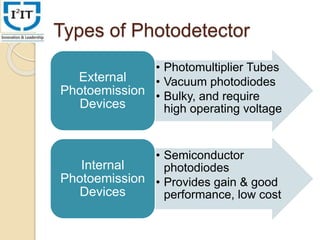
The document provides an overview of optical detectors, emphasizing their critical role in optical fiber communication by converting optical signals into electrical ones. It outlines performance and compatibility requirements, such as high sensitivity, low noise, and stability, while detailing various types of photodetectors, including photomultiplier tubes and semiconductor photodiodes. Additionally, it discusses the evolution from first to third generation photodetectors, highlighting advancements in wavelength sensitivity and materials used.