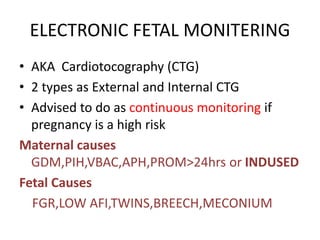
Intrapartum fetal surveillance involves monitoring the fetus during labor and delivery to ensure well-being and prevent acute hypoxia, which can cause neurological problems or stillbirth. Current monitoring methods include intermittent auscultation for low-risk pregnancies and electronic fetal monitoring, scalp blood sampling, and fetal stimulation tests for high-risk pregnancies. These methods aim to detect signs of hypoxia like changes in heart rate patterns, scalp pH levels, lactate levels, or a lack of heart rate acceleration in response to stimulation. Clinical assessments like checking for meconium or maternal fever are also important parts of surveillance. Effective monitoring requires integrating results from different tests and timely interventions when needed.