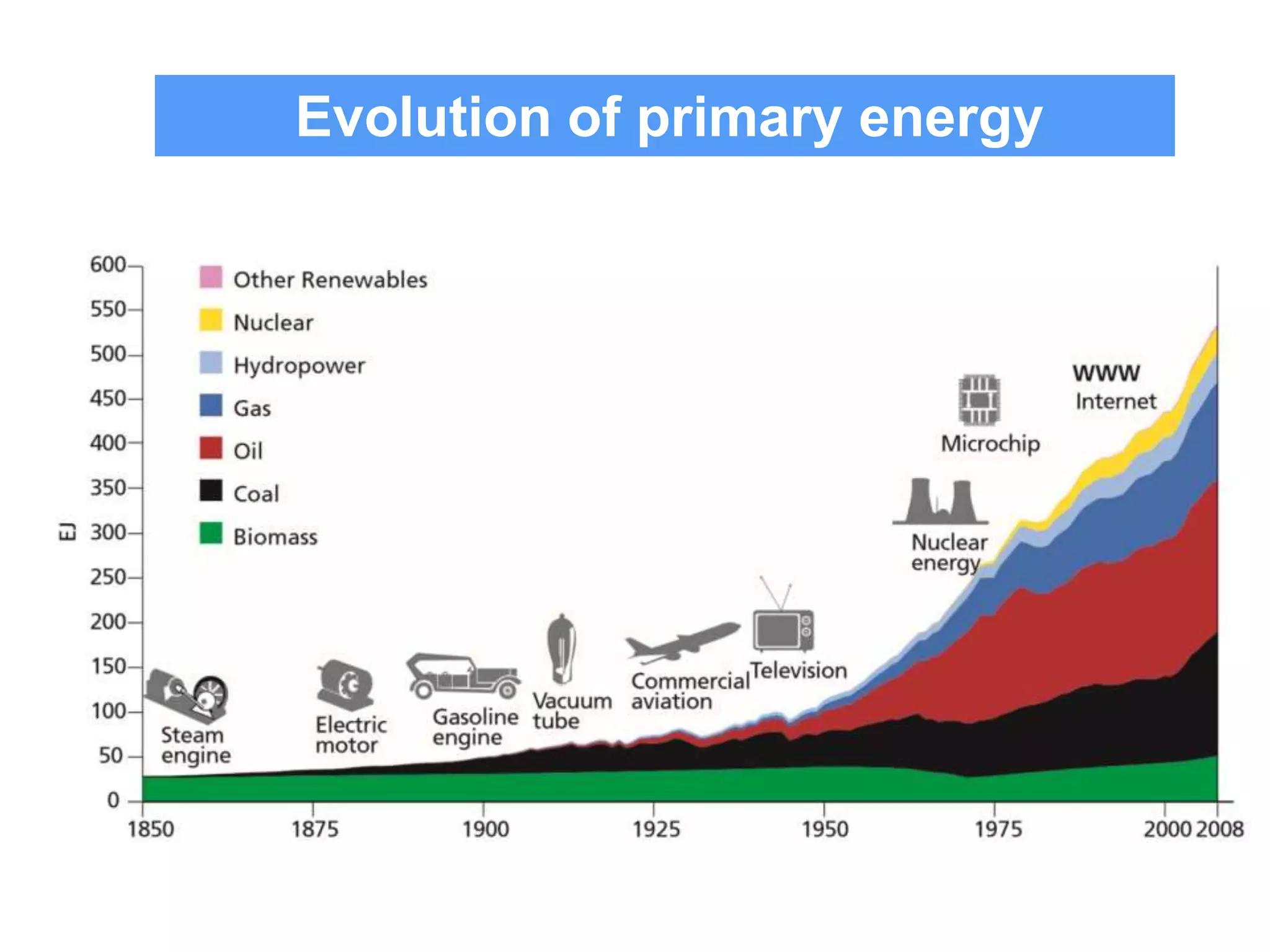
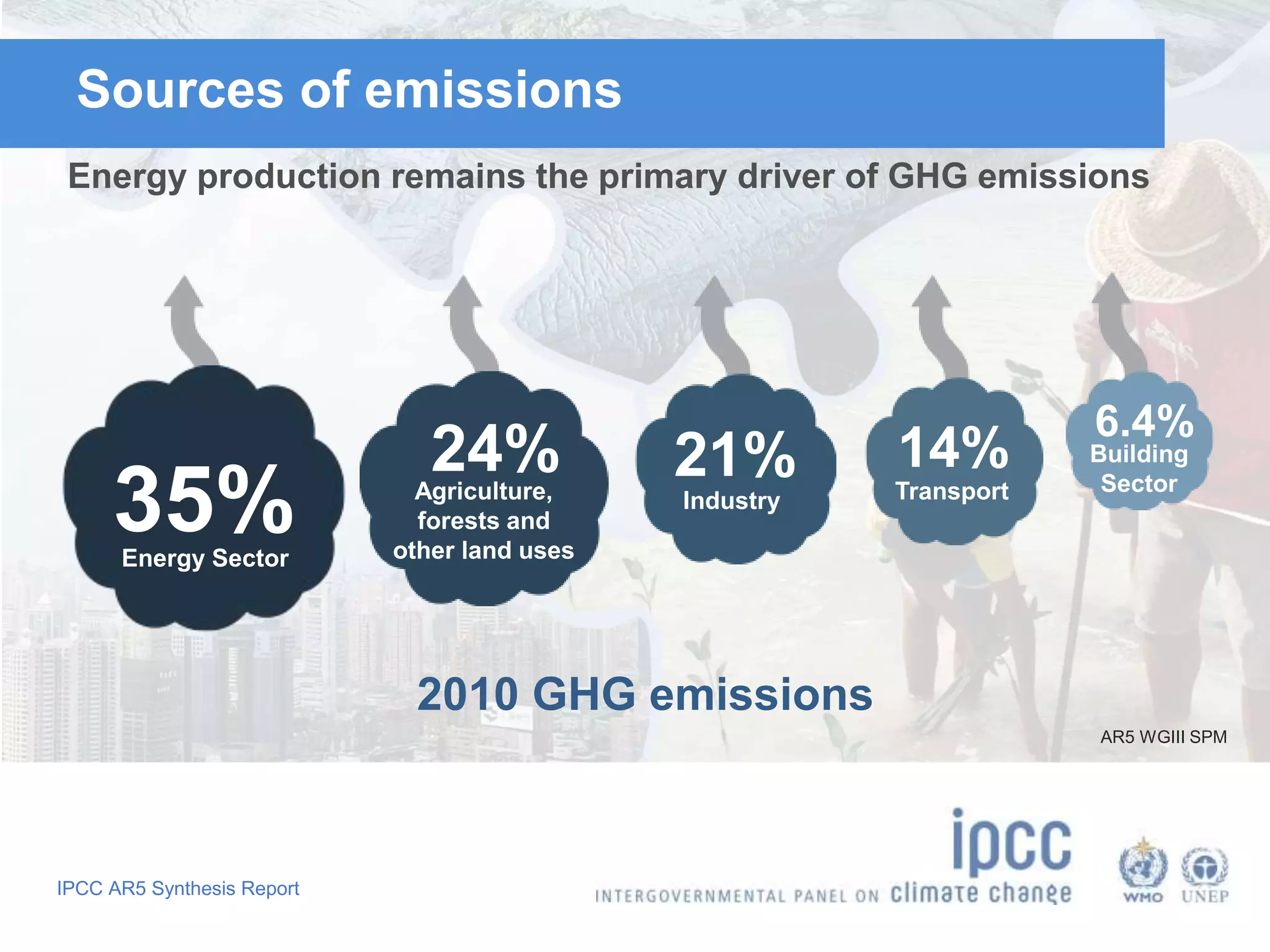
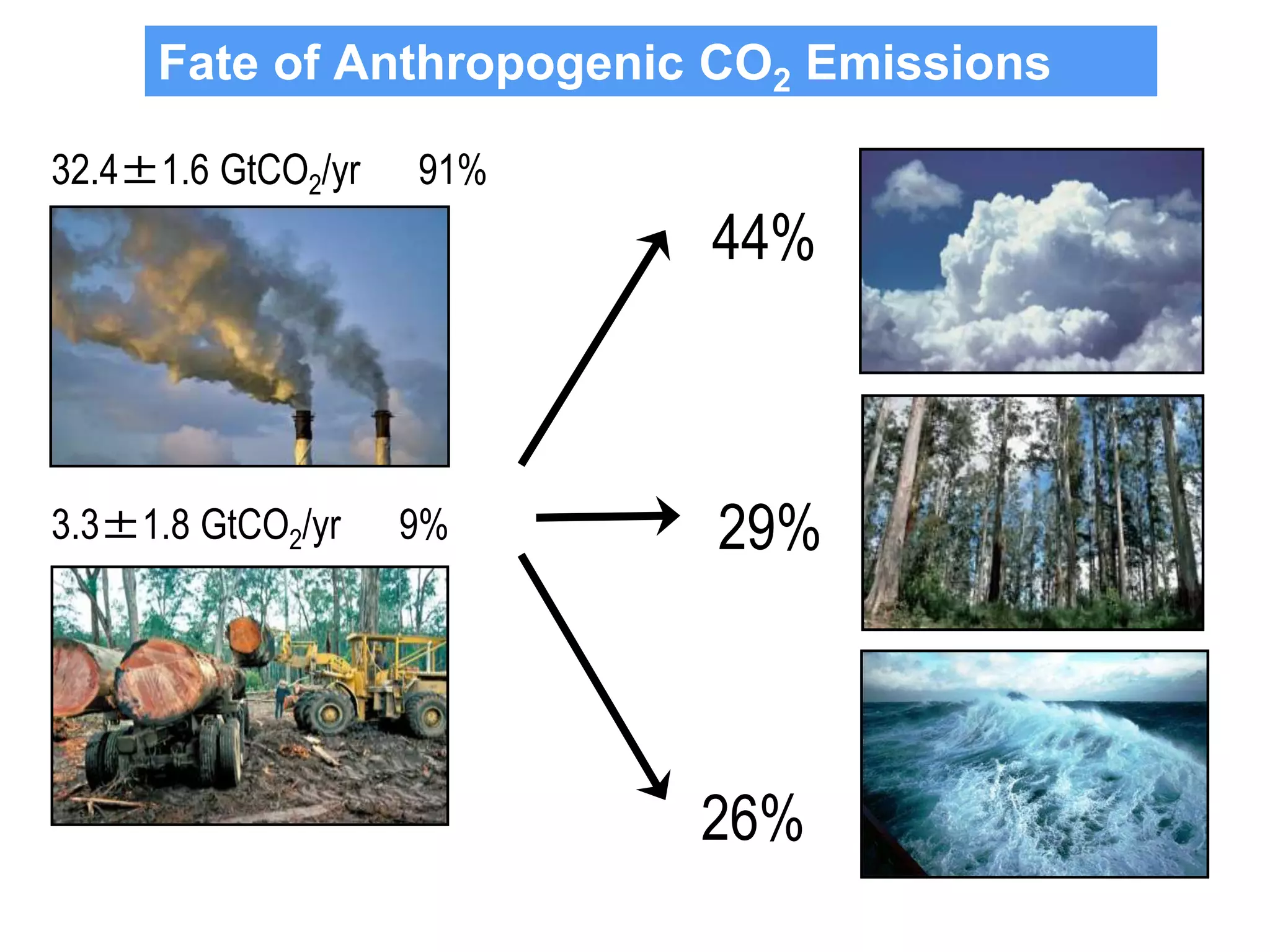
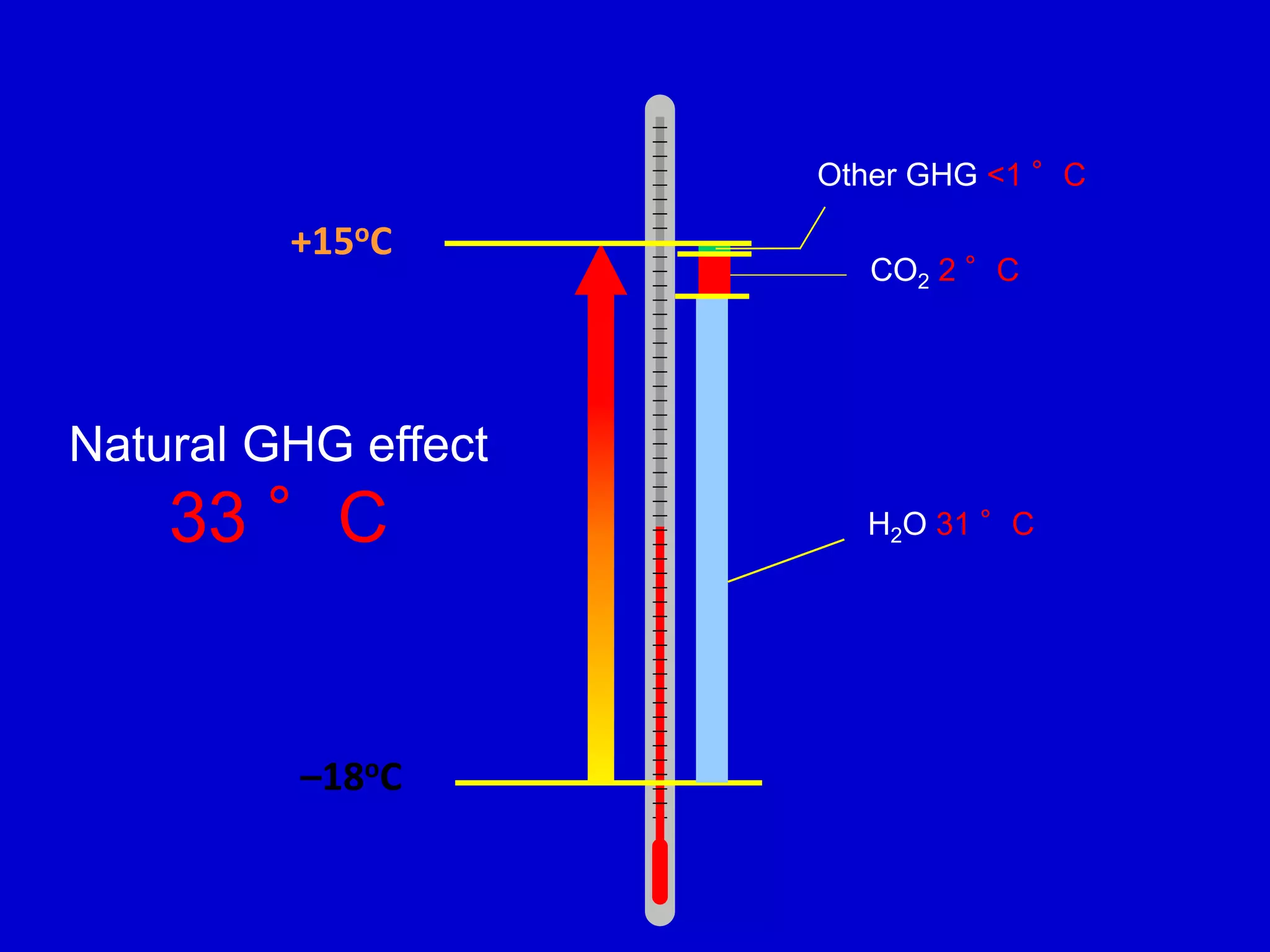
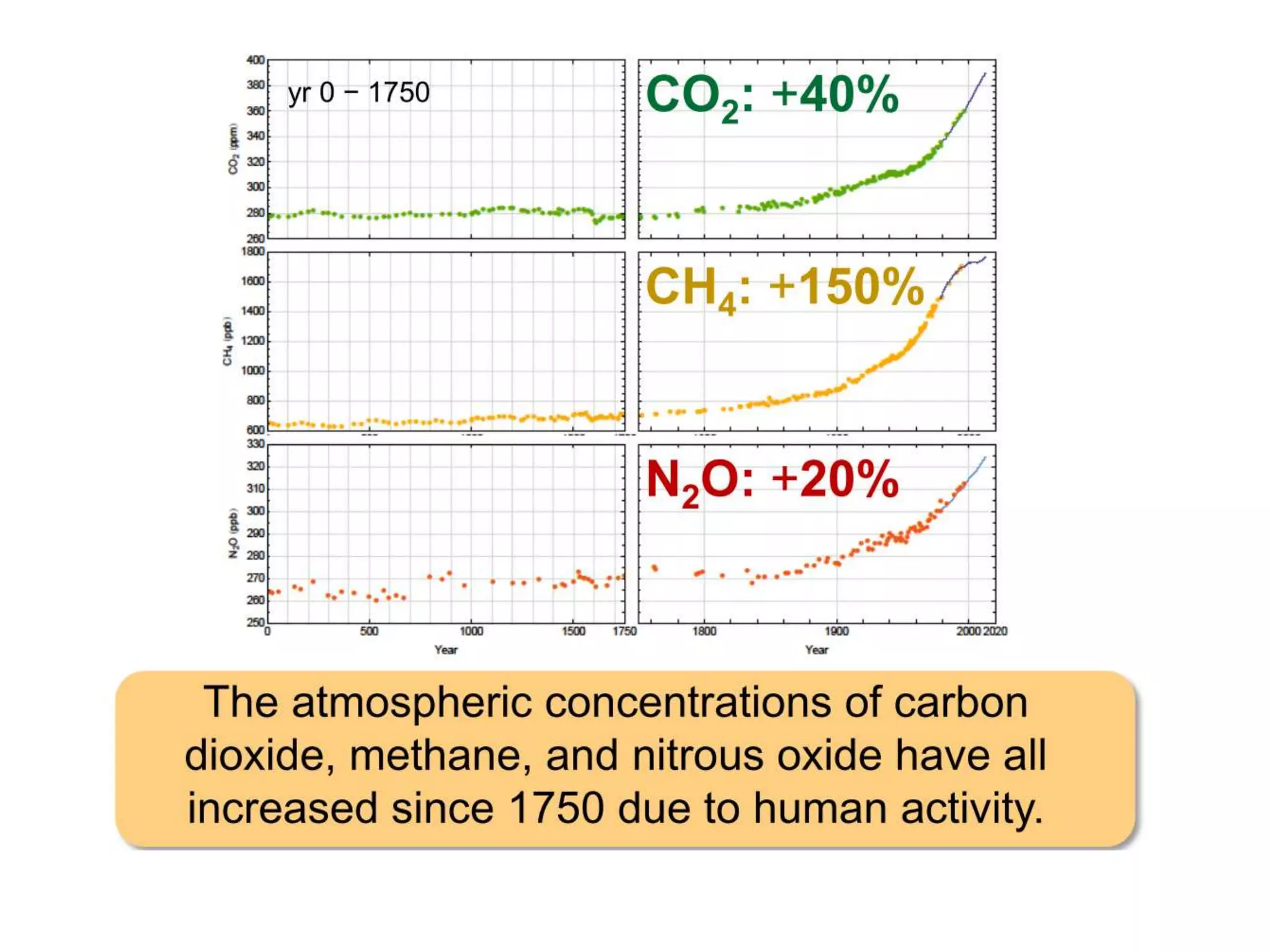
