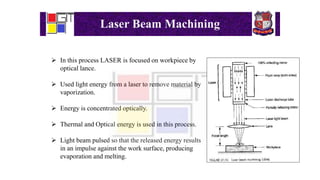
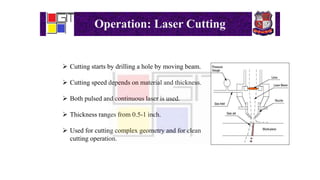
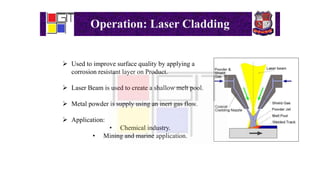
Laser beam machining is a process that uses a focused laser beam to remove material from a workpiece through vaporization. The laser beam is concentrated optically to deliver thermal and optical energy to the workpiece. Material is removed by either pulsing the laser beam to create an impulse against the surface, or using a continuous laser beam. Laser beam machining can be used for operations like cutting, welding, and cladding. It offers advantages like being non-contact, allowing machining of hard and soft materials, and flexibility. However, it also has disadvantages like requiring trained operators, being a slow process, needing expensive equipment, and consuming a lot of energy.