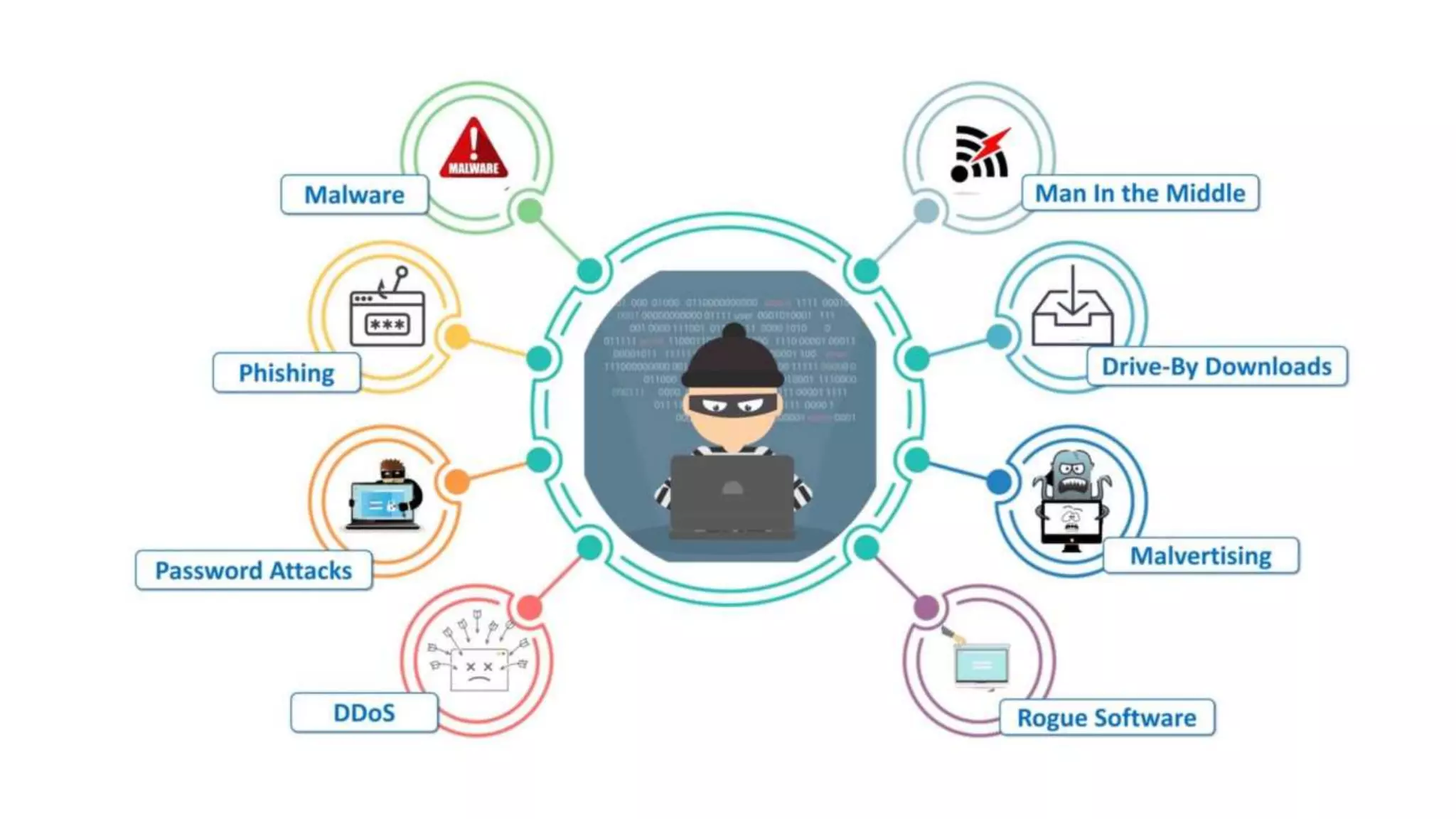
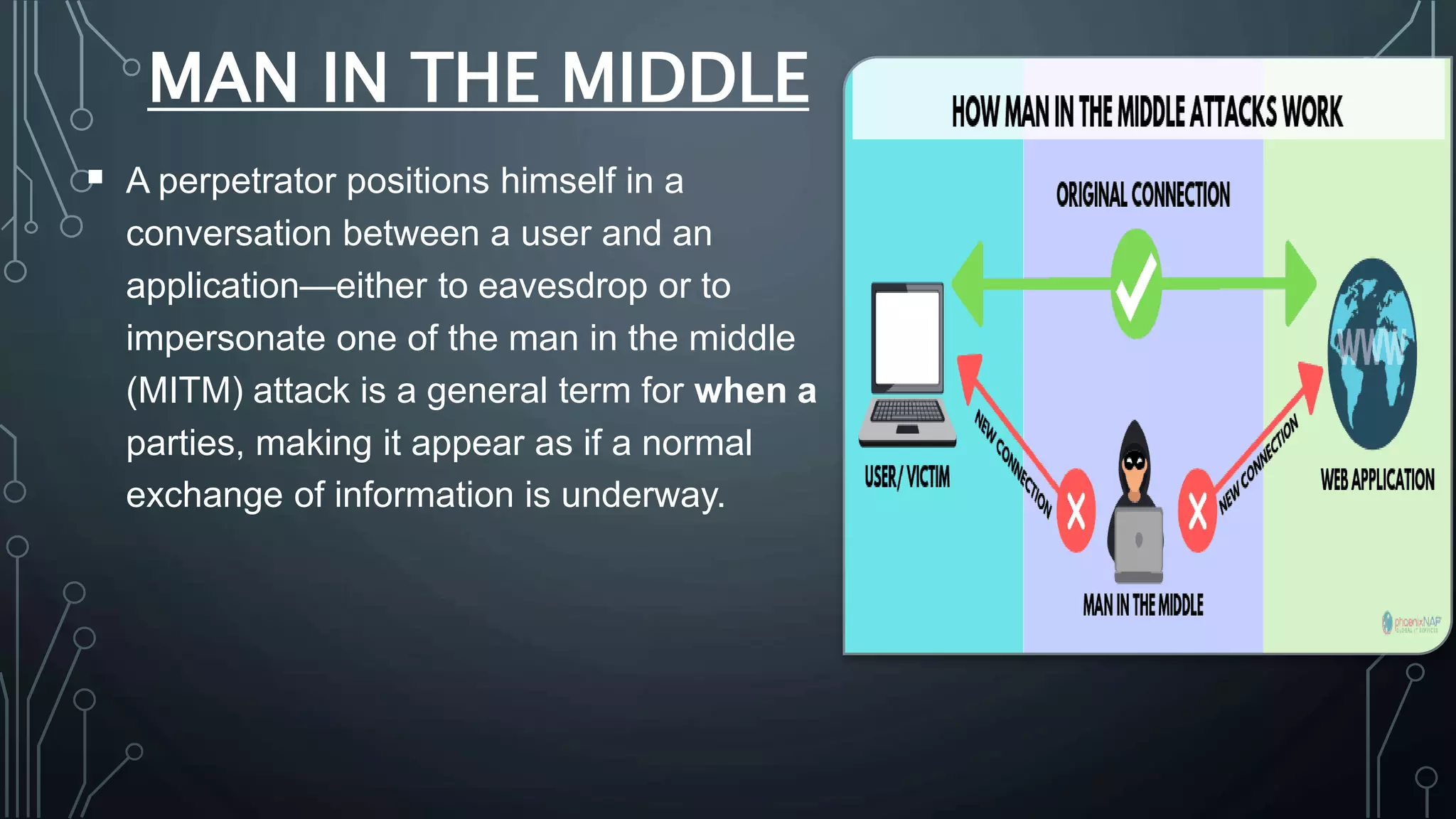
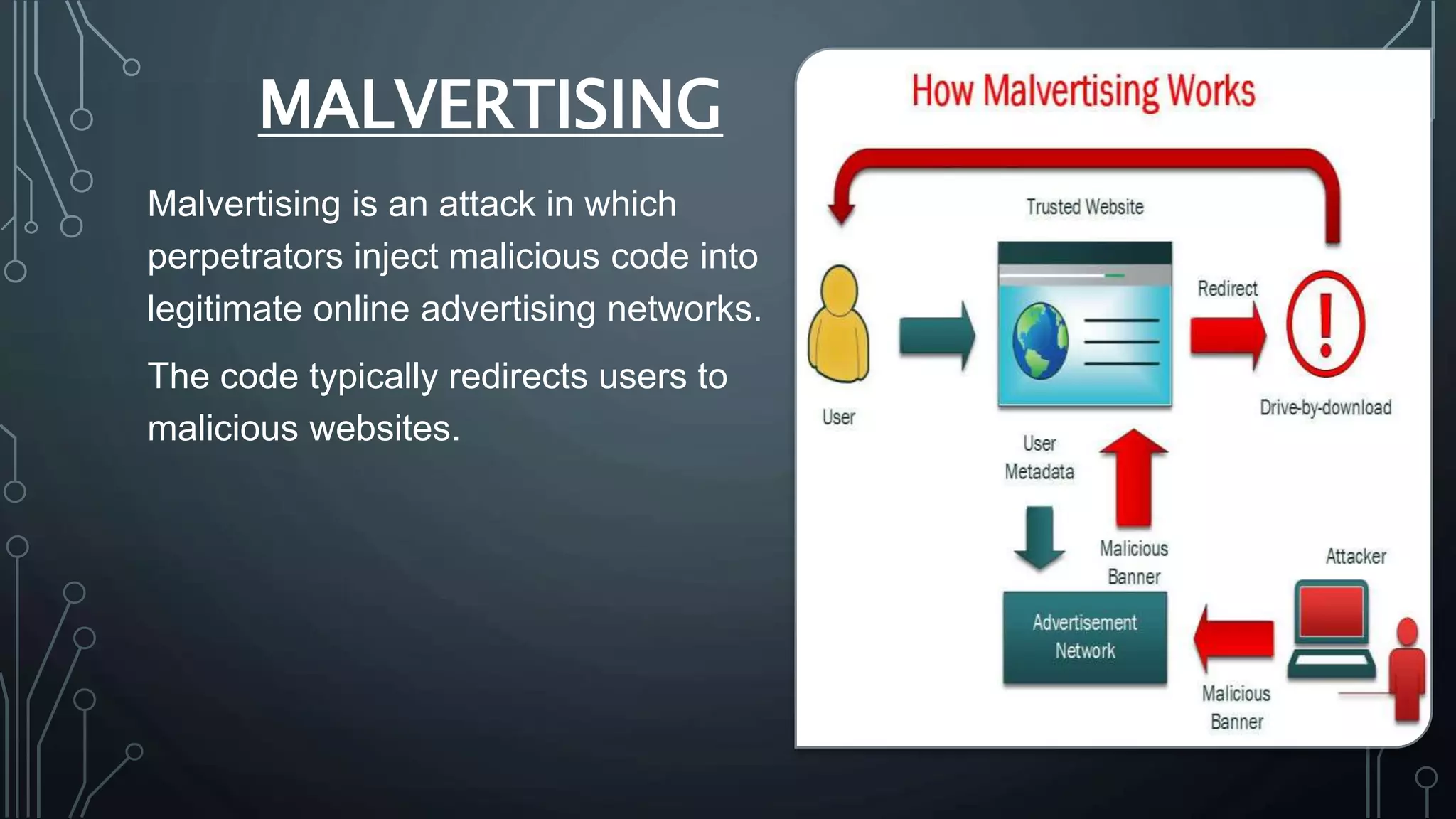
Cyber security protects systems, networks, and data from cyber threats such as cybercrime, cyberattacks, and cyberterrorism. It involves technologies, processes, and controls to secure networks, applications, information, and operations. Common cyber threats include phishing scams, password attacks, distributed denial of service attacks, rogue security software, man-in-the-middle attacks, drive-by downloads, malvertising, and malware such as viruses, Trojans, spyware, and ransomware. While cyber security helps protect valuable information, privacy, and systems from risks, it can also slow systems and require expertise to properly configure and update protections.