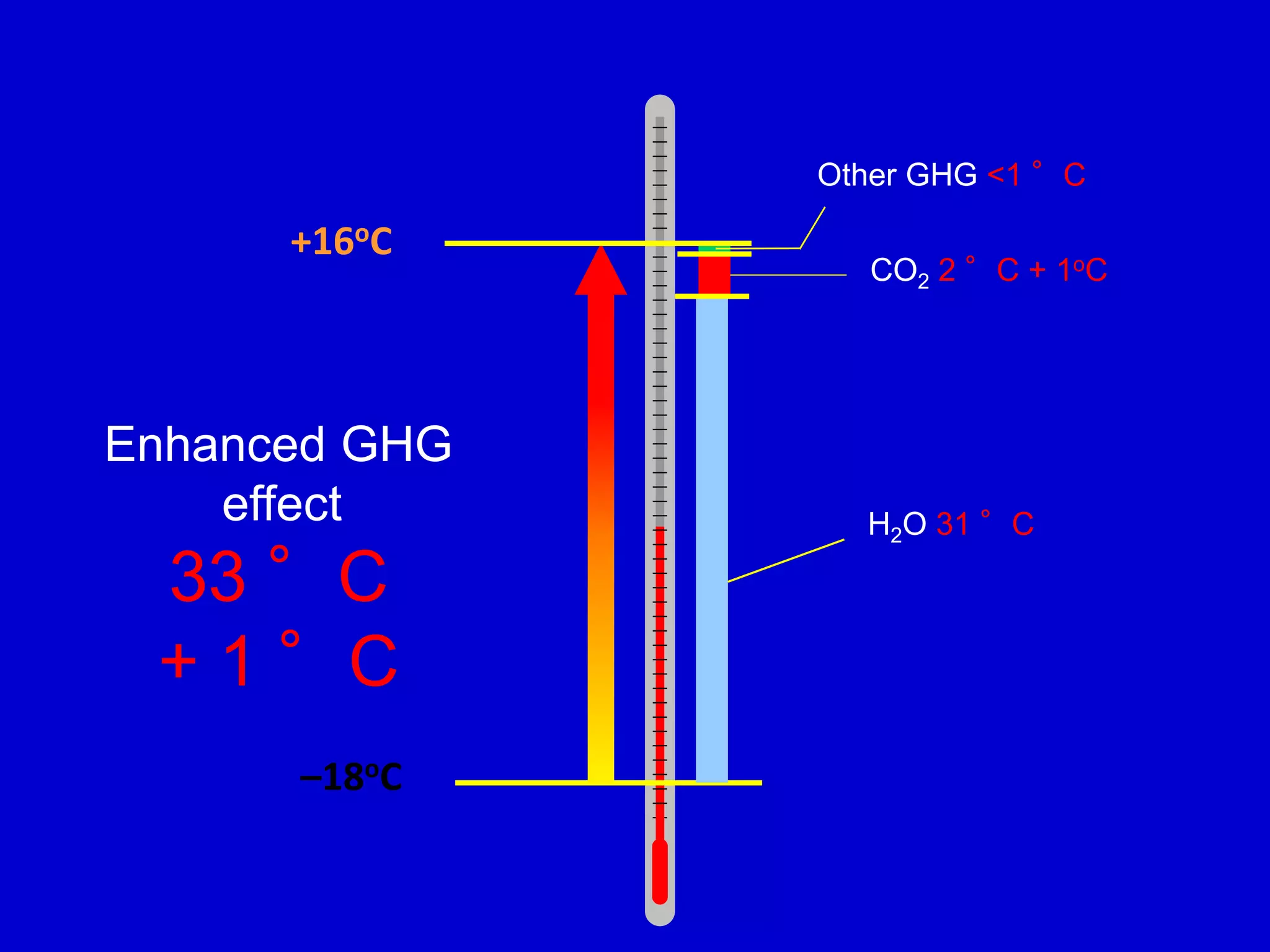
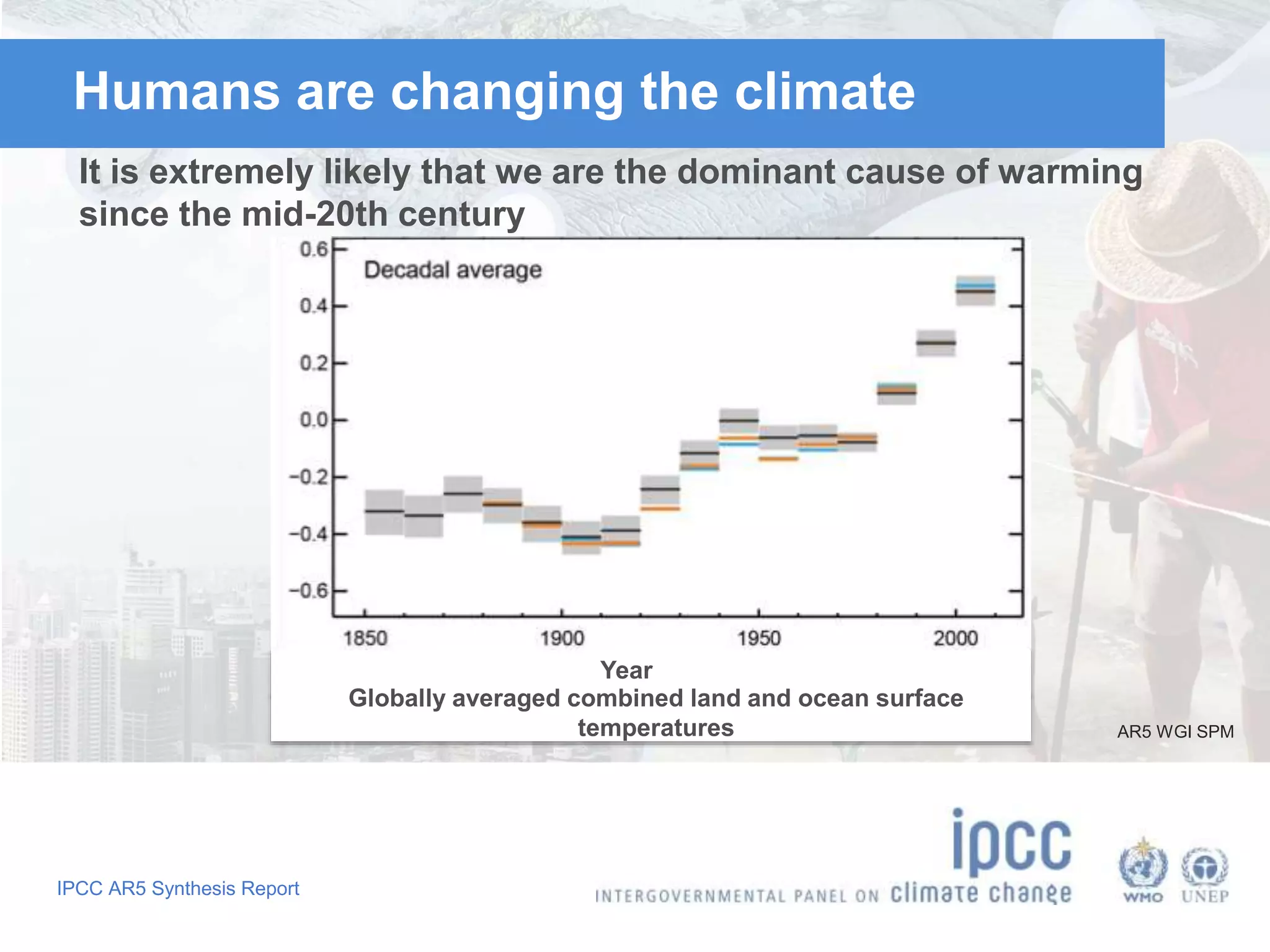
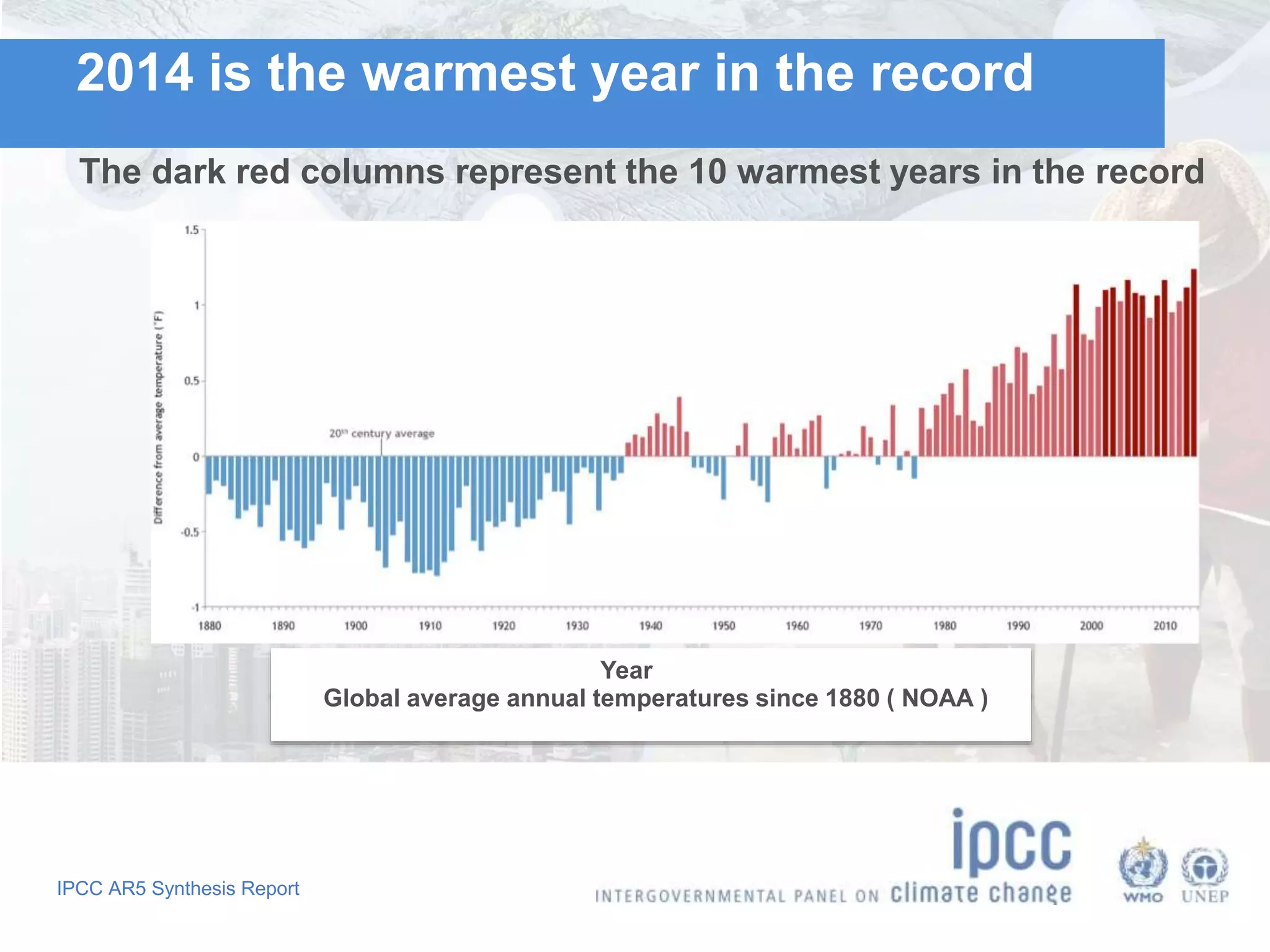
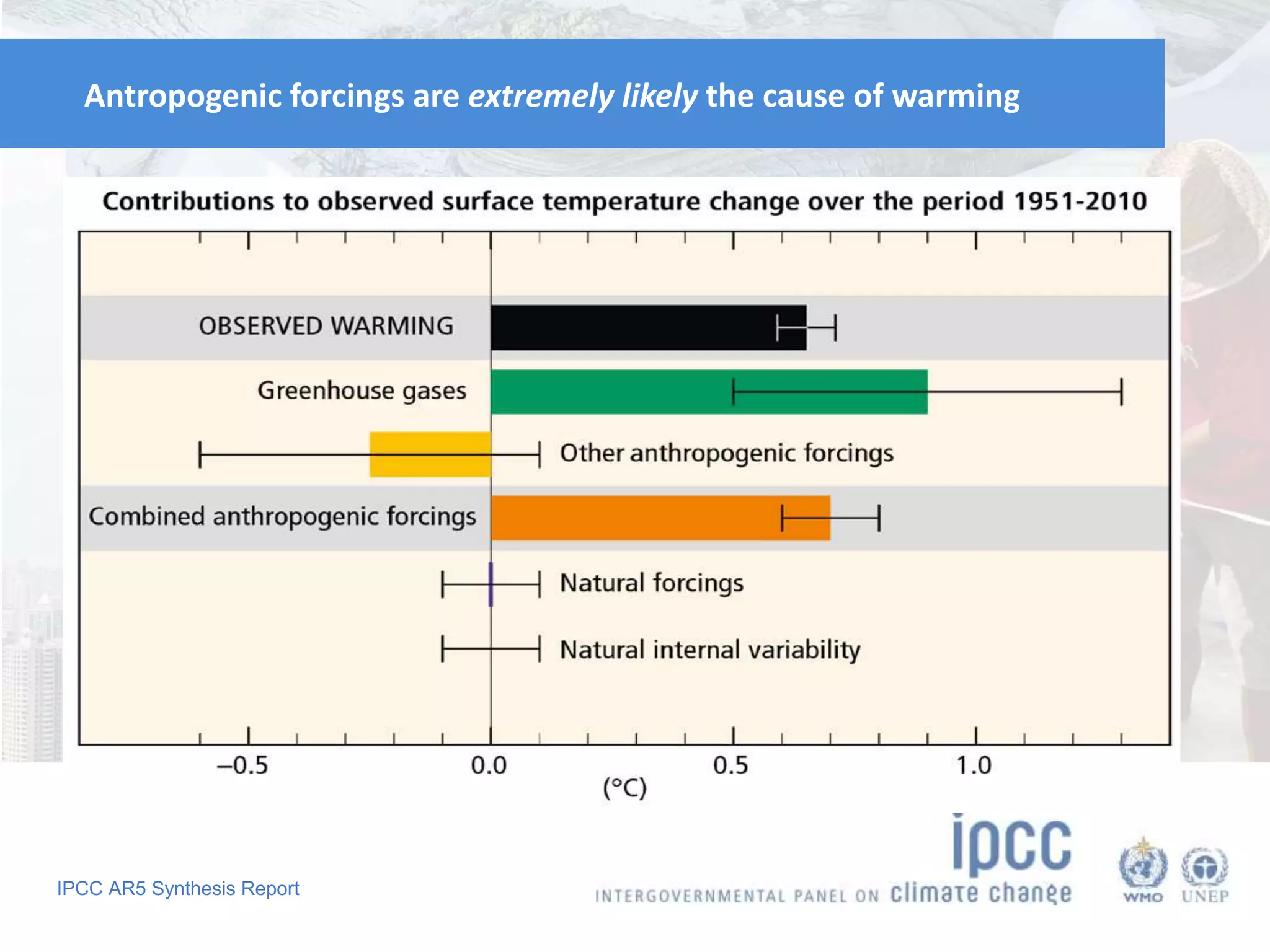
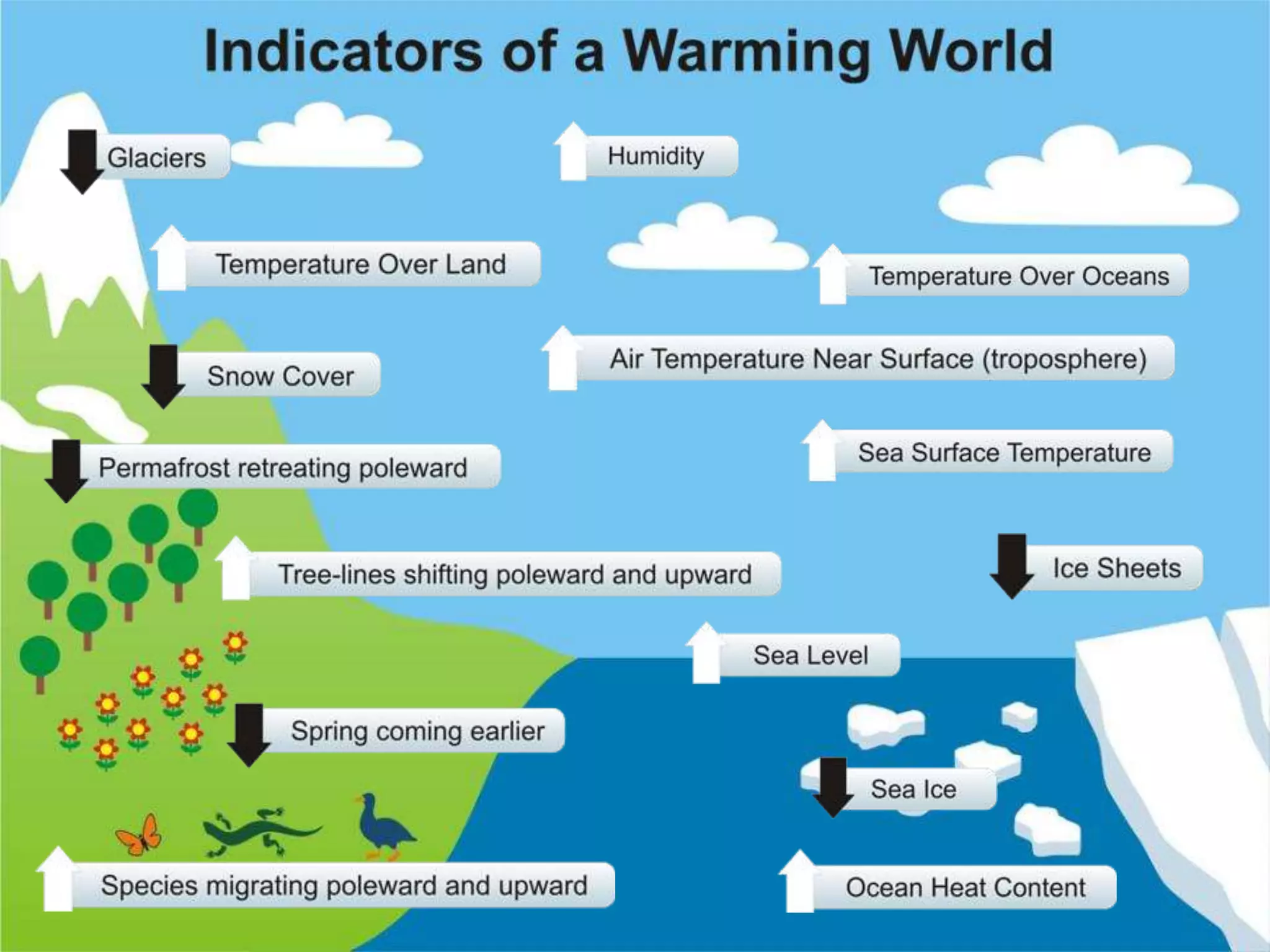
