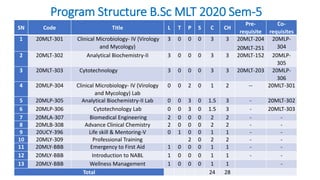
Cobalt is a trace mineral that is vital for human health but can become toxic at high levels. Cobalt toxicity occurs when a person is exposed to excess cobalt, often through metal hip prostheses or occupational exposure. Symptoms of cobalt toxicity include thyroid abnormalities, heart failure, and neurological issues. Diagnosis involves blood and urine tests to measure cobalt levels. The main treatment for systemic cobalt toxicity is revision or removal of the metallic prosthesis and temporary chelation therapy using NAC.