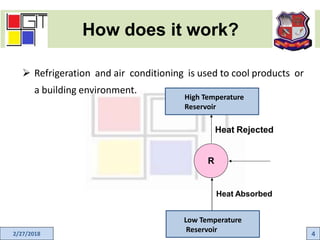
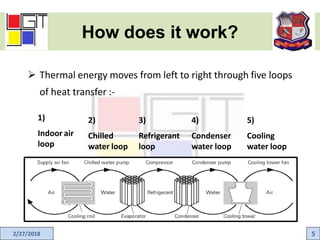
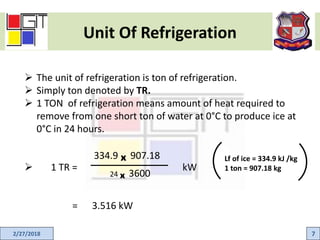
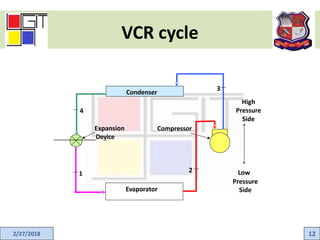
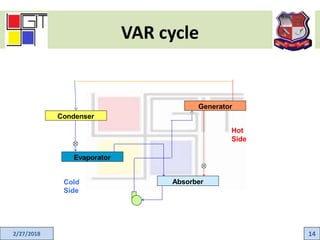
This document provides an active learning assignment on refrigeration for an elements of mechanical engineering course. It includes an introduction to refrigeration, how refrigeration systems work, common refrigerants, the unit of refrigeration, applications, and the two main types of refrigeration systems - vapor compression and vapor absorption. The vapor compression refrigeration cycle is explained in detail through labeled diagrams showing the four processes of expansion, vaporization, compression, and condensation.