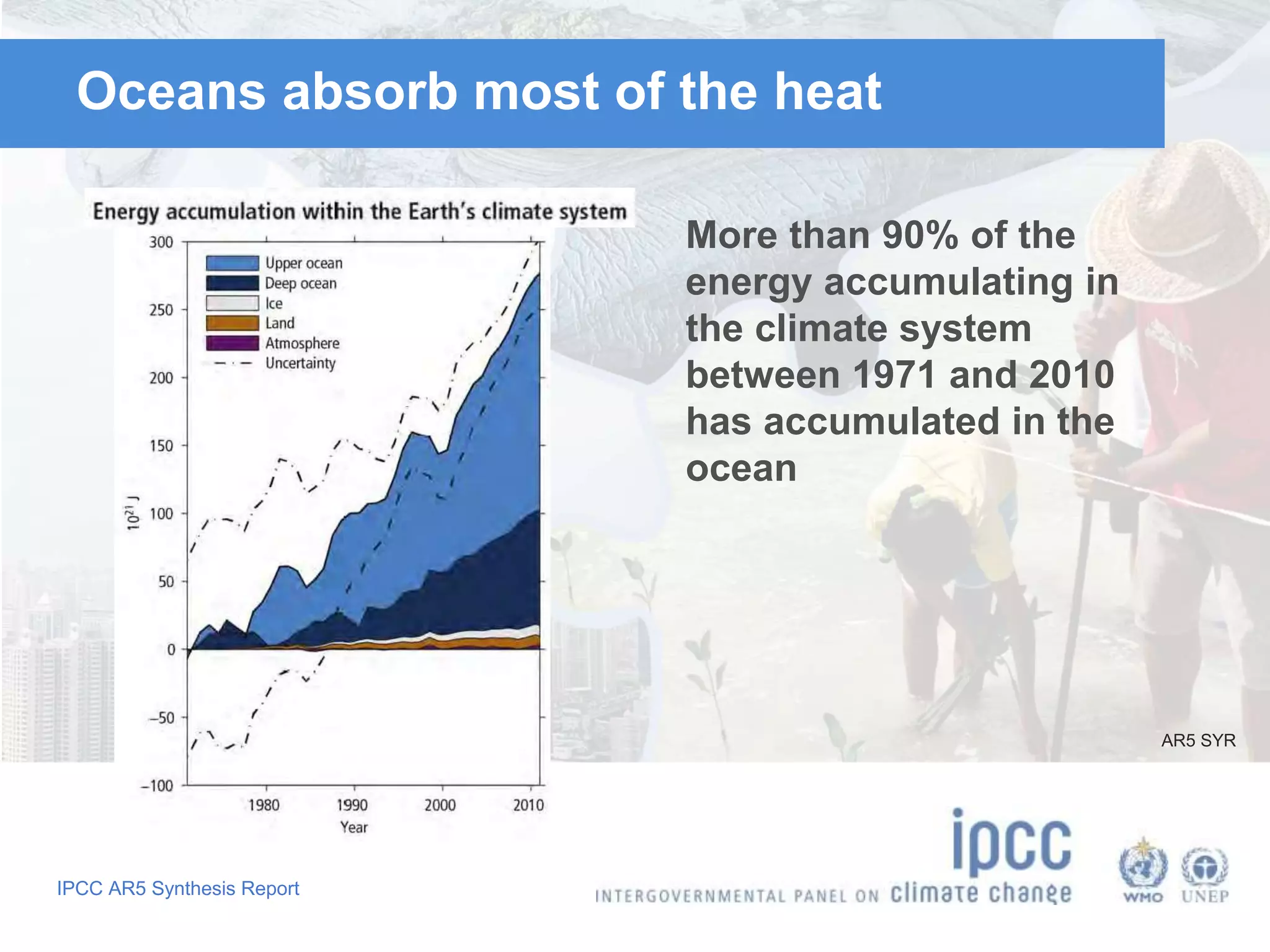
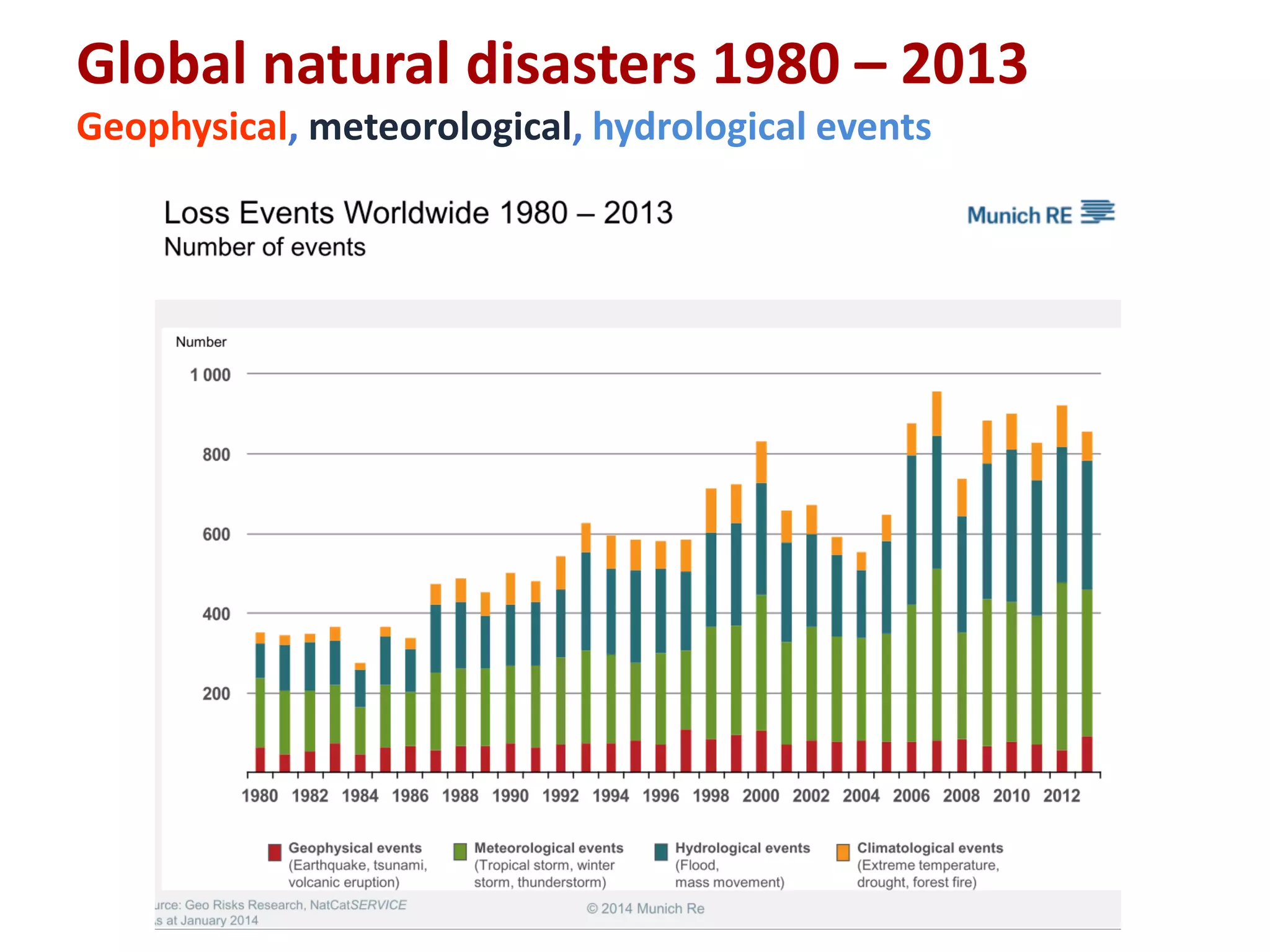
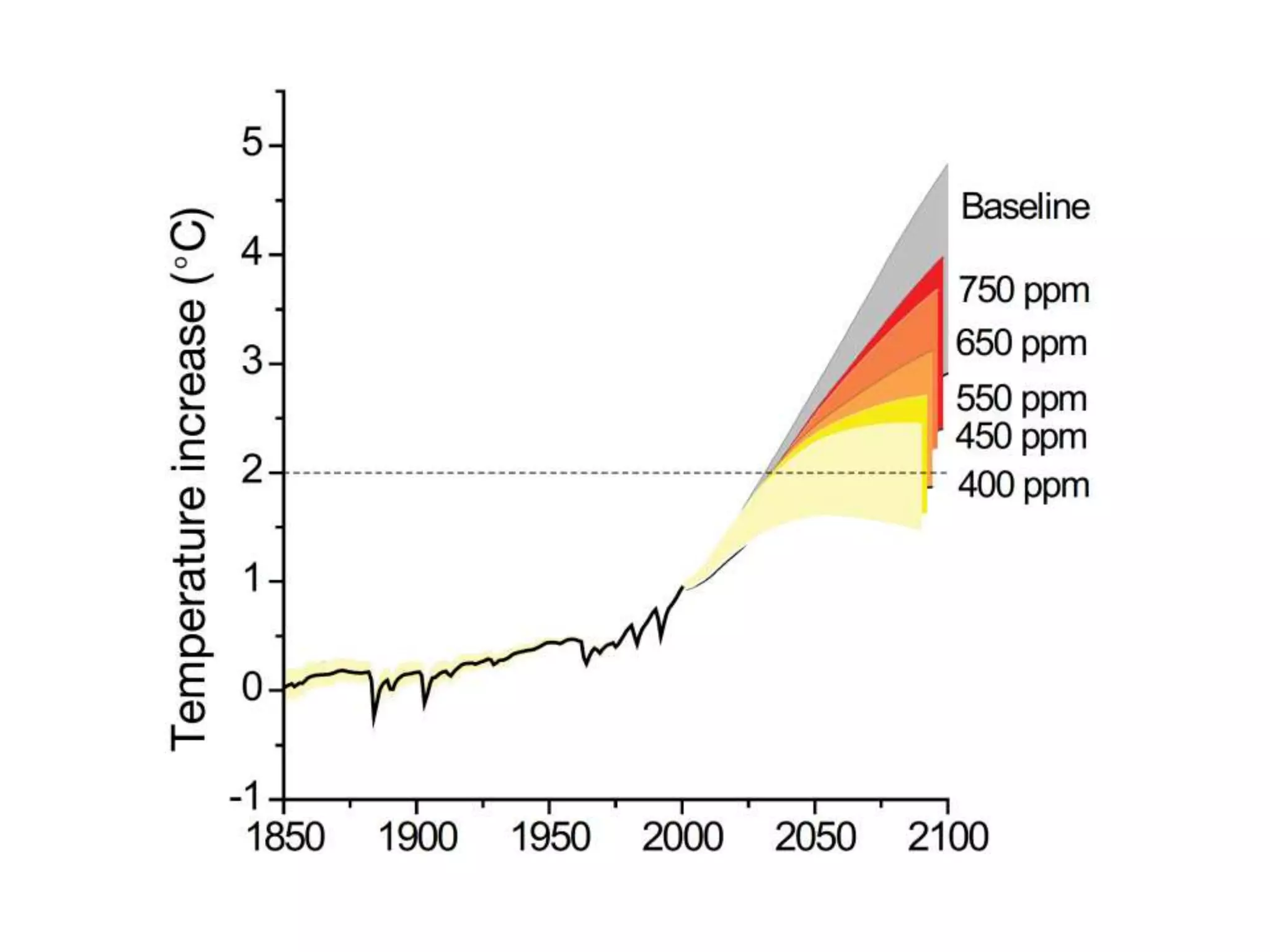
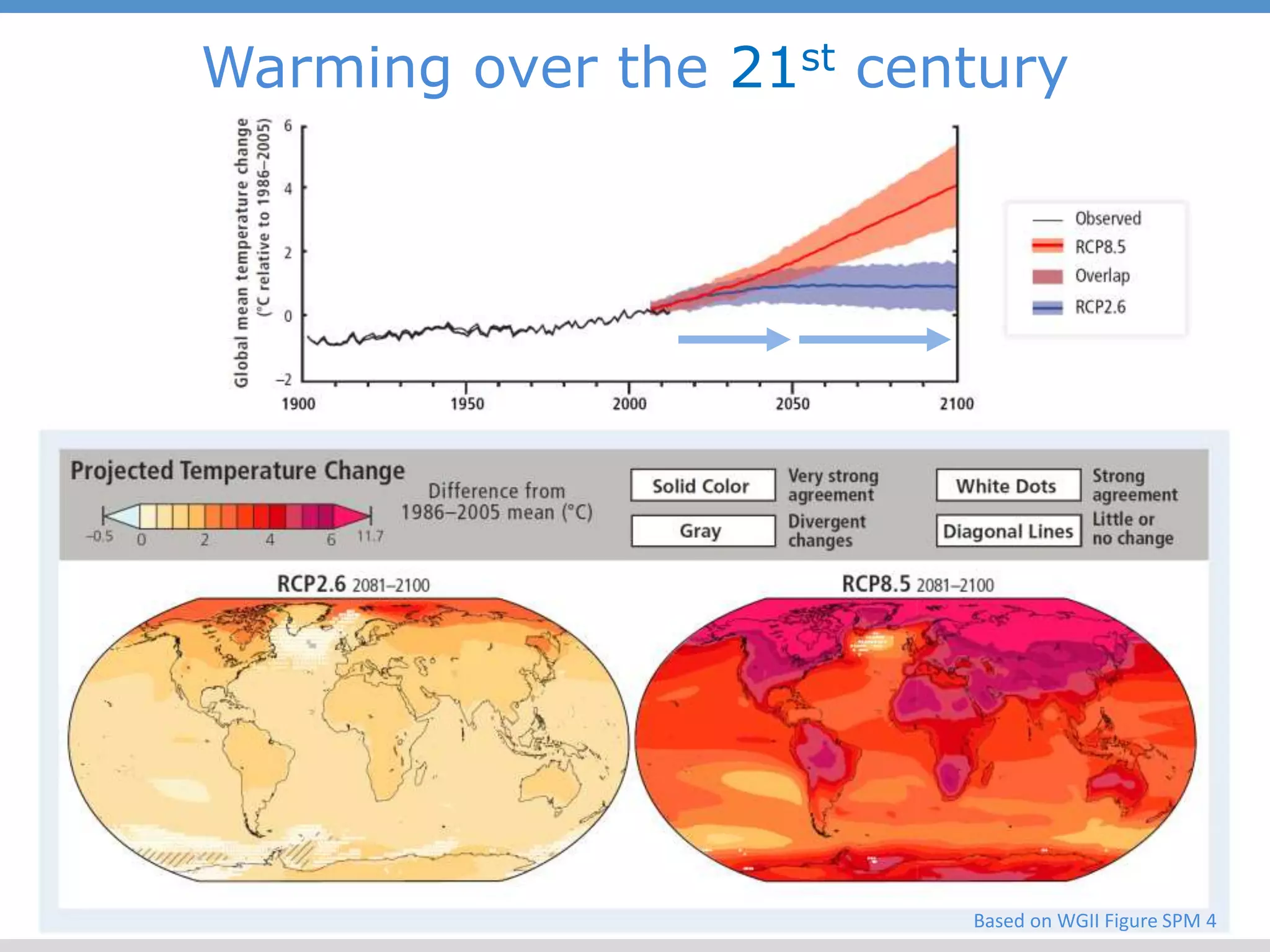
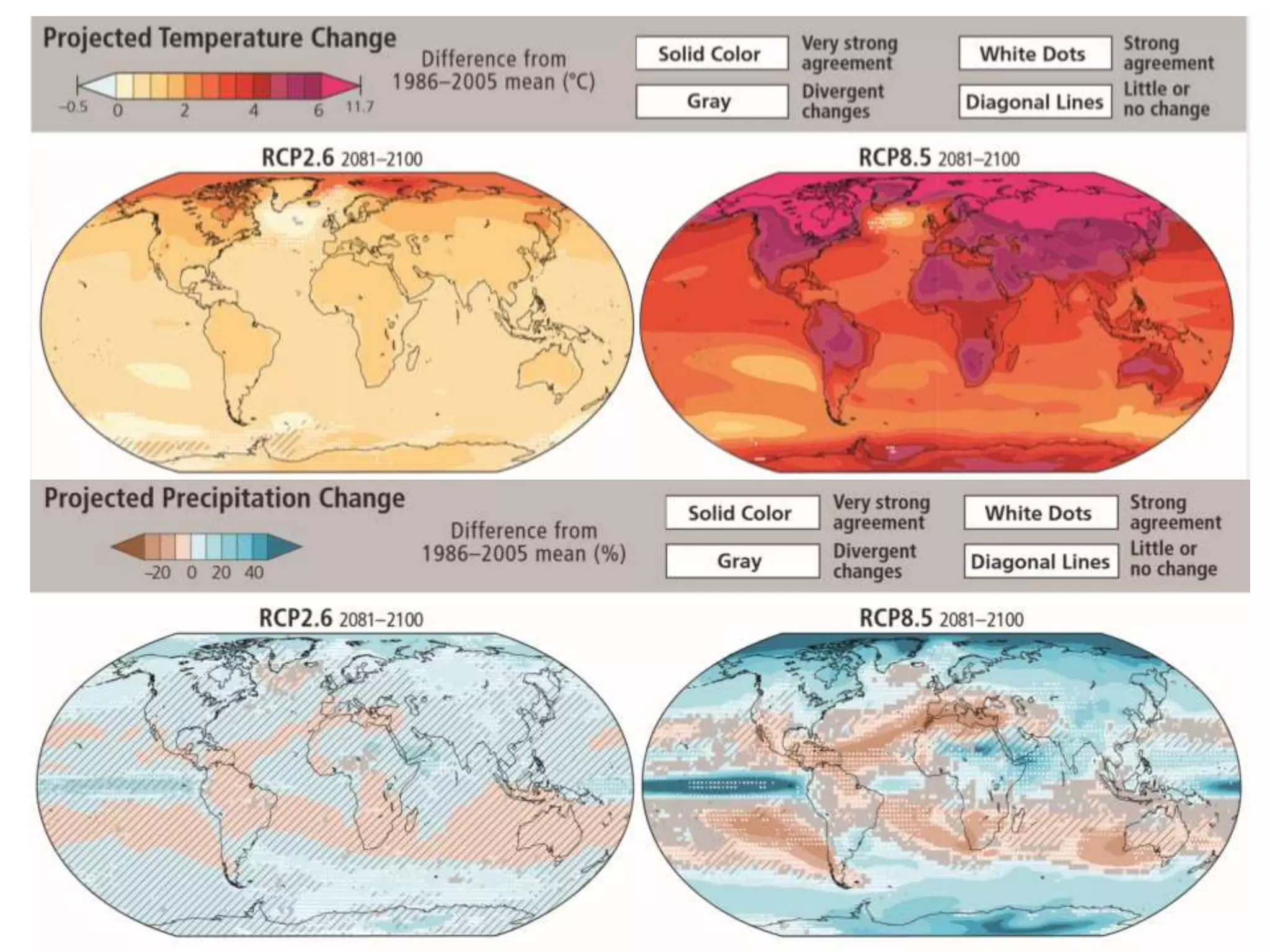
