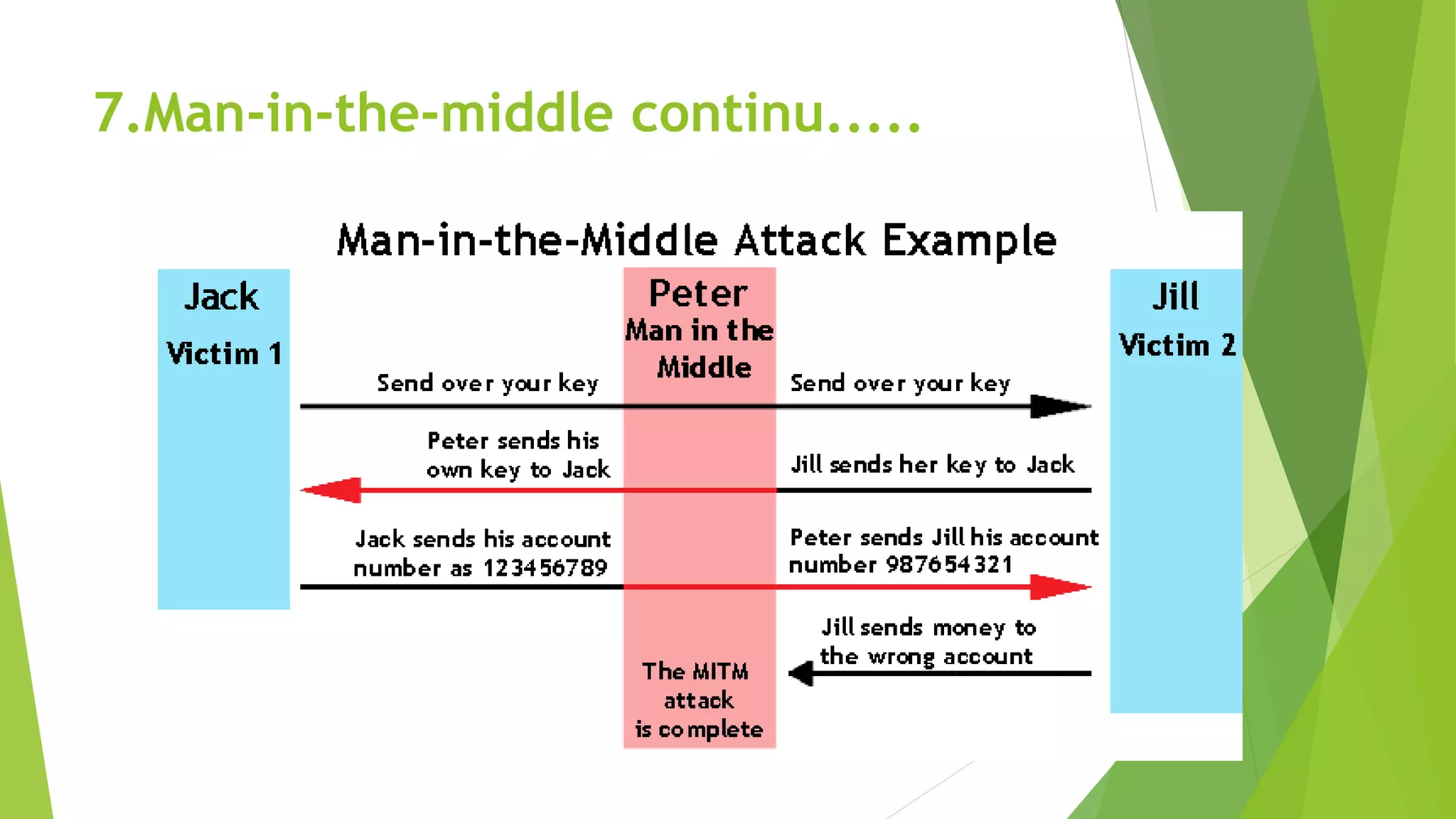
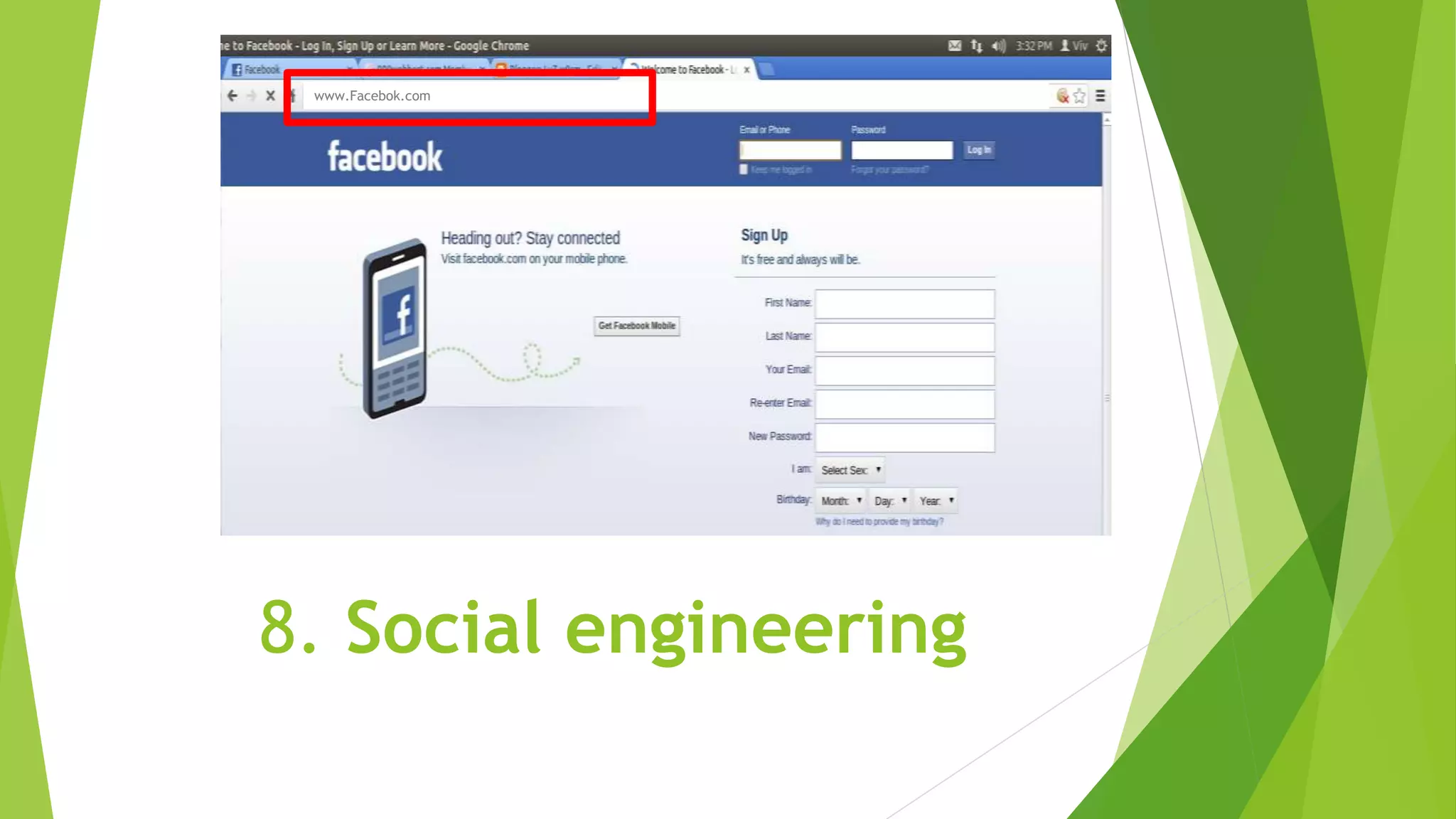
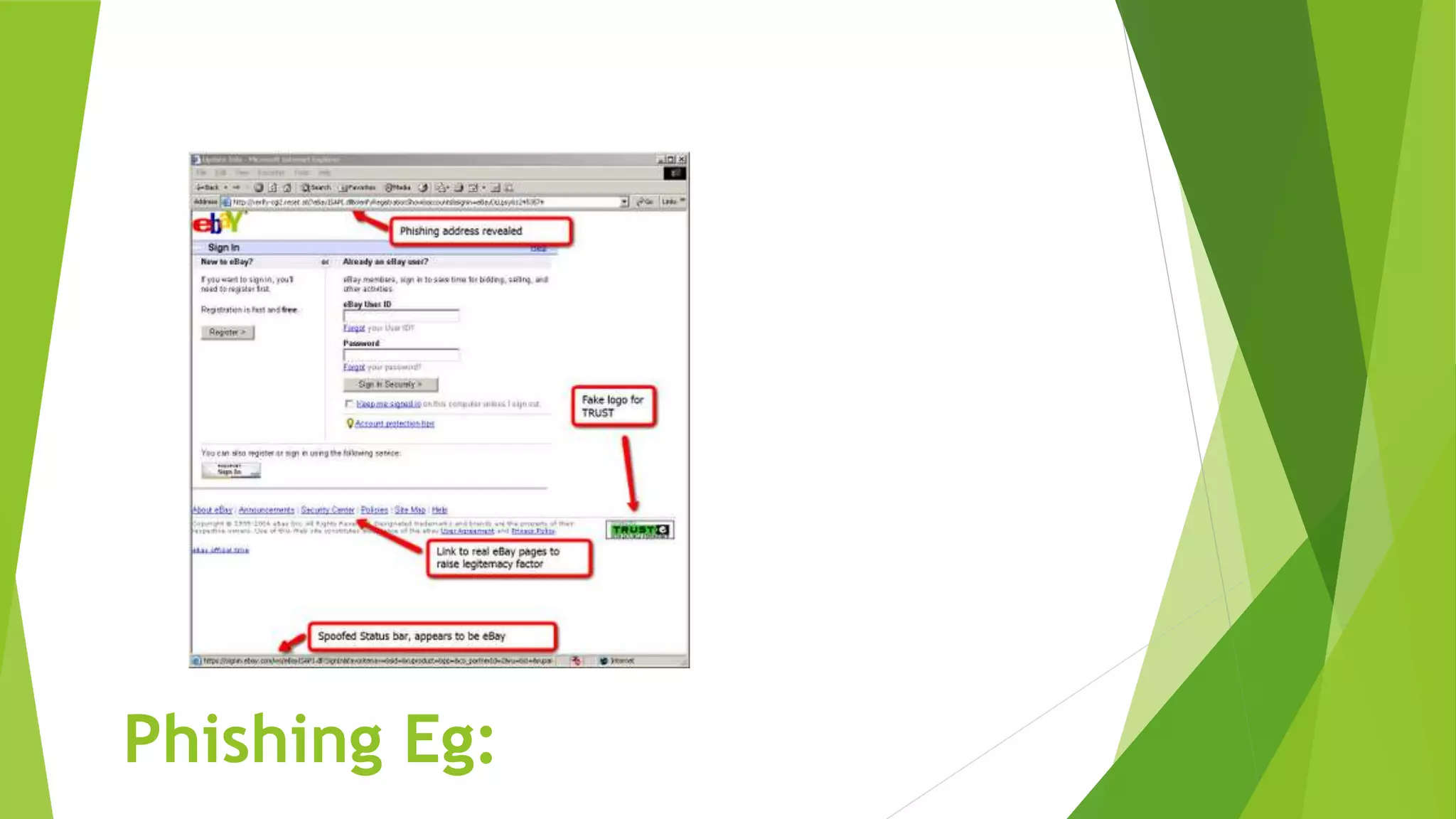
The document discusses common cybersecurity concepts including vulnerabilities, threats, and exploits. It defines vulnerabilities as weaknesses that can be exploited, threats as potential events that can harm systems or data, and exploits as techniques used to breach security. Examples of threats include natural disasters, human threats from insiders like employees or hackers, and technology threats such as malware, denial of service attacks, and social engineering. Common types of malware are discussed like viruses, worms, Trojans, and ransomware, as well as attack methods like backdoors, brute force attacks, spoofing, and man-in-the-middle assaults. Social engineering tricks people using phishing, baiting, pretexting, and scareware.