Embed presentation
Downloaded 41 times



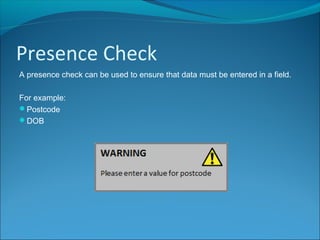
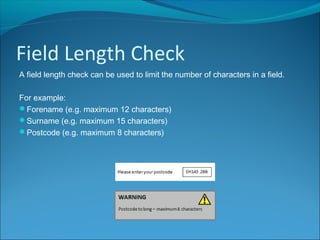
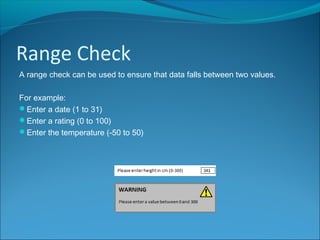
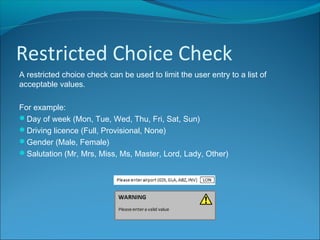
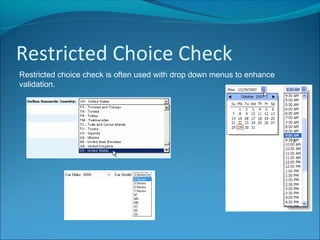
Validation is a process to ensure data meets certain rules to reduce incorrect entries. It helps by checking for a field's presence, length, being within a range, or being a choice from an acceptable list. While validation cannot prevent all wrong data, it can help by limiting user mistakes and misunderstandings that lead to erroneous entries.