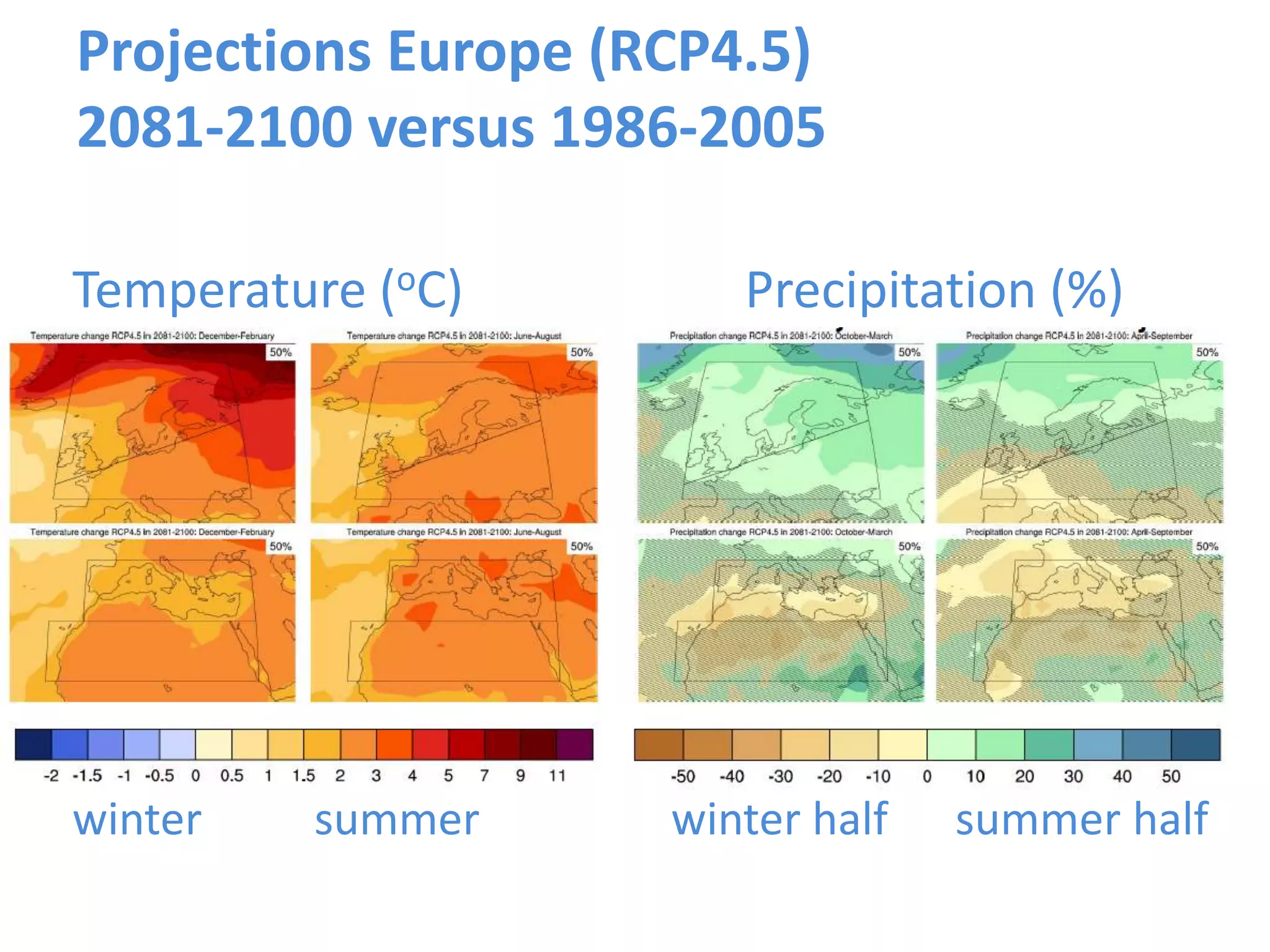
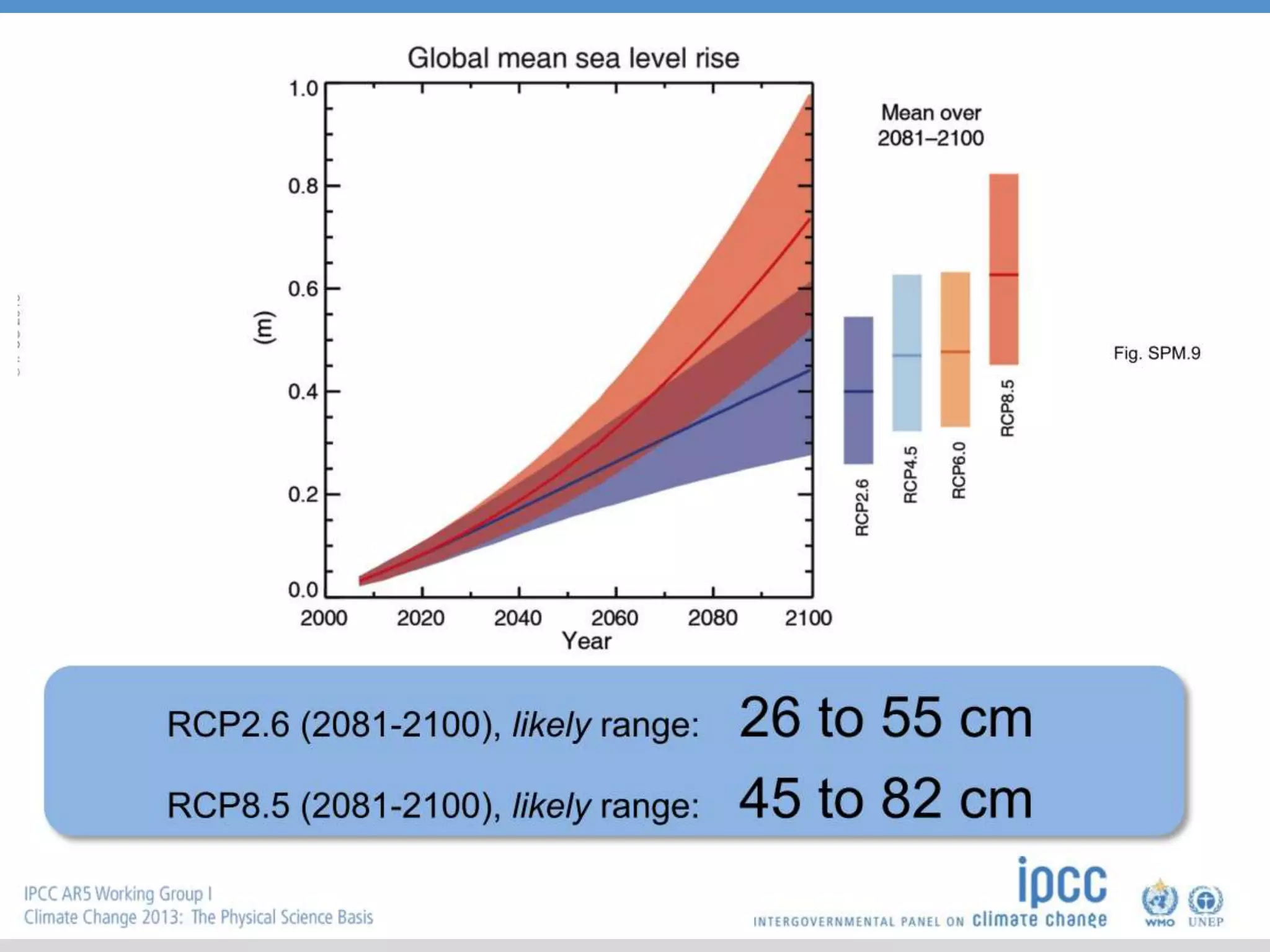
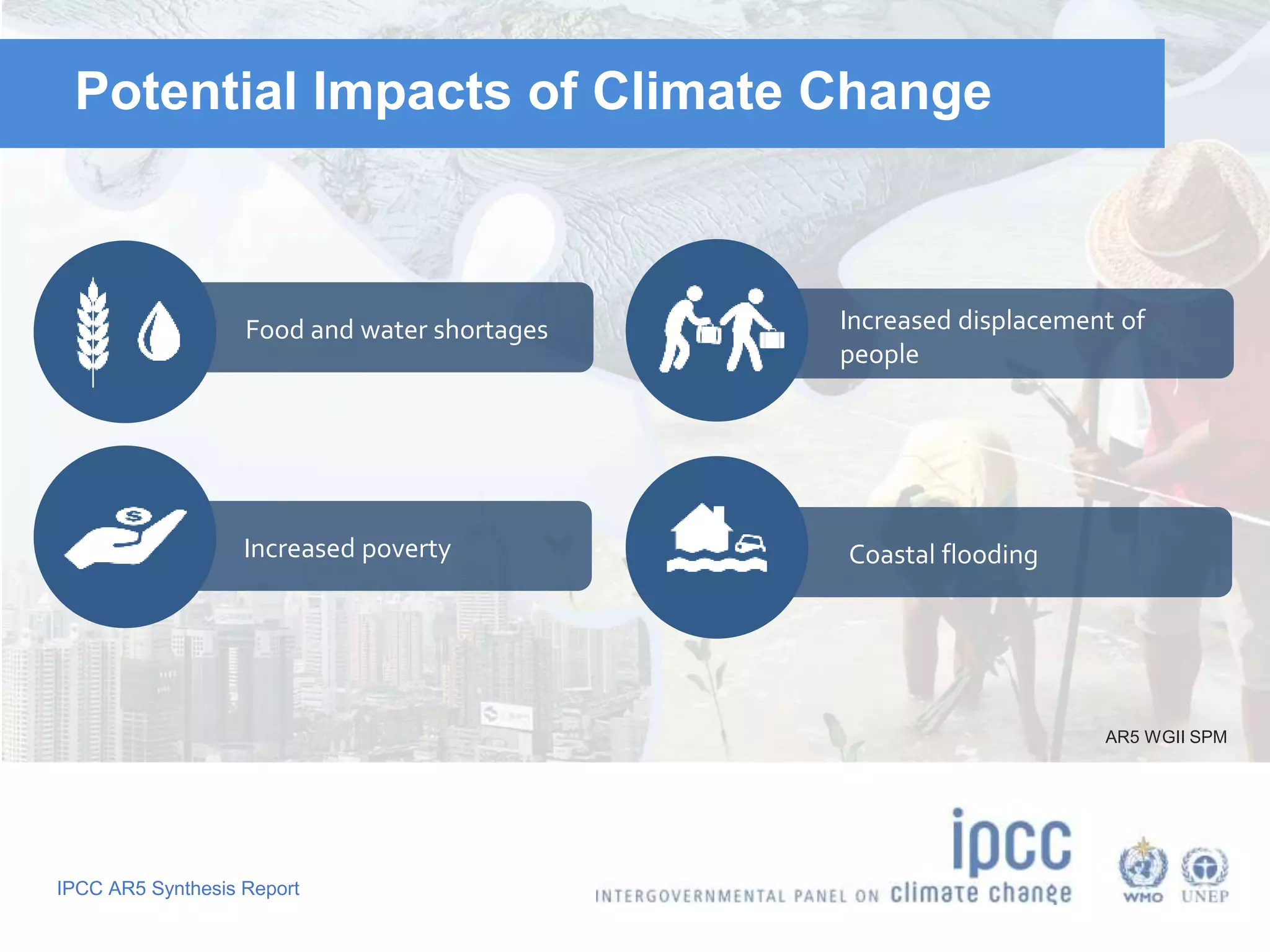
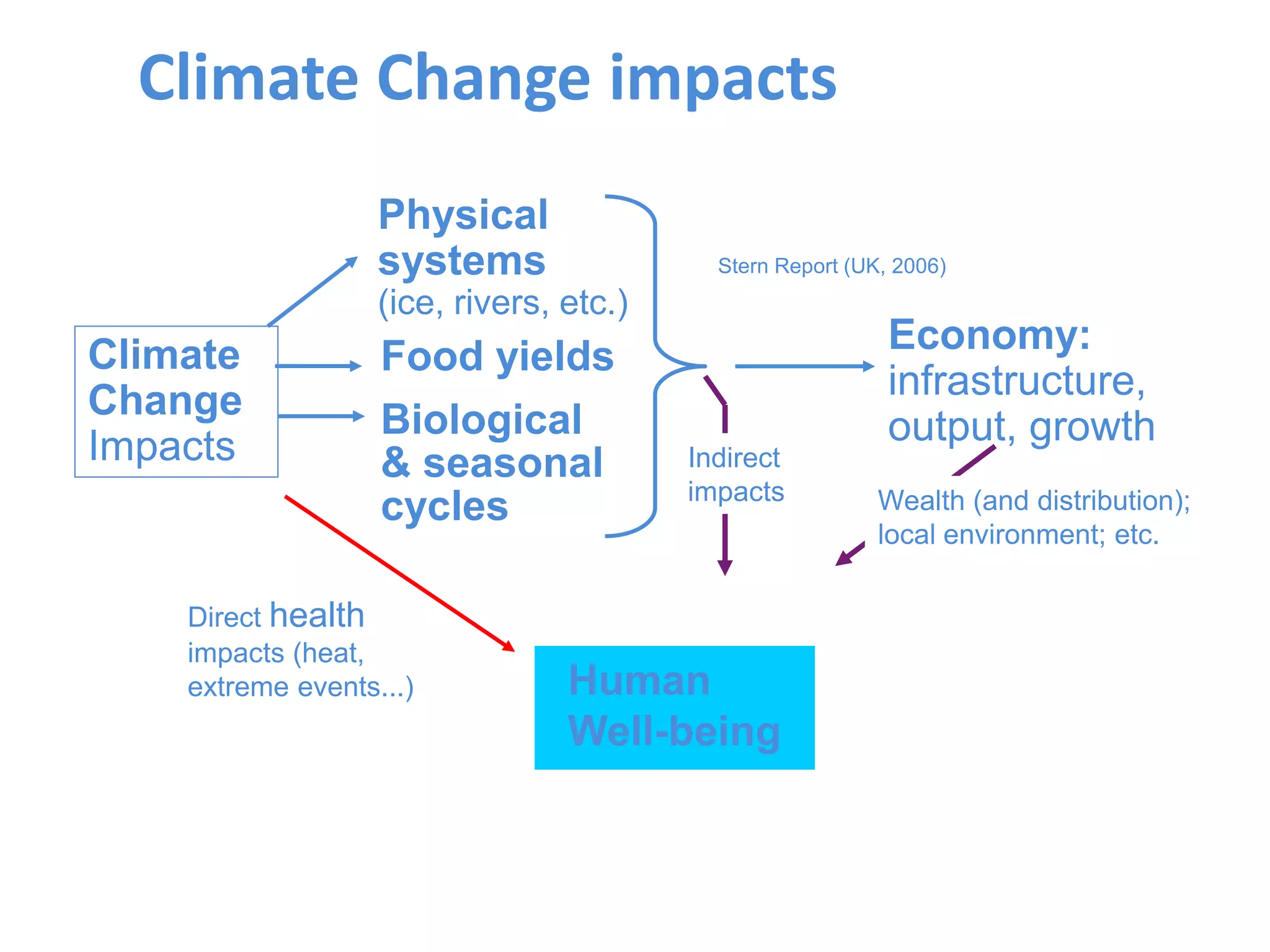
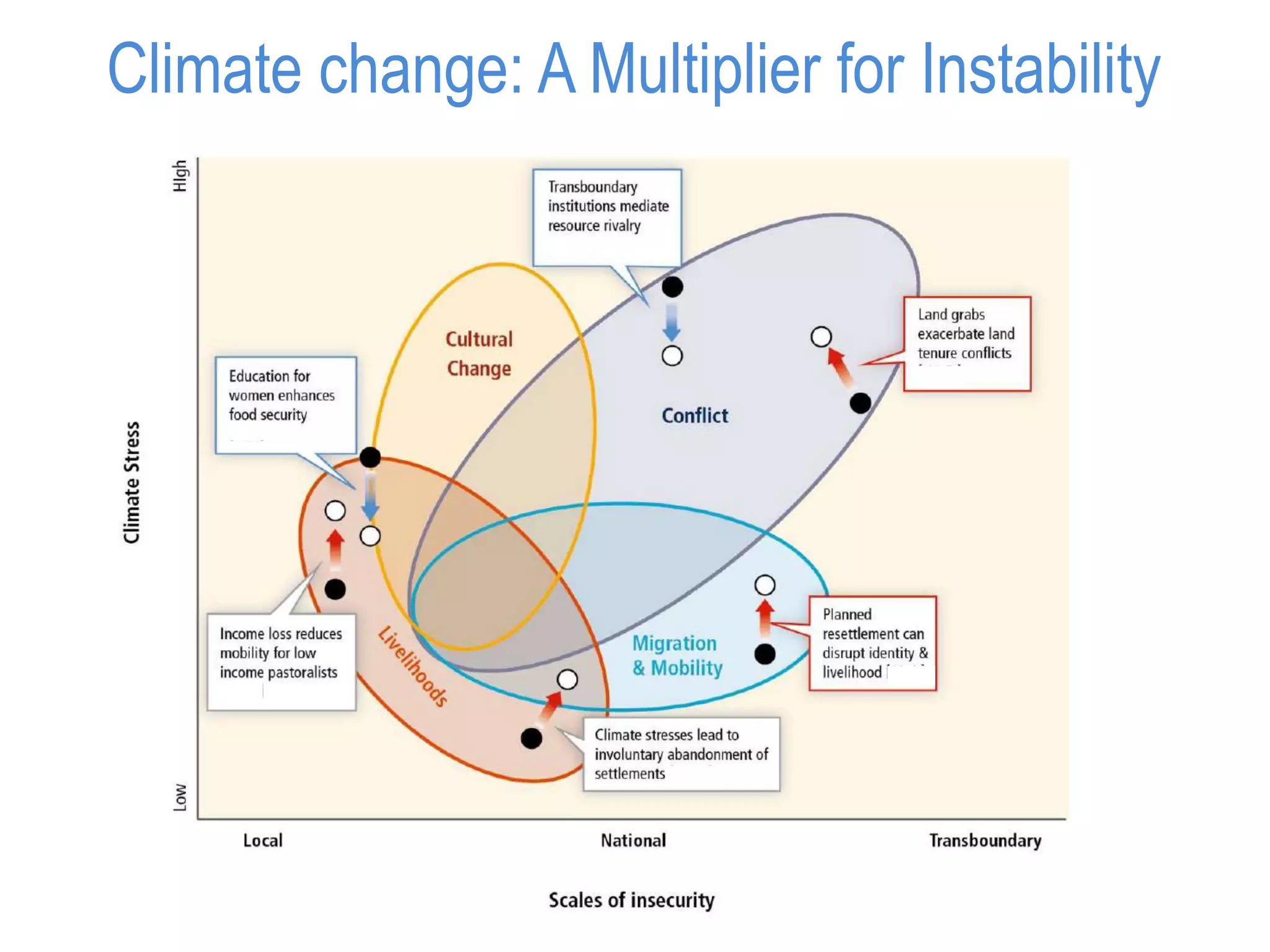
