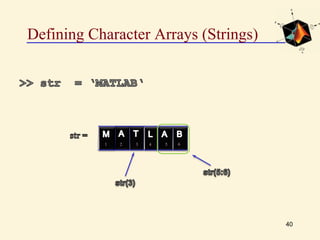
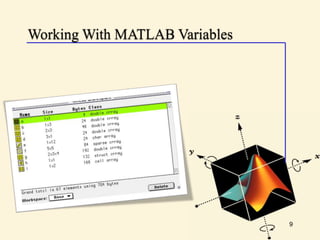
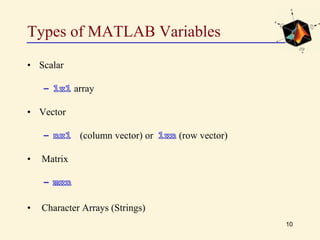
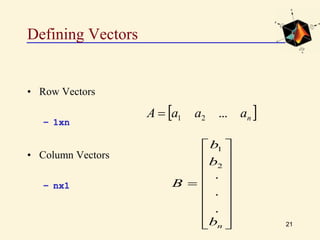
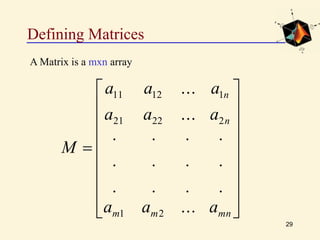
This document provides an introduction to basic MATLAB commands and operations. It discusses how to enter and exit MATLAB, lists some common commands like clearing the screen and workspace. It also covers defining different variable types like scalars, vectors, matrices, and character arrays. It provides examples of arithmetic operations on arrays and defines matrices. Exercises are included to practice these concepts.















![Defining Row Vectors
22
To create a row vector A simply type in:
A = [2 0 1 4 7 1 5 6 4]
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
A(5)A(2)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec-5msdspr-150515153021-lva1-app6892/85/matlab-22-320.jpg)
![Defining Row Vectors
23
v = [2 0 1 4 7 1 5 6 4]
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
A(6:9)A(1:4)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec-5msdspr-150515153021-lva1-app6892/85/matlab-23-320.jpg)
![Defining Column Vectors
24
To create a column vector B simply type in:
B = [3; 5; 0; 0; 1; 4; 9; -1; 1]
1
-1
9
4
1
0
0
5
3 1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
B = 9x1 vector
B(5)
B(3)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec-5msdspr-150515153021-lva1-app6892/85/matlab-24-320.jpg)
![Defining Column Vectors
25
B = [3; 5; 0; 0; 1; 4; 9; -1; 1]
1
-1
9
4
1
0
0
5
3 1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
9x1 vector
B(7:9)
B(2:5)
B =](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec-5msdspr-150515153021-lva1-app6892/85/matlab-25-320.jpg)

![Exercise#2
27
Investigate the effect of the following commands:
V=[2 4 7 5] and w=[1 3 8 9]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec-5msdspr-150515153021-lva1-app6892/85/matlab-27-320.jpg)
![Exercise#3
28
Investigate the effect of the following commands.
z=[1; 1; 0; 0]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec-5msdspr-150515153021-lva1-app6892/85/matlab-28-320.jpg)

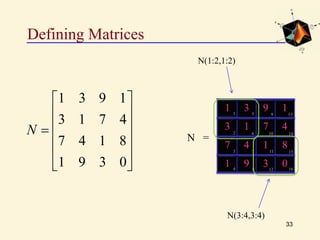
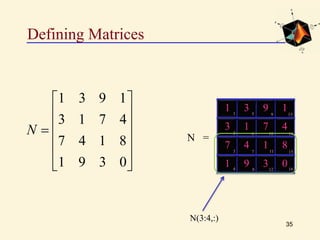
![Defining Matrices
31
0391
8147
4713
1931
N
1 3
3 1
9 1
7 4
7 4
1 9
1 8
3 0
1
2
3
4
5
8
9
6
7
10
11
12
14
15
16
13
N =
N(1,3) or N(9)
N(4,3) or N(12)
N=[1 3 9 1; 2 1 7 4; 7 4 1 8; 1 9 3 0]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec-5msdspr-150515153021-lva1-app6892/85/matlab-31-320.jpg)
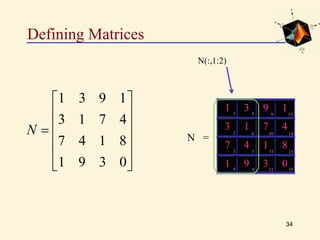
![Defining Matrices
32
0391
8147
4713
1931
N
1 3
3 1
9 1
7 4
7 4
1 9
1 8
3 0
1
2
3
4
5
8
9
6
7
10
11
12
14
15
16
13
N =
N(1:4)
N(10:12)
N=[1 3 9 1; 2 1 7 4; 7 4 1 8; 1 9 3 0]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec-5msdspr-150515153021-lva1-app6892/85/matlab-32-320.jpg)
![Exercise#4
36
Investigate the effect of the following commands:
M=[1 2; 3 4] N=[-1 3; 5 2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec-5msdspr-150515153021-lva1-app6892/85/matlab-36-320.jpg)
![Exercise#5
37
Investigate the effect of the following commands:
43
21
MM=[1 2; 3 4]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec-5msdspr-150515153021-lva1-app6892/85/matlab-37-320.jpg)