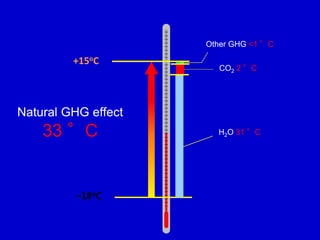
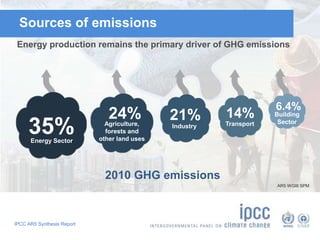
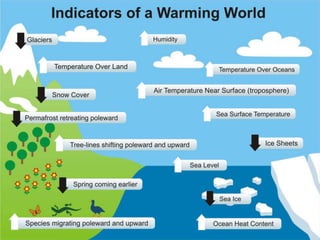
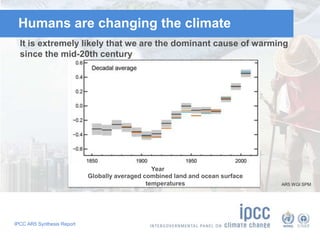
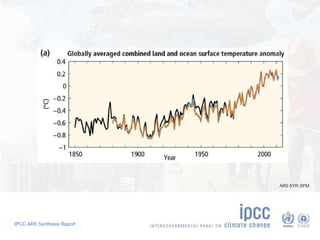
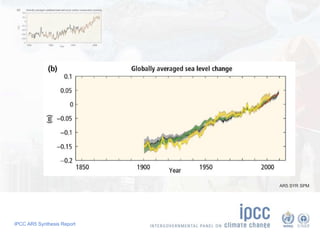
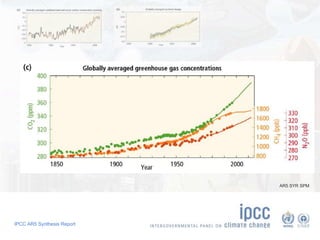
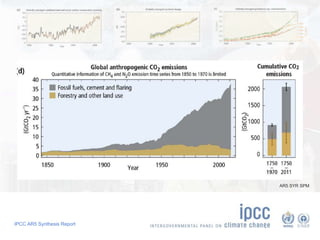
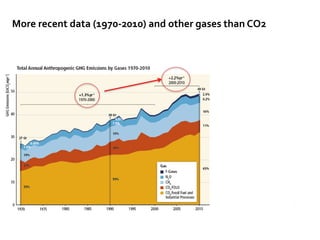
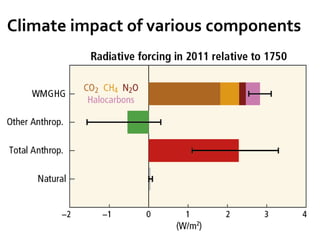
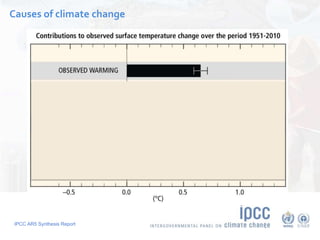
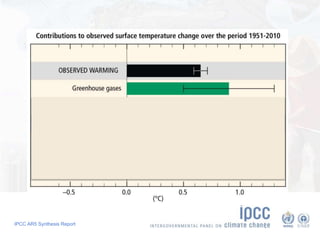
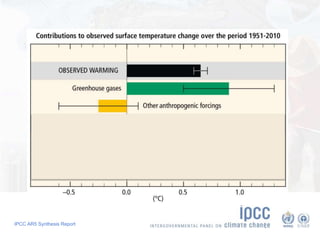
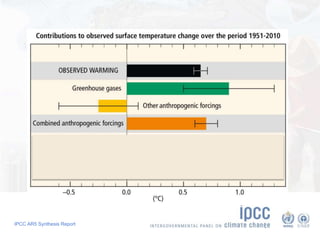
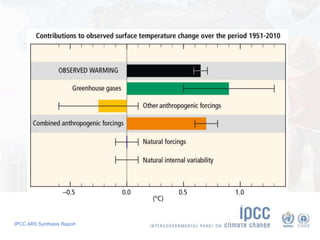
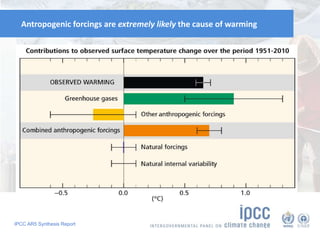
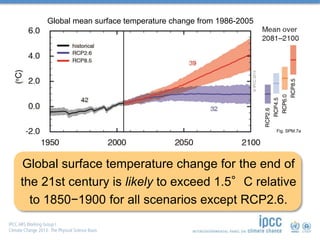
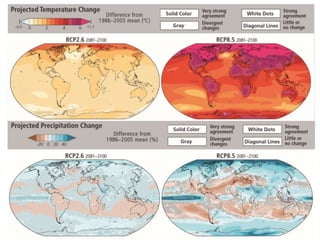
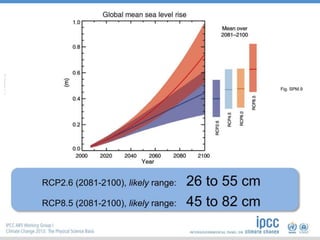
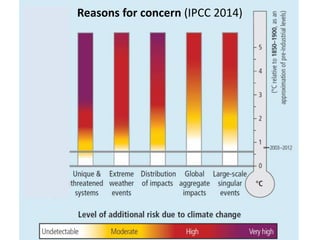
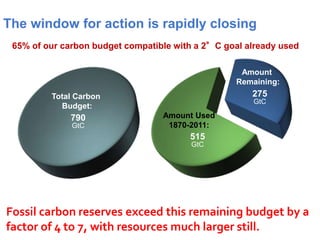
The document summarizes key findings from the IPCC AR5 Synthesis Report. It finds that human activity, including emissions from energy production, agriculture and other sources, is extremely likely the dominant cause of global warming since the mid-20th century. Continued emissions of greenhouse gases will lead to further warming and changes in the climate system such as sea level rise and loss of Arctic sea ice. Limiting global temperature increase to 2°C will require substantial reductions in emissions by 2050 through policy measures and technological changes. Delaying mitigation actions will make limiting warming to 2°C significantly more difficult.













![Warming in the climate system
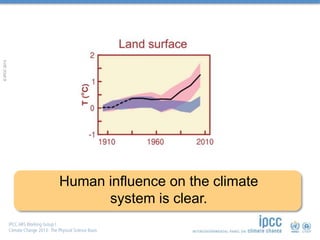
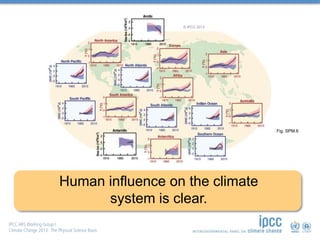
is unequivocal, […]
Human influence on the
climate system is clear.
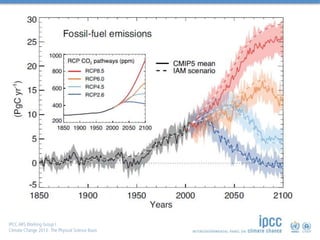
Limiting climate change will require
substantial and sustained reductions of
greenhouse gas emissions.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jan-170429100352/85/Introduction-to-Climate-Science-38-320.jpg)

