The document outlines the use of MATLAB for creating and manipulating matrices, including syntax for defining row and column vectors, accessing elements, and performing mathematical operations. It covers built-in functions, logical operations, and how to extract portions of matrices, as well as provides examples of matrix manipulations. Additionally, it discusses various powerful matrix functions available in MATLAB for advanced operations.

![1. >> for = 5
??? for = 5
Error: The expression to the left of the equals sign is not a valid target
for an assignment
2. >> else =6
??? else = 6
Error: Illegal use of reserved keyword "else"
3. >> cos = 2; cos(0)
??? Subscript indices must either be real positive integers or logicals
4. >> A = [1,2,3]; sum(A)
ans = 6
>> sum = 7; sum(A)
??? Index exceeds matrix dimensions
2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontomatlablec2of4-150201034438-conversion-gate02/85/Introduction-to-matlab-lecture-2-of-4-2-320.jpg)



![ A matrix with only one row is called a row
vector.
A row vector can be created in Matlab as
follows (note the commas or you can use
spaces):
» rowvec = [12 , 14 , 63]
rowvec =
12 14 63
6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontomatlablec2of4-150201034438-conversion-gate02/85/Introduction-to-matlab-lecture-2-of-4-6-320.jpg)
![ A matrix with only one column is called a
column vector.
A column vector can be created in MATLAB as
follows (note the semicolons):
» colvec = [13 ; 45 ; -2]
colvec =
13
45
-2
7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontomatlablec2of4-150201034438-conversion-gate02/85/Introduction-to-matlab-lecture-2-of-4-7-320.jpg)
![ A matrix can be created in Matlab as follows
(note the commas AND semicolons):
» matrix = [1 , 2 , 3 ; 4 , 5 ,6 ; 7 , 8 , 9]
matrix =
1 2 3
4 5 6
7 8 9
8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontomatlablec2of4-150201034438-conversion-gate02/85/Introduction-to-matlab-lecture-2-of-4-8-320.jpg)



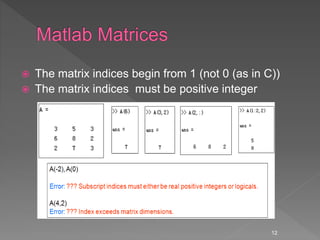
![ Accessing Single Elements of a Matrix A(i,j)
Accessing Multiple Elements of a Matrix
A(1,4) + A(2,4) + A(3,4) + A(4,4)
A([1,3,4], :)= all of rows 1, 3 and 4
sum(A(1:4,4))
sum(A(:,end))
The keyword end refers to the last row or column.
Deleting Rows and Columns: to delete the second column
of X, use X(:,2) = []
Concatenating Matrices A and B C=[A;B]
13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontomatlablec2of4-150201034438-conversion-gate02/85/Introduction-to-matlab-lecture-2-of-4-13-320.jpg)
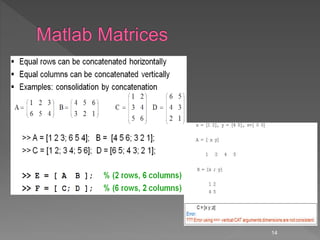
![Logic--searching with find
Find--searches for the truth (or not false)
› b=[1 0 -1 0 0];
› I=find(b)
I=1 3 b(I) is an array without zeros
› I=find(ones(3,1)*[ 1 2 3]==2)
I= 4 5 6
› [I,J]=find(ones(3,1)*[ 1 2 3]==2)
I= 1 2 3
J= 2 2 2
15](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontomatlablec2of4-150201034438-conversion-gate02/85/Introduction-to-matlab-lecture-2-of-4-15-320.jpg)

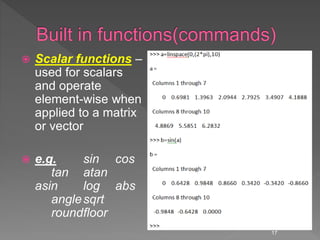


![ X = zeros(r,c) % Creates
matrix full with zeros
A = diag(x) % Creates
squared matrix with vector
x in diagonal
[r,c] = size(A) % Return
dimensions of matrix A
B = rand(r,c) %creates a
matrix of random numbers.
20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontomatlablec2of4-150201034438-conversion-gate02/85/Introduction-to-matlab-lecture-2-of-4-20-320.jpg)
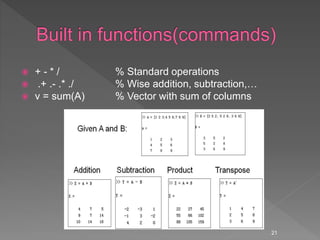
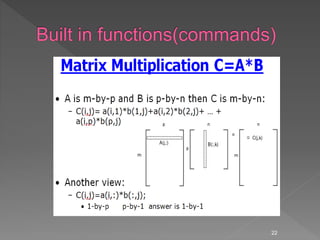
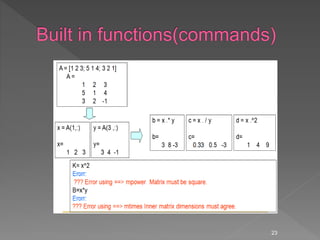
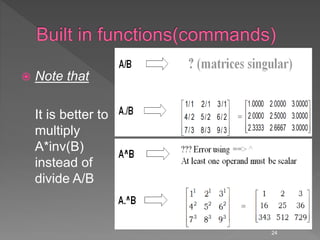
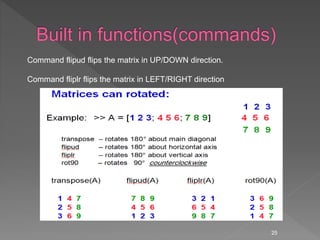
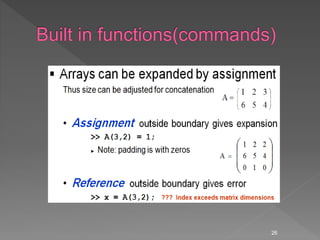
![Some powerful matrix functions in Matlab
X = A’ % Transposed matrix
(A transpose operation changes the column of a matrix into rows, and
rows into columns)
X = inv(A) % Inverse matrix squared matrix
X = pinv(A) % Pseudo inverse
X = chol(A) % Cholesky decomp.
d = det(A) % Determinant
[X,D] = eig(A) % Eigenvalues and eigenvectors
[Q,R] = qr(X) % QR decomposition
[U,D,V] = svd(A) % singular value decomp
27](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontomatlablec2of4-150201034438-conversion-gate02/85/Introduction-to-matlab-lecture-2-of-4-27-320.jpg)


![1. A=[1, 2.7, 8.9, -8, 4, 3.5]
2. B>0;
3. Return the sum and mean value of all the
elements in A.
4. Return the max value of all elements in A.
5. fix(A)
34](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontomatlablec2of4-150201034438-conversion-gate02/85/Introduction-to-matlab-lecture-2-of-4-34-320.jpg)
![1. A=[1, 2.7, 8.9, -8, 4, 3.5; 6.5, 8.9, 5, -0.9,
3, 19] ;
2. Set every element in six column to be 0.7.
3. Remove the second column in A;
4. Return the mean value of every column in
A;
5. Return the mean value of whole A;
35](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontomatlablec2of4-150201034438-conversion-gate02/85/Introduction-to-matlab-lecture-2-of-4-35-320.jpg)