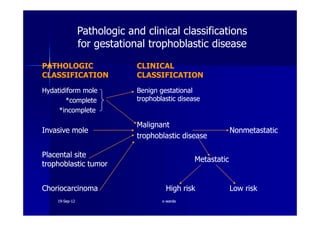
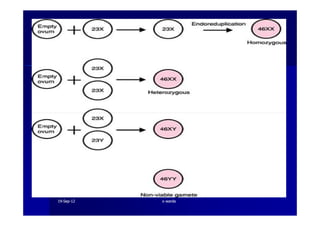
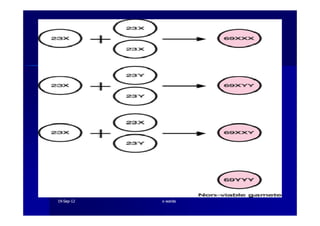
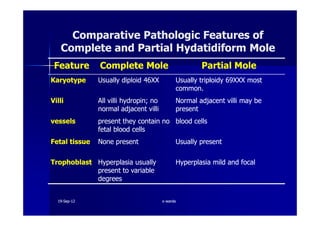
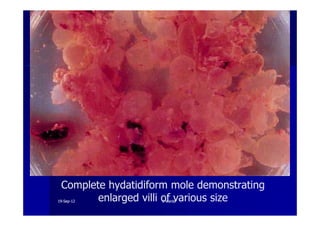
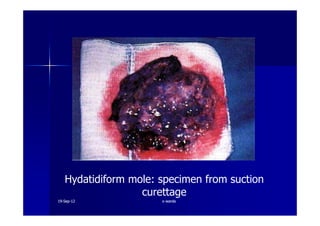
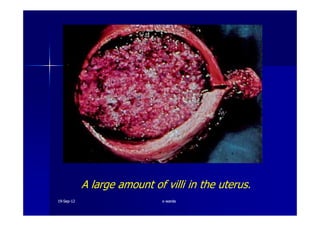
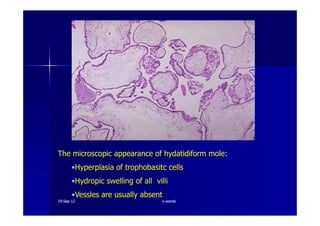
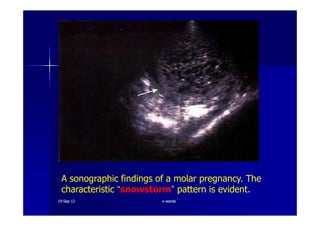
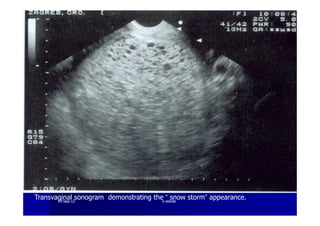
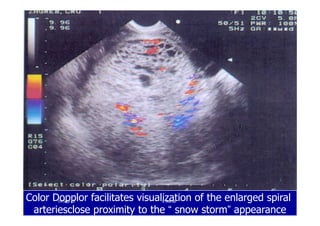
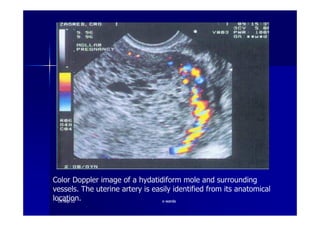
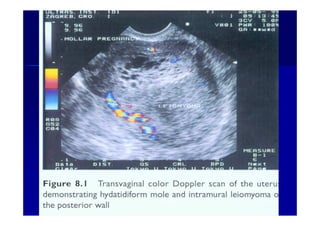
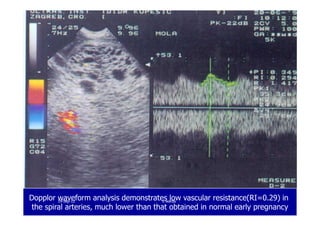
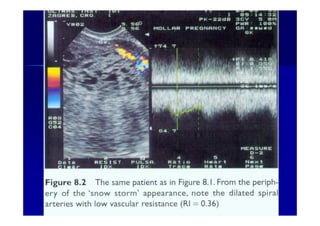
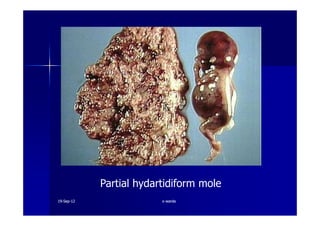
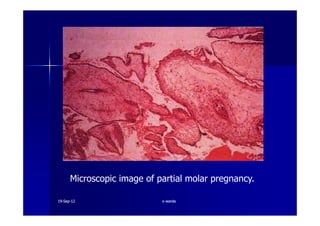
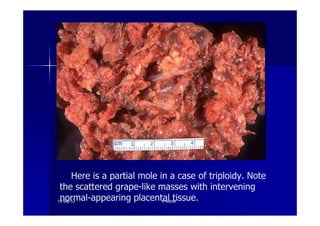
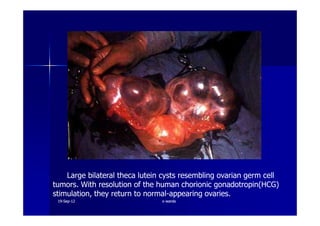
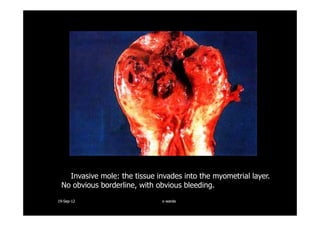
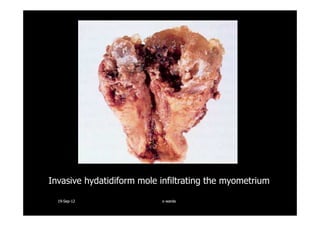
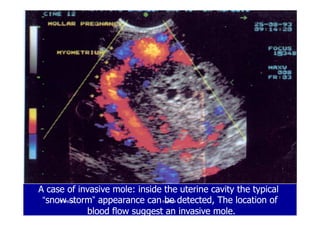
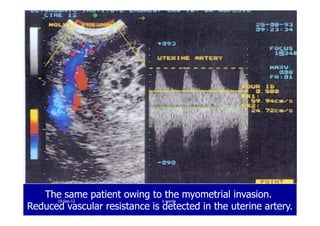
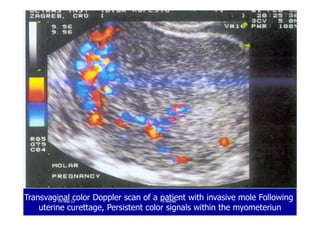
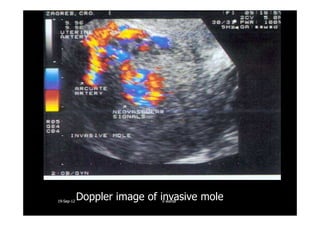
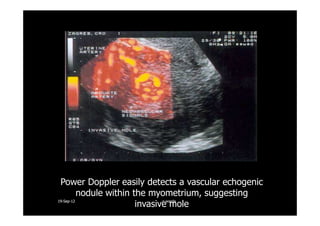
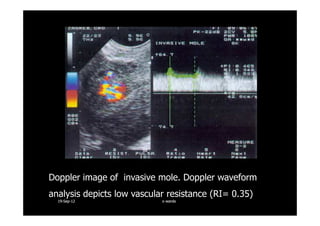
