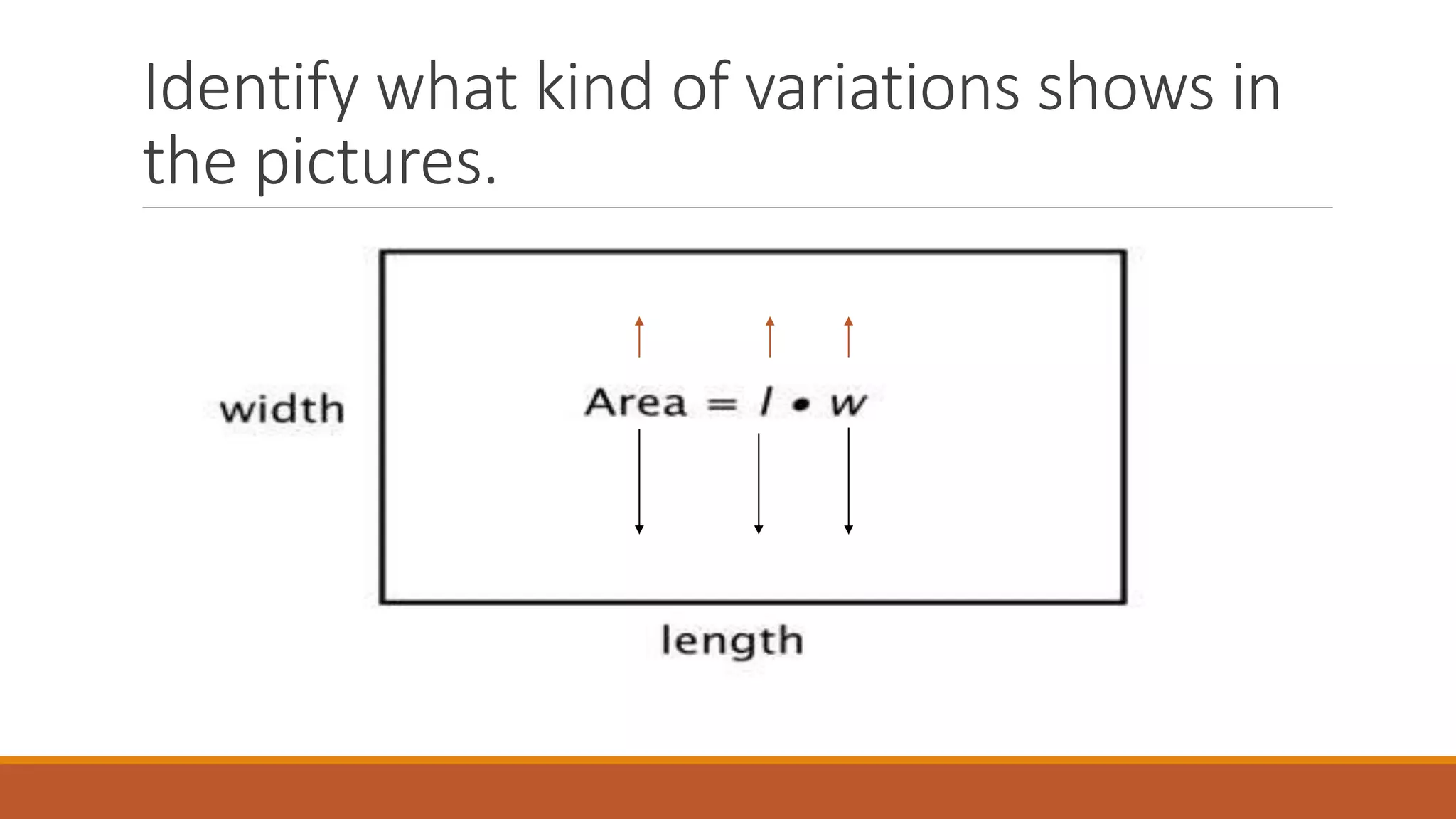
The document outlines objectives and methods for solving problems involving variation, including direct, inverse, joint, and combined variations. It provides formulas for translating statements into equations and several examples demonstrating how to find the constants of variation. Additionally, it includes offline activities and assessments to reinforce learning outcomes.