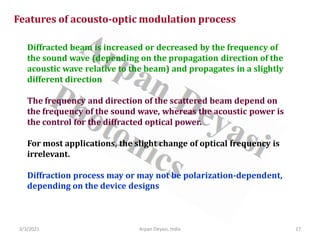
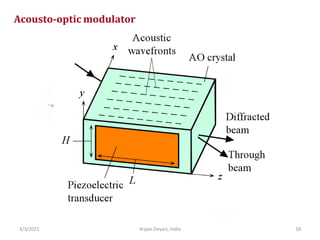
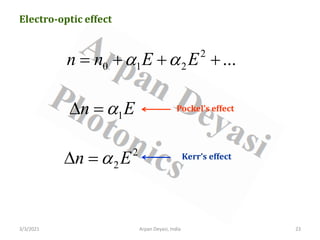
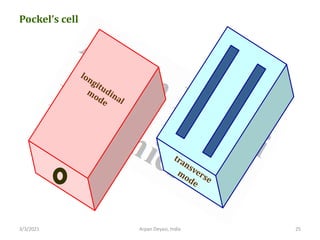
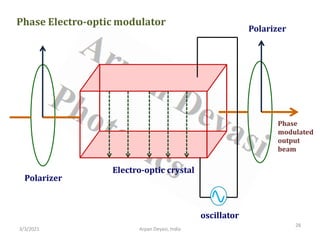
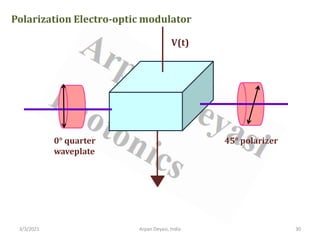
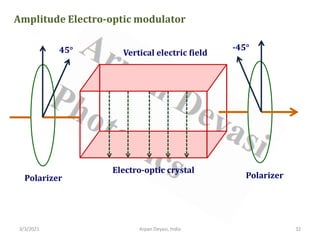
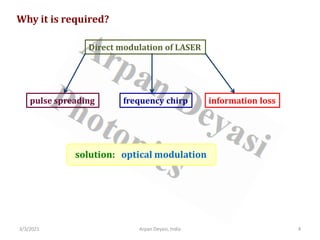
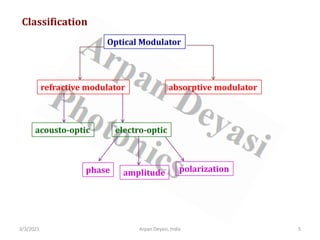
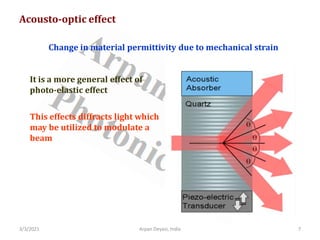
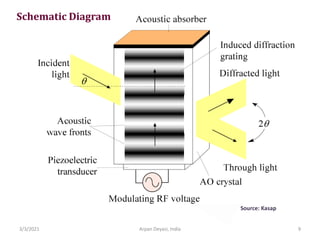
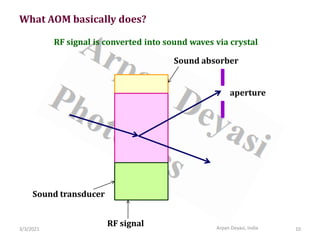
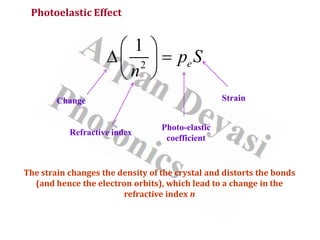
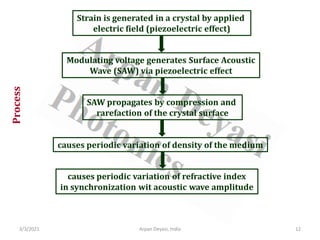
The document discusses optical modulators, specifically acousto-optic and electro-optic modulators. It describes how acousto-optic modulators use the acousto-optic effect to diffract and modulate a laser beam using a sound wave, while electro-optic modulators use the electro-optic effect to change an optical property like phase with an electric field. It provides details on the operating principles, materials used, and applications of these two types of optical modulators.




![3/3/2021 13
Arpan Deyasi, India
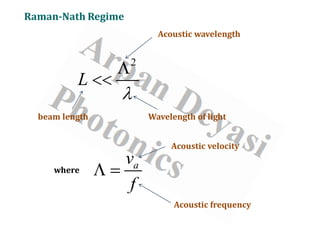
Acousto-Optic Modulation Regime
Raman-Nath regime ---- Diffraction occurs from a line grating
Occurs at relatively low frequency
[f< 10 MHz]
Smaller acousto-optic interaction
length
Occurs for arbitrary angle of
incidence
Multiple diffracted beam at
output
Source: Kasap](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationopticalmodulator-210303071729/85/Optical-Modulator-13-320.jpg)
![3/3/2021 15
Arpan Deyasi, India
Acousto-Optic Modulation Regime
Source: Kasap
Bragg regime ---- Diffraction occurs from through beam
Occurs at relatively higher
frequency [f< 10 MHz]
Larger acousto-optic
interaction length
Only one diffracted beam at
output
Scattering effect is negligible](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationopticalmodulator-210303071729/85/Optical-Modulator-15-320.jpg)