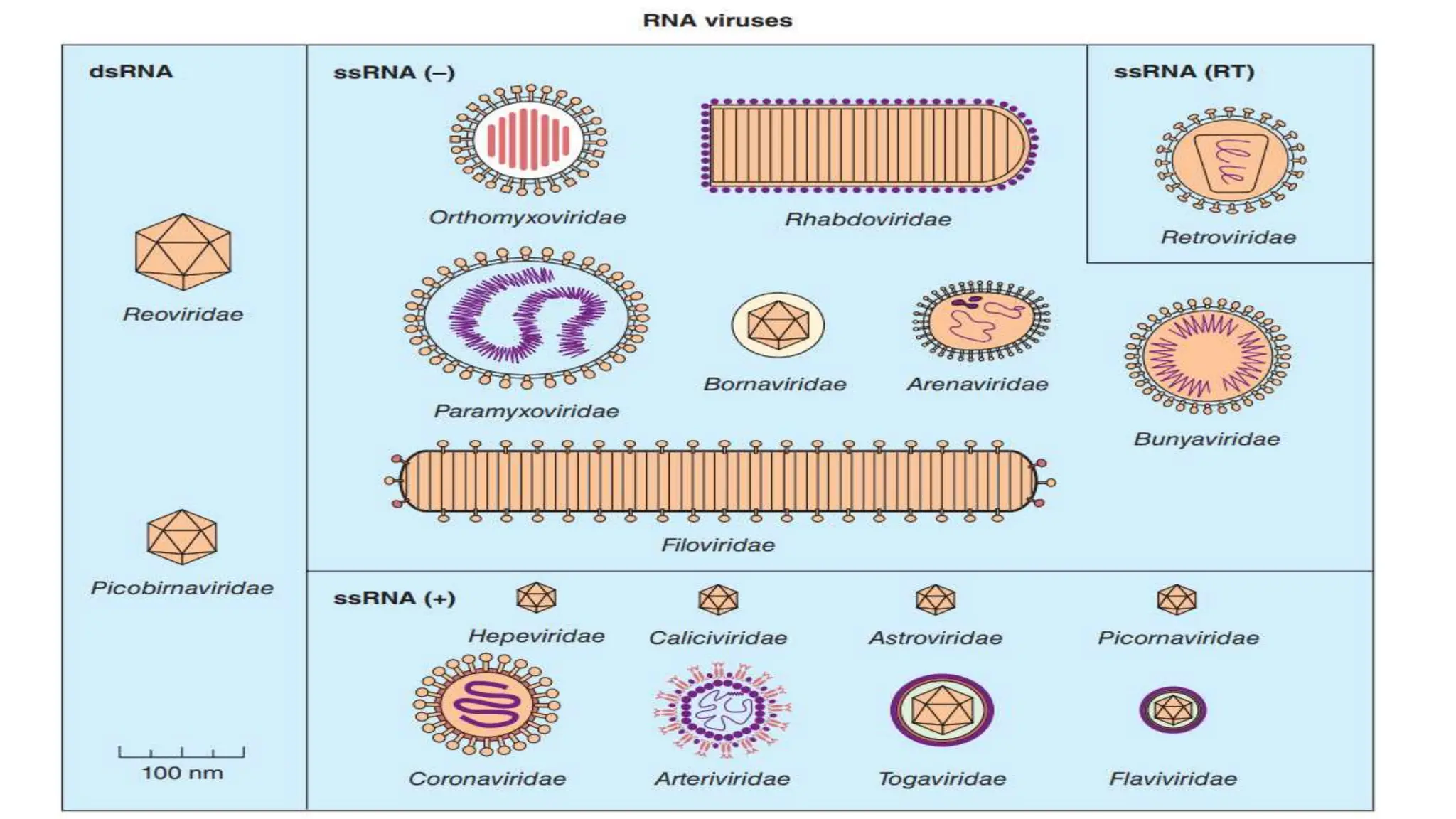
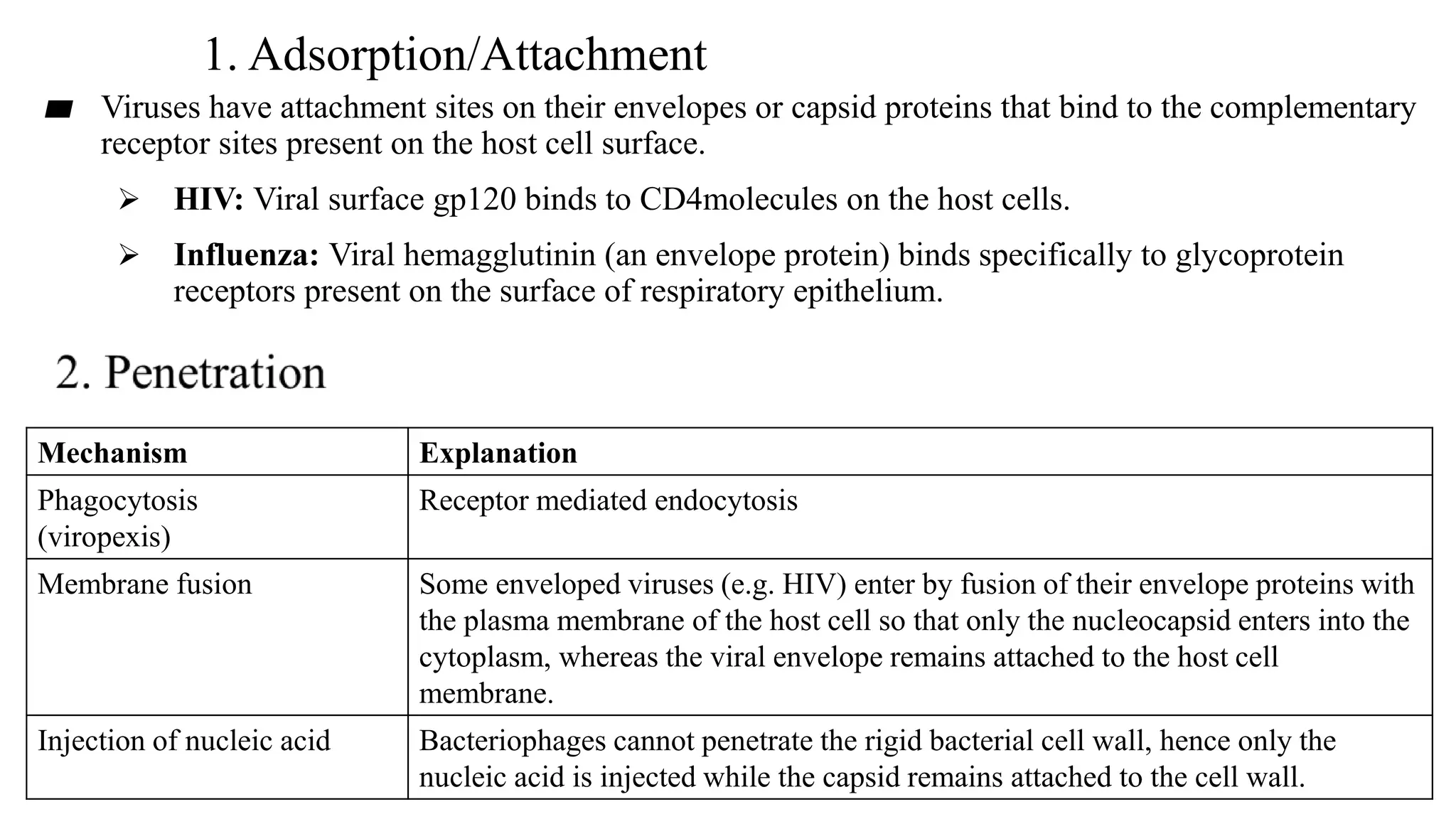
Viruses are the smallest infectious agents that can only replicate inside living cells. They contain nucleic acid, either DNA or RNA, encased within a protein shell called a capsid. Some viruses have an outer envelope as well. Viruses infect cells by binding to specific receptors on the host cell and introducing their genetic material. Inside the cell, viruses use the host cell's machinery to produce new virus particles that are then released to infect other cells. Viruses are classified based on properties like morphology, genome type, replication strategy, and antigenic characteristics. Major virus families include DNA viruses like herpesviruses, adenoviruses and parvoviruses, and RNA viruses like picornaviruses, flavivir