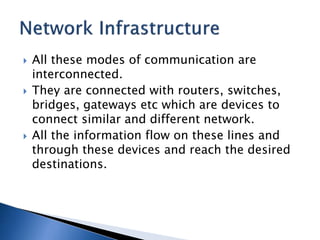
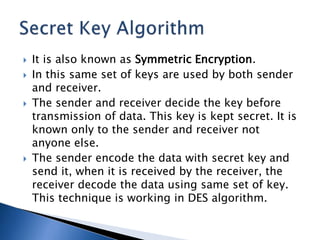
The document explains the concept of commerce and electronic commerce (e-commerce), emphasizing its role in the exchange of goods and services through digital platforms. It highlights the benefits of e-commerce for businesses and consumers, such as improved efficiency, market access, and customer convenience, while also addressing challenges like security, infrastructure, and legal issues. Furthermore, it discusses various dimensions of e-commerce technology, such as ubiquity, global reach, and personalization, which enhance the overall business landscape.
















































































































































































![Digital cash must have the following four
properties:
Monetary value,
Interoperability,
Retrievability, and
Security (KALA96].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/newmicrosoftofficepowerpointpresentation-150523042115-lva1-app6892/85/e-retailing-180-320.jpg)