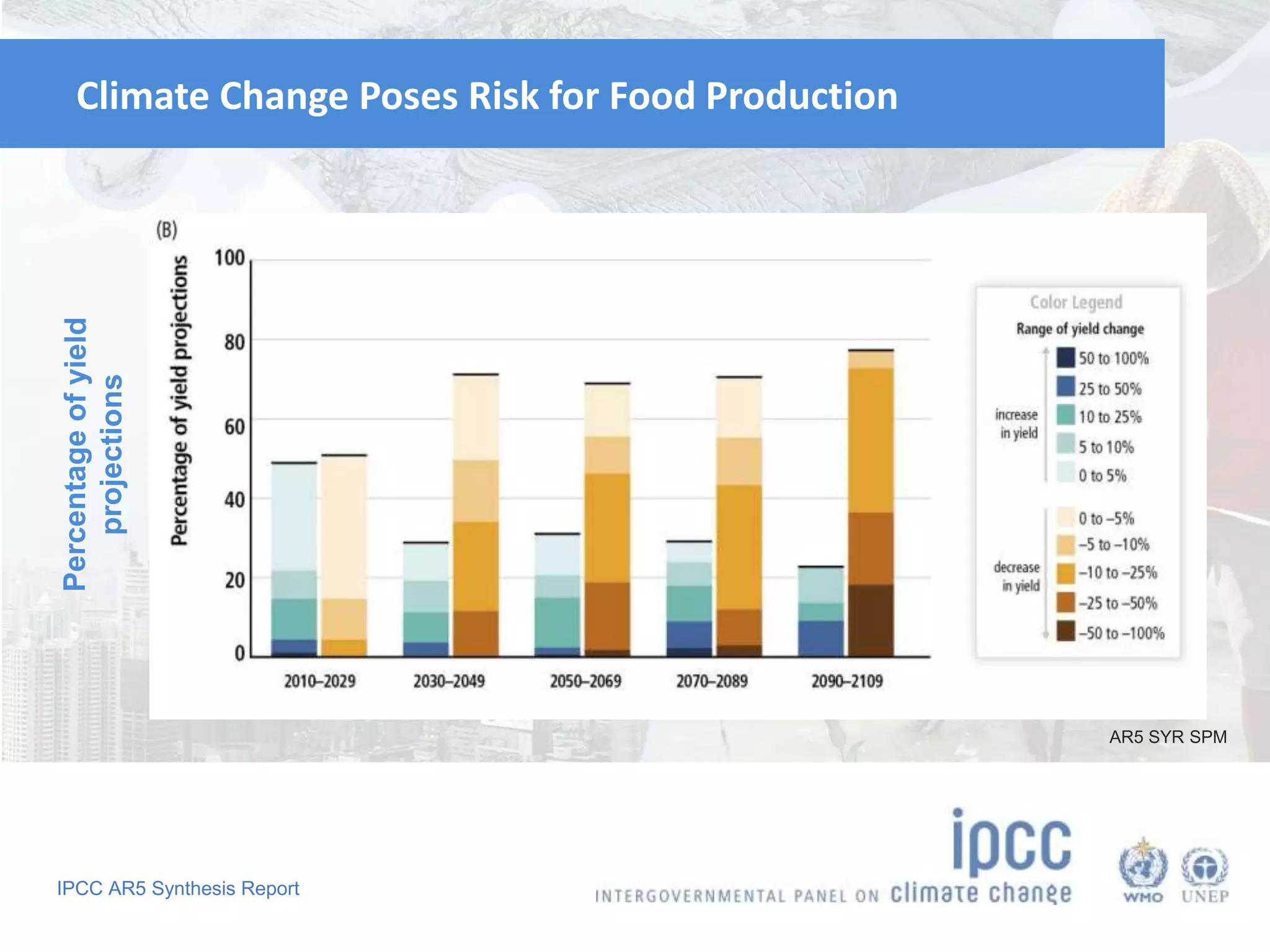
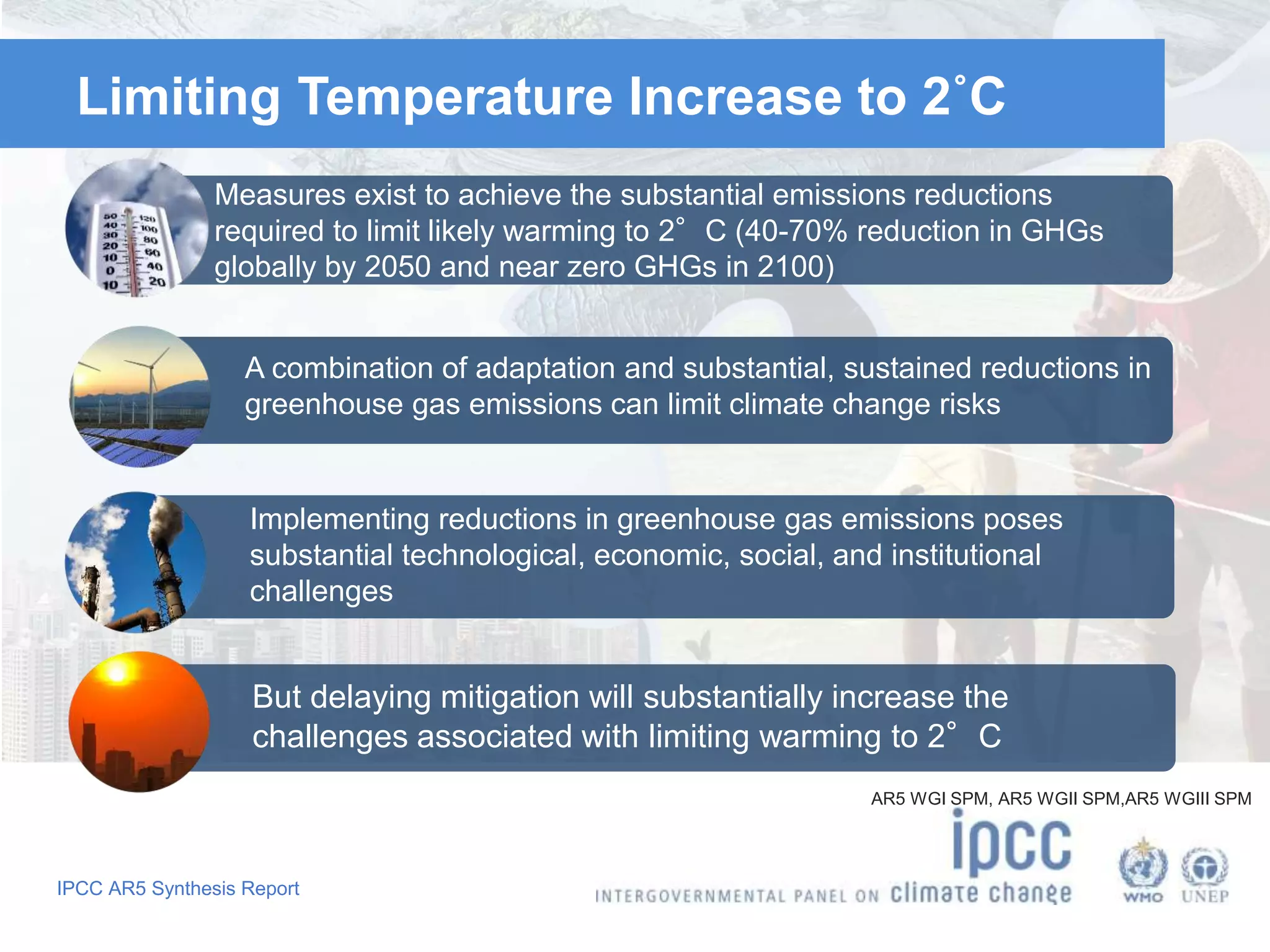
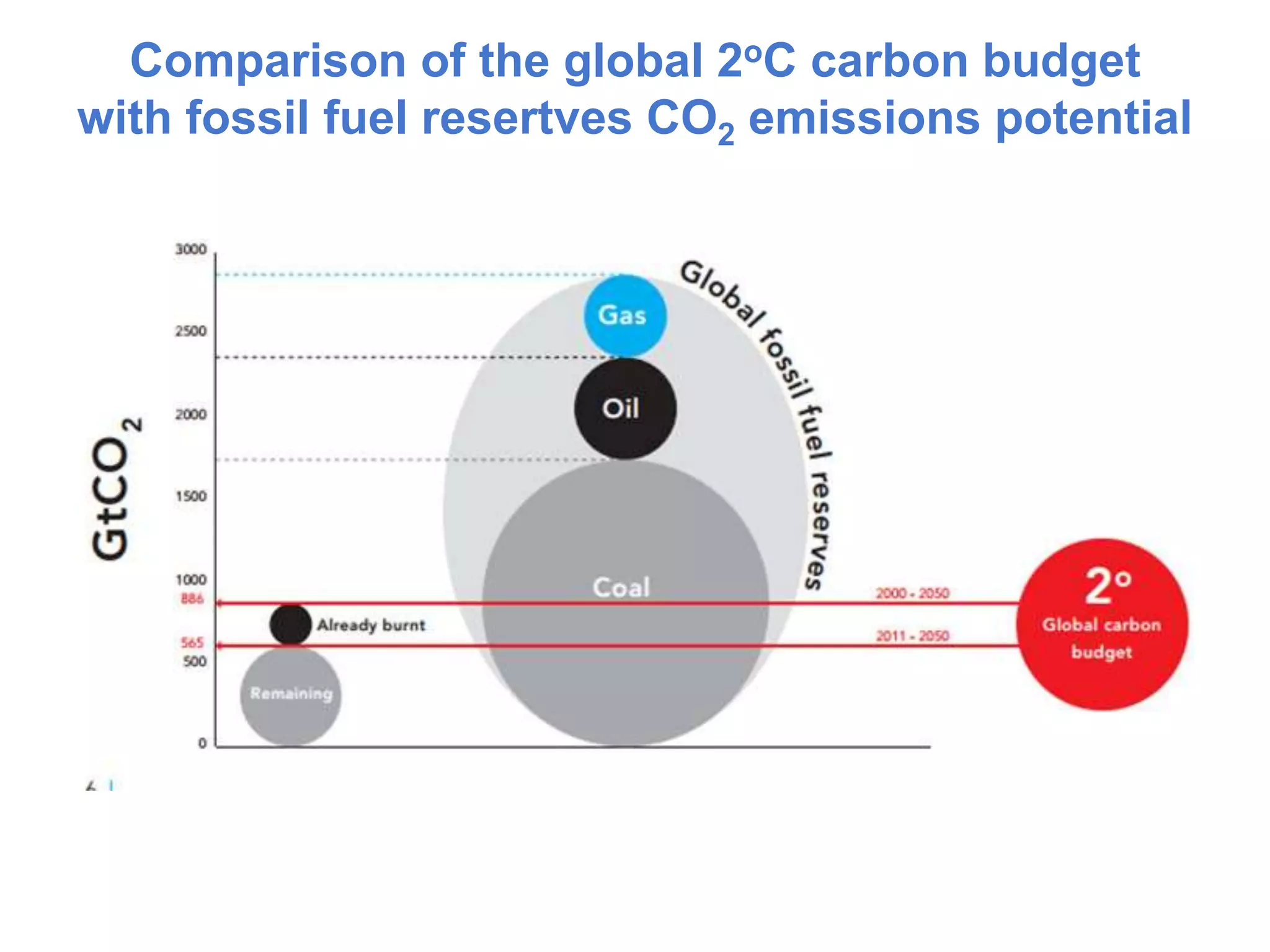
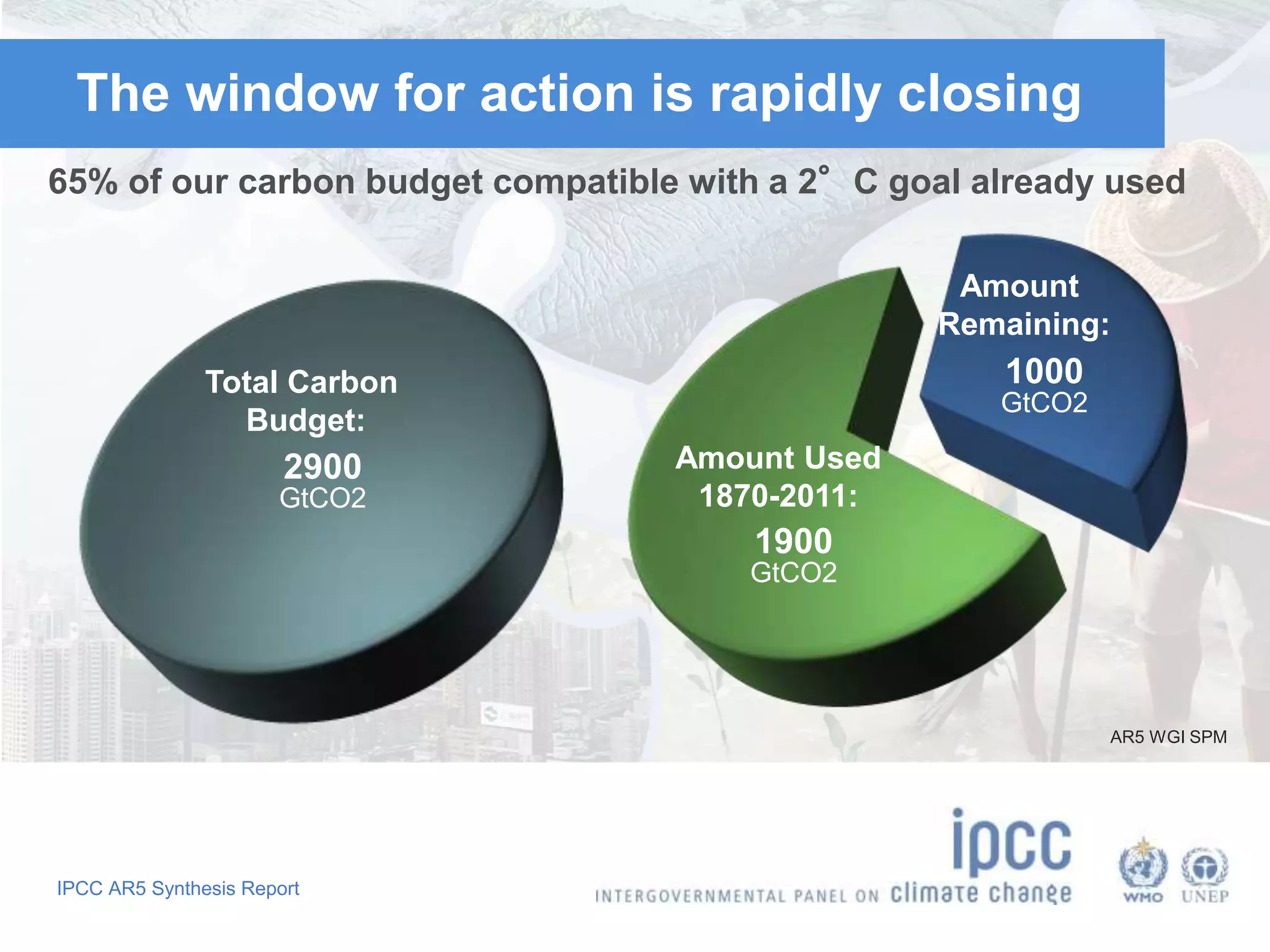
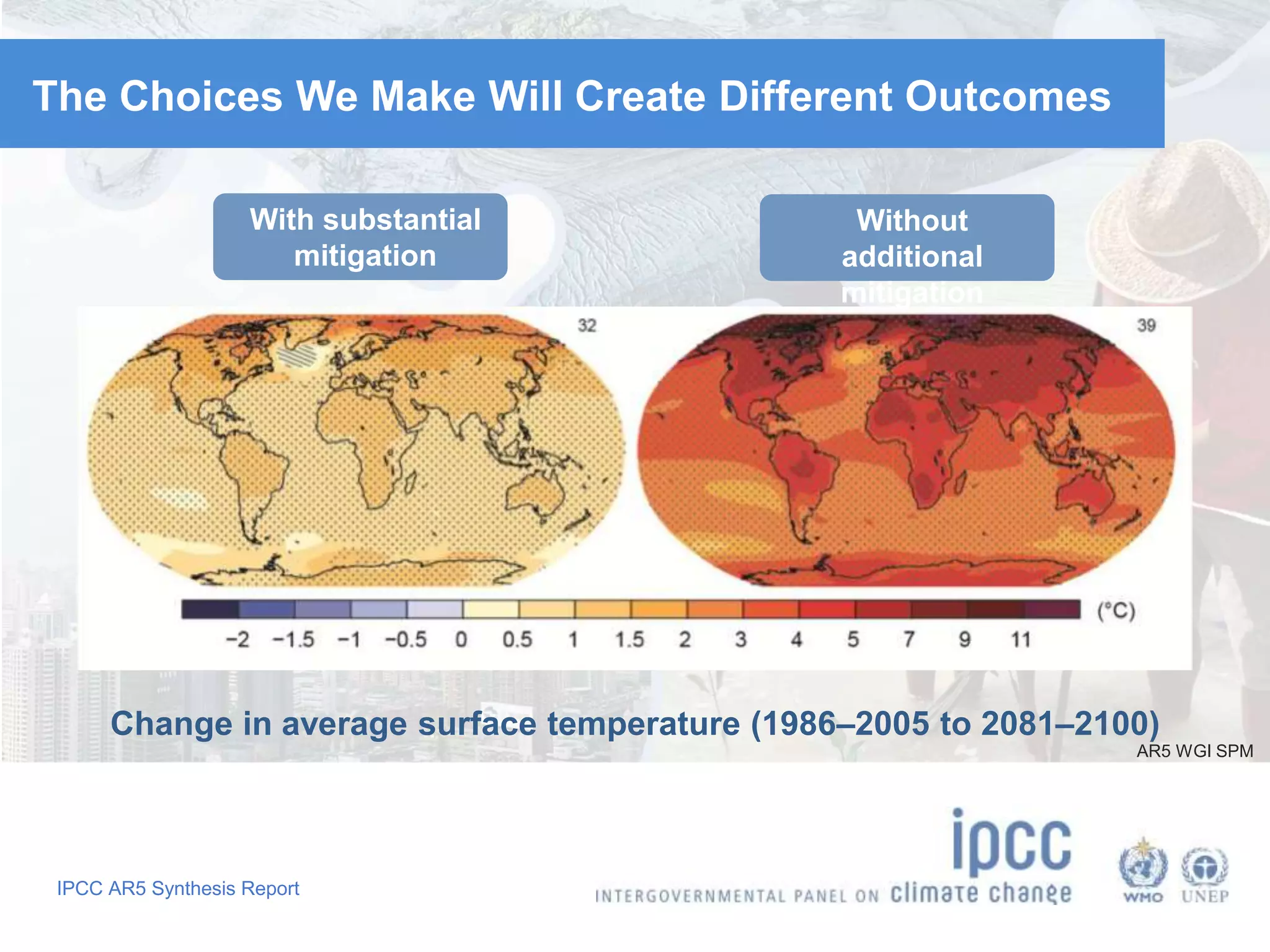
