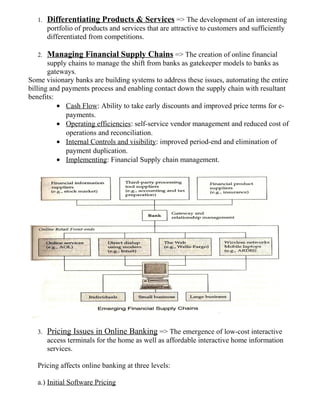
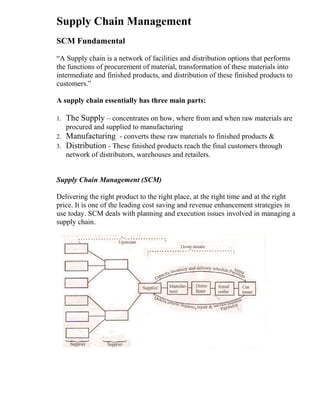
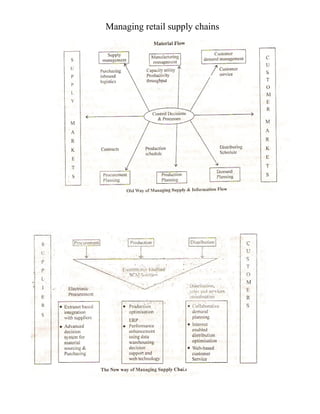
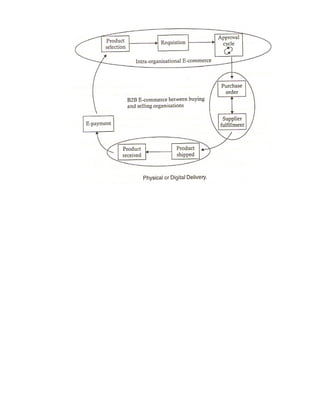
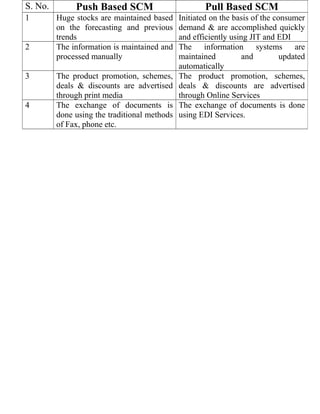
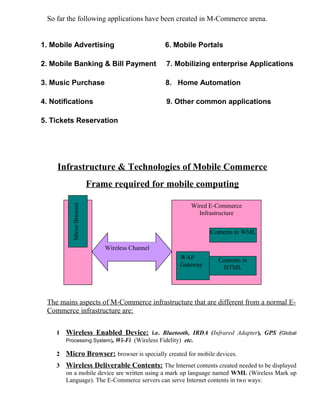
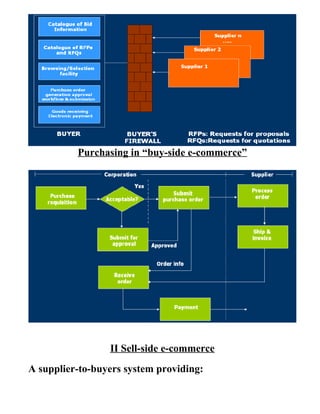
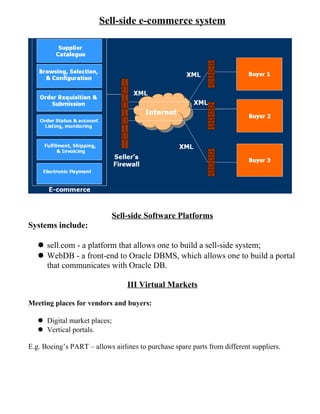
This document provides an introduction to e-business and e-commerce. It defines e-business as conducting business electronically, including e-commerce as well as other applications like re-engineering processes, e-commerce systems, and enterprise collaboration. E-commerce is defined as a subset of e-business focused on online buying and selling. The document then discusses the history and development of e-business from the 1970s onward, outlines different e-business models and applications, and provides details on concepts like electronic data interchange and business-to-business e-commerce.


































![Electronic Payments
The Electronic Payments allow sellers and consumers to clear payments, dues
and engage in cash payments, dues and engage in cashless trading on the
internet. Electronic payment is a financial exchange that takes place online
between buyer & seller. The information as a financial exchange is usually
some form of digital financial instrument (Electronic Cash, Electronic checks &
encrypted plastic card numbers) that is indirectly produced by a bank or an
intermediary.
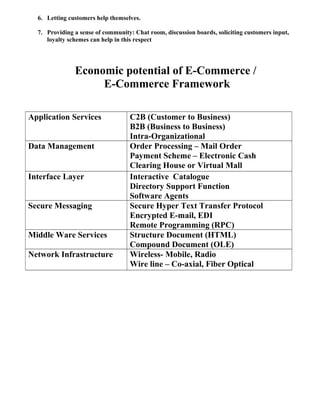
Electronic Payment System [EPS]
o Electronic Payment Systems are indispensable in today’s business process as
companies are looking for innovating ideas to serve customers faster and at
low cost.
o Prompt and secure payment, clearing and settlement of credit or debit claims
are the important aspects of electronic payment system.
o E-commerce capability of reducing transaction time, its cost and providing
security is the main reason of its growth.
Issues while designing e-payment system
1. Payment instruments must be secure, have a low processing cost and be
accepted widely as global currency tender.
2. The forms and characters of payment instrument e.g. electronic cash,
credit/debit cards should be desirable to consumer.
3. The issues regarding privacy, fraud, mistakes, bank features should be
guarded by proper security features as authentication / privacy etc.
4. The issues regarding the protocols that connect one financial institution to
the other.
Types of Electronic Payment System:
Electronic Payment System (EPS) or Electronic Funds Transfer (EFT) can be divided into
three broad categories:
1. Large Scale and Financial Payments
o Whole Sale Payments (e.g. Bank to Bank Transfer)
o Retail Payments (e.g. ATM)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/electroniccommercesystems-190310073417/85/Full-Notes-on-E-Commerce-Study-Material-for-E-Commerce-45-320.jpg)