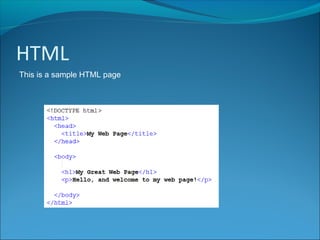
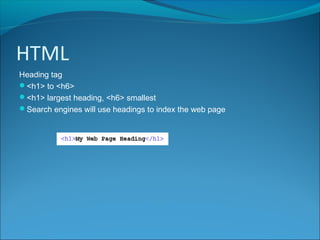
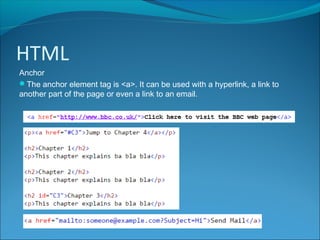
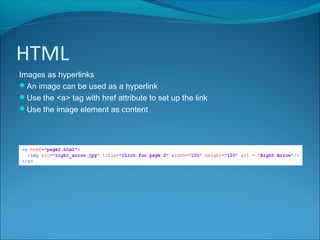
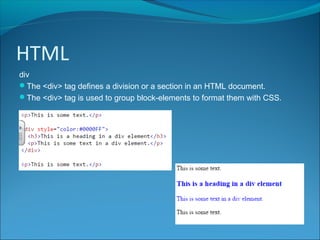
HTML is a markup language used to define the structure and layout of web pages. It uses tags to surround and provide metadata for different types of content, such as paragraphs, headings, images, and links. Key HTML elements include the <head> and <body> tags which define the head and body sections, and tags like <p>, <h1>-<h6> for paragraphs and headings, <img> for images, and <a> for hyperlinks. Attributes provide additional information about elements, like the src, width, and height attributes for images. HTML also supports lists, divisions of content, and embedding of audio and video.