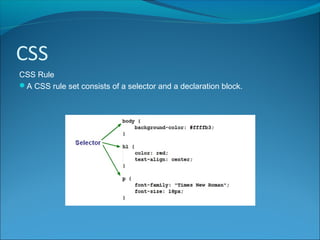
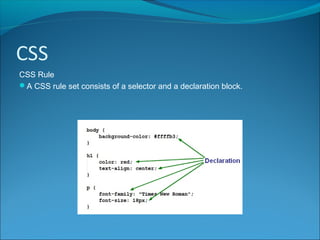
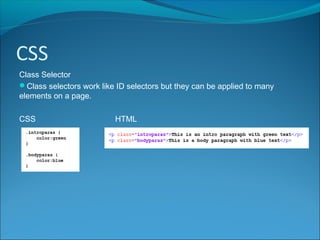
CSS (Cascading Style Sheets) is a style sheet language used to describe the presentation of HTML documents. HTML was intended for describing content, not design, so CSS separates style information from HTML pages. CSS rules consist of selectors that specify which elements to style and declaration blocks that define the styles. CSS can be applied inline, internally in <style> tags, or externally in separate files, which allows changing the style across all pages by editing one file. ID and class selectors target individual or groups of elements. External CSS is linked to HTML pages using <link> tags.