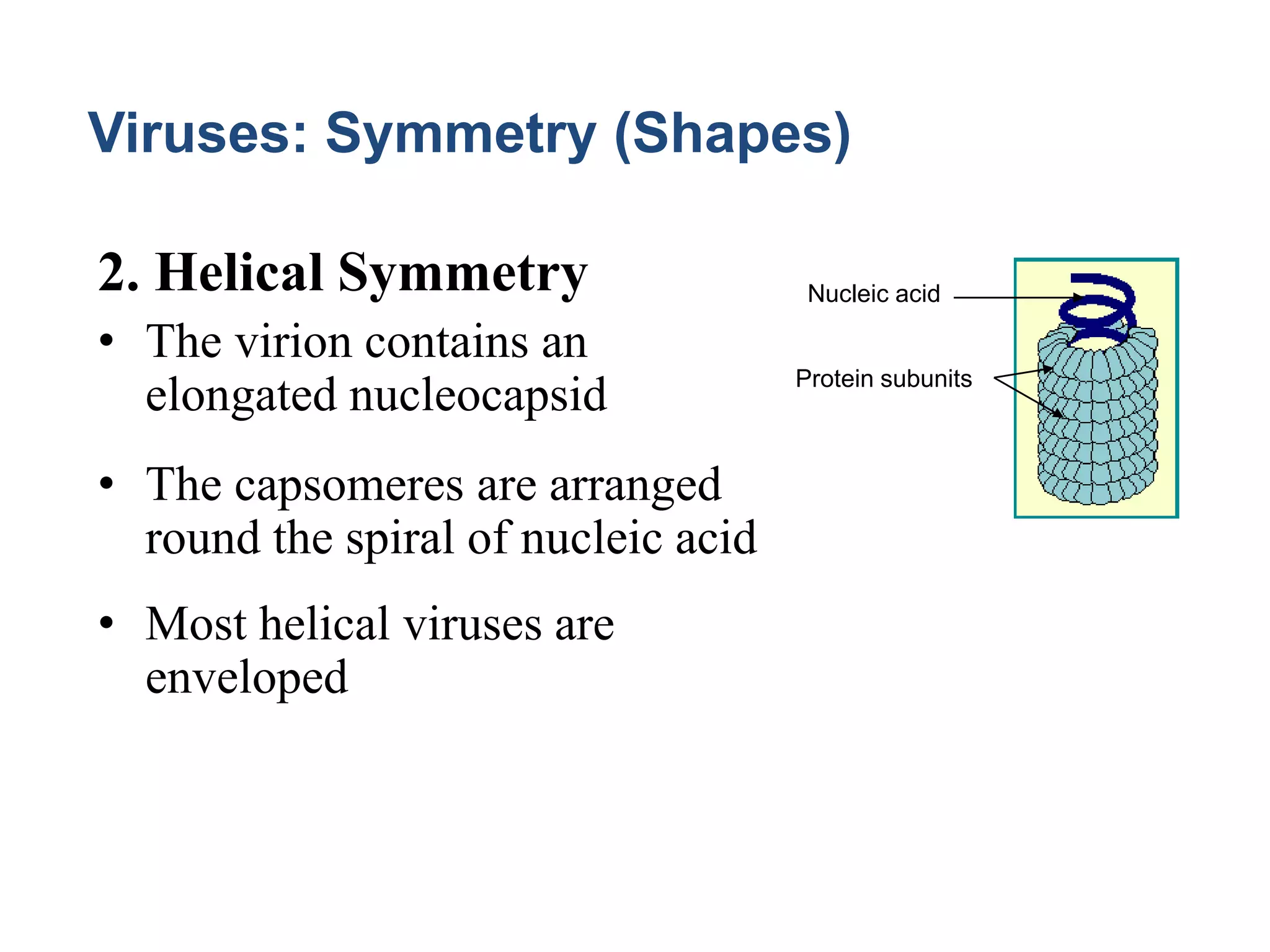
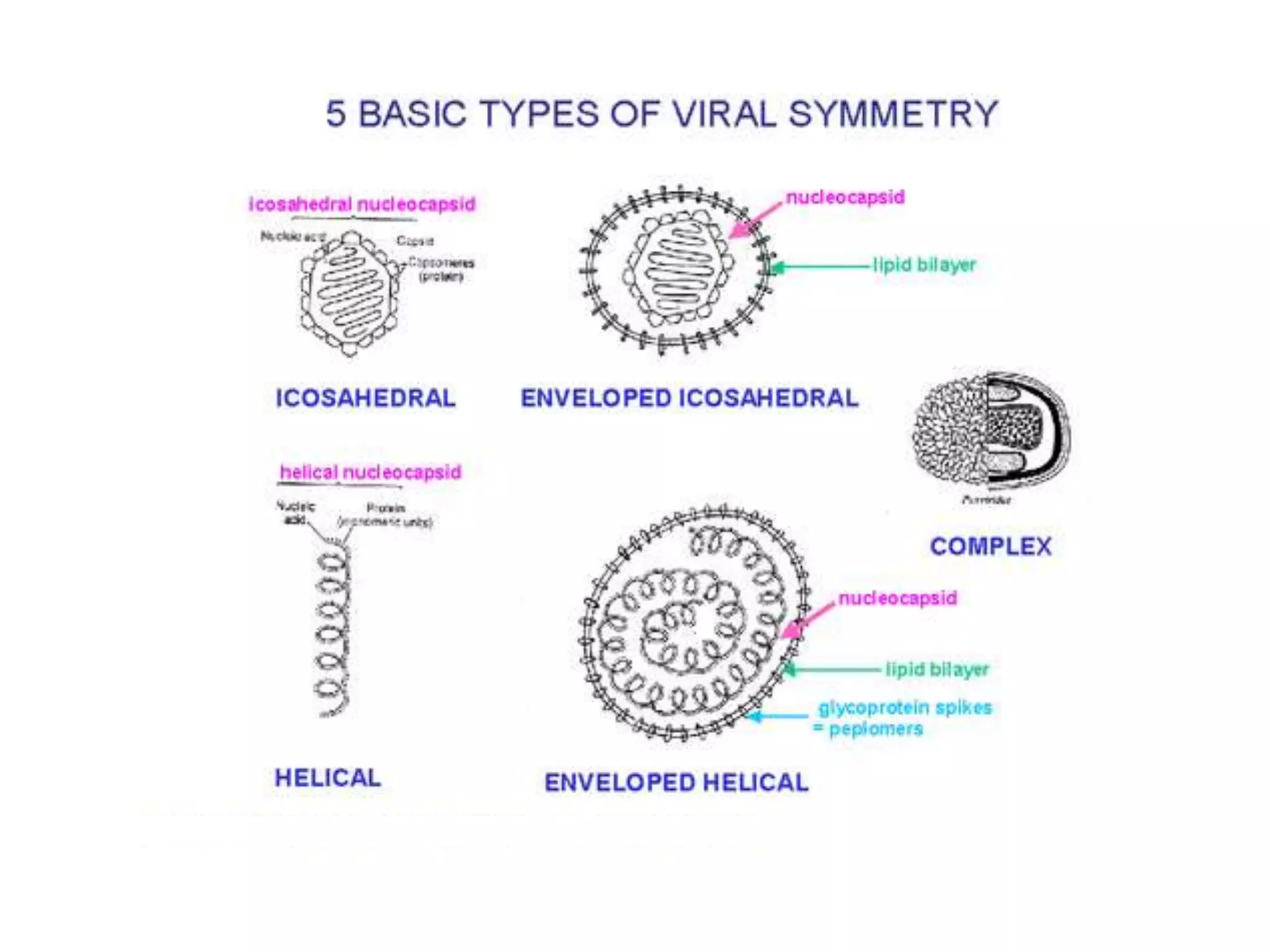
This document provides an introduction to medical virology, discussing the general properties and structure of viruses. Viruses are the smallest infectious agents, lacking organelles and only being able to replicate inside host cells. They contain either DNA or RNA as their genetic material and have a protein coat called a capsid that protects the genome. Some viruses also have an outer envelope. Viruses come in different shapes defined by their symmetry, either icosahedral, helical, or complex. The structure of viruses determines aspects like stability and transmission route. Defective viruses and atypical agents like viroids and prions are also briefly mentioned.