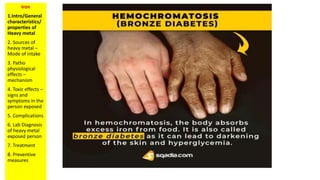
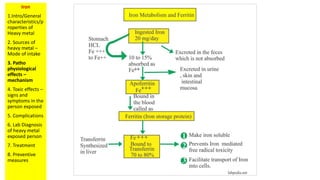
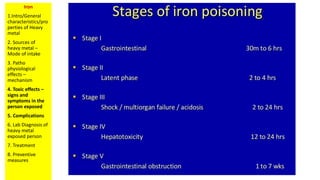
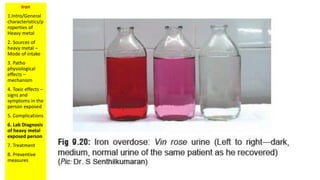
The document discusses iron toxicity and provides an overview of the key points to address for any heavy metal toxicity. These include an introduction to the heavy metal, sources of exposure, pathophysiological effects, toxic effects and symptoms, complications, laboratory diagnosis, treatment, and preventive measures. Specifically for iron, sources of excess iron include supplements and accidental ingestion of iron-containing objects. Toxic effects can include vomiting, diarrhea, shock, and organ damage. Laboratory tests to diagnose iron overload include serum ferritin levels and liver biopsy. Treatment involves gastric lavage, chelation therapy, and supportive care.