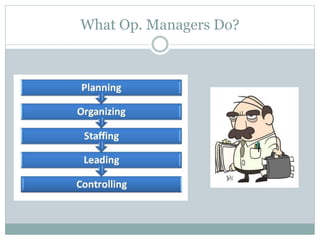
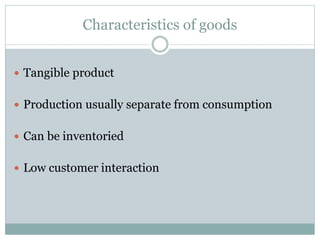
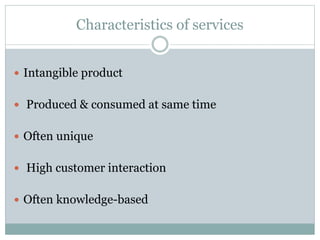
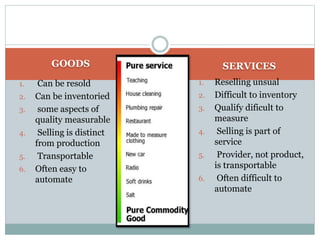
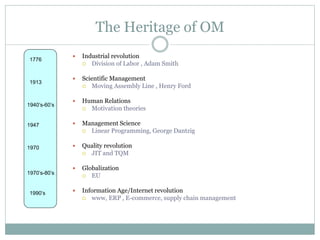
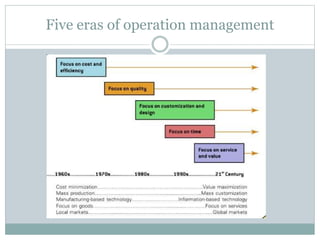
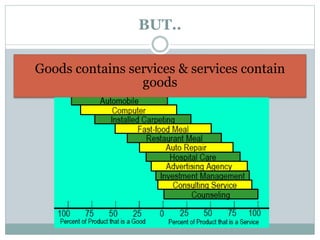
The document discusses operations management (OM), defined as the science and art of ensuring successful creation and delivery of goods and services. It outlines the significance of studying OM as it integrates various business functions, enhances productivity, and is essential in diverse industries. Additionally, it differentiates between goods and services, their characteristics, and traces the history and evolution of OM through key eras and concepts.