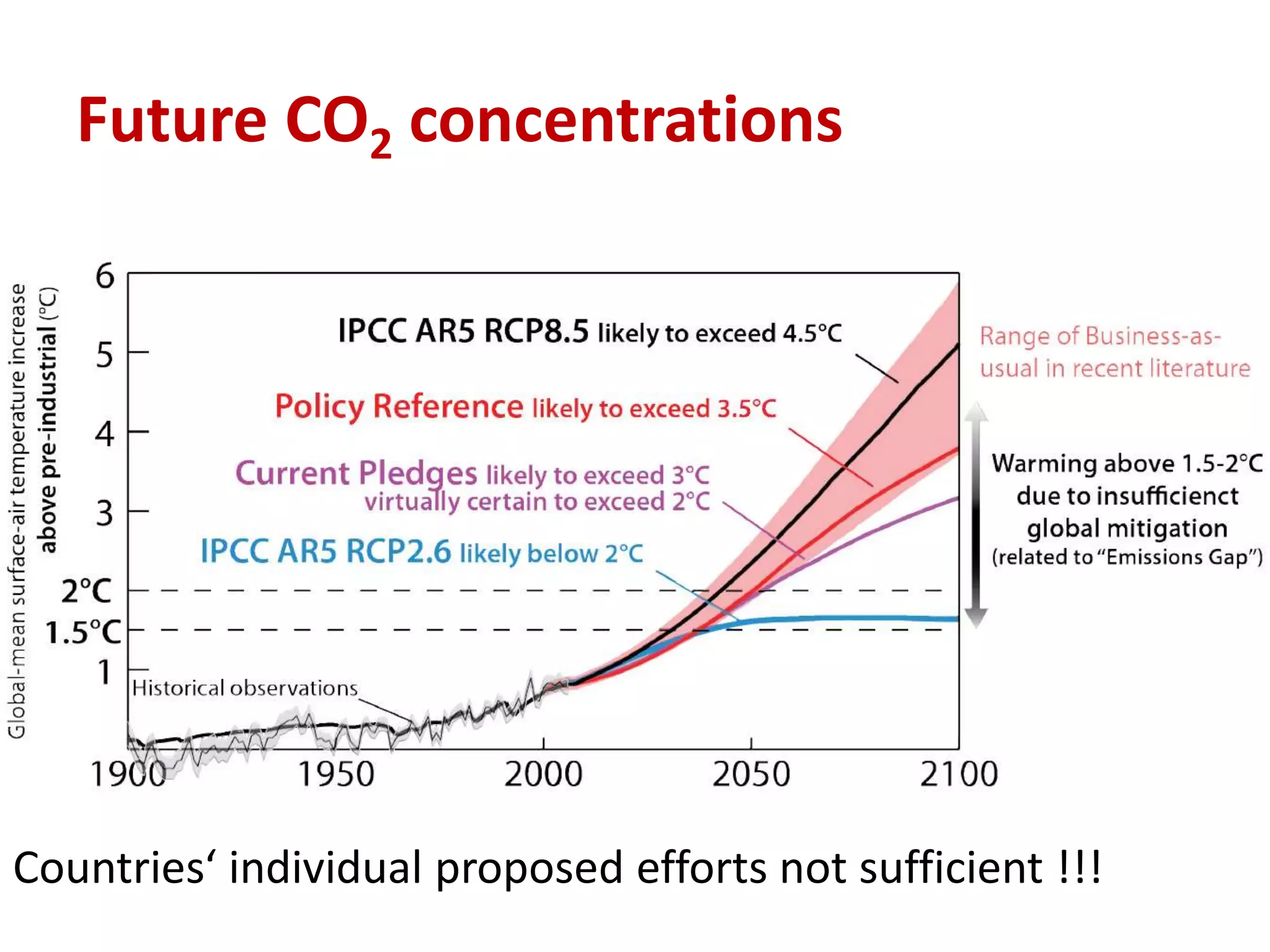
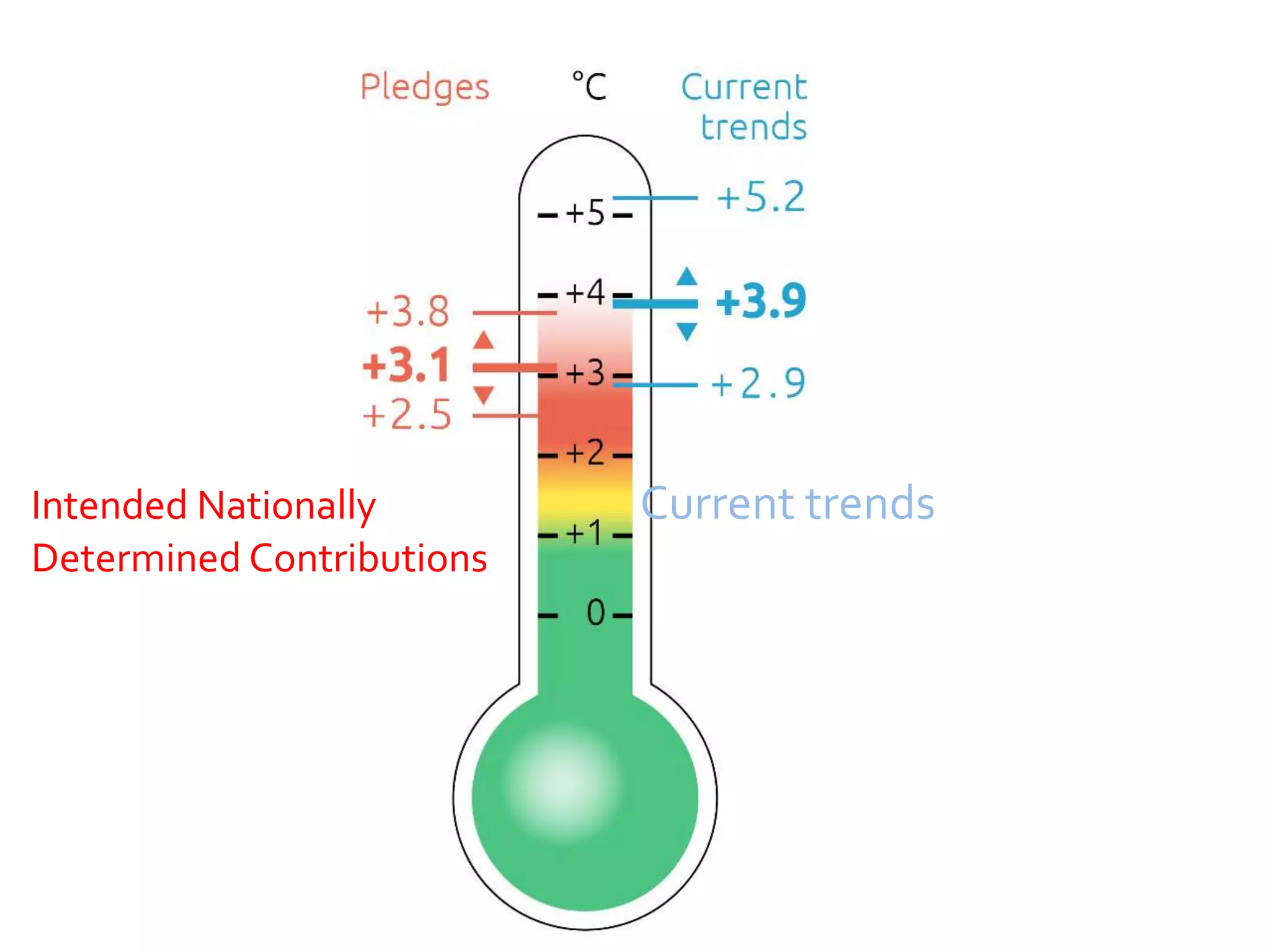
The document summarizes key findings from the IPCC Fifth Assessment Report. It finds that human activity is extremely likely the dominant cause of global warming since the mid-20th century. If greenhouse gas emissions continue, the report warns of consequences like more extreme weather, water shortages, displaced populations, and impacts on food production. However, the summary also finds that limiting global temperature rise to 2°C is possible with ambitious emissions reductions, though the window for action is closing rapidly.