This document contains an assignment on complex numbers and functions for a BE Mechanical engineering course. It covers the following topics in 3 paragraphs or less each:
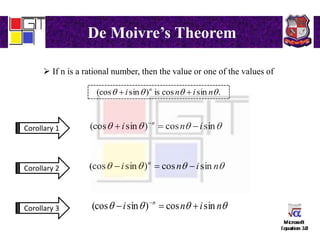
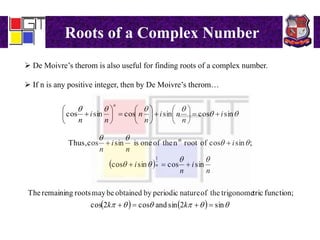
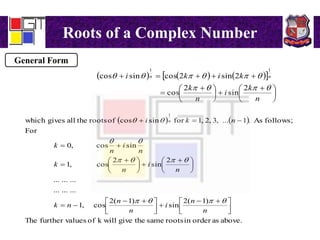
1) De Moivre's theorem and its corollaries for representing complex numbers as polar coordinates. Roots of a complex number using De Moivre's theorem.
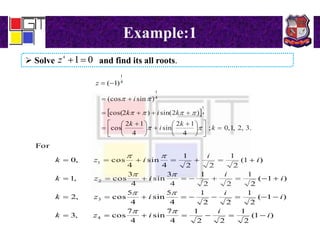
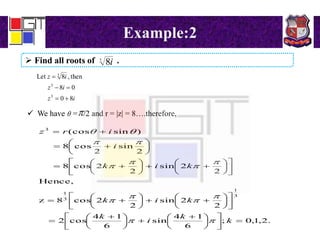
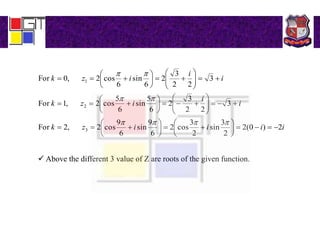
2) Examples of using De Moivre's theorem to find all roots of complex numbers.
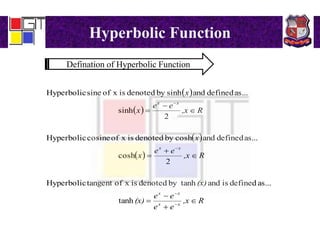
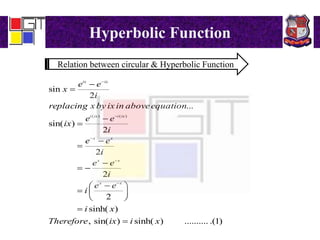
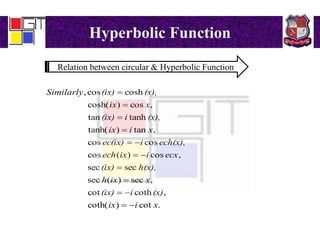
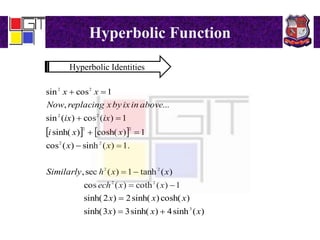
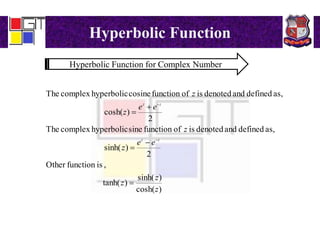
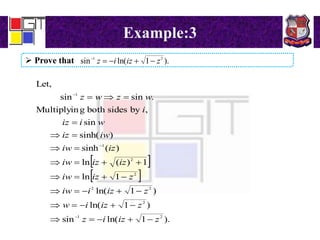
3) Definitions of hyperbolic functions as extensions of circular functions to complex numbers. Relations between circular and hyperbolic functions and identities for hyperbolic functions. An example problem proving an identity for a hyperbolic function of a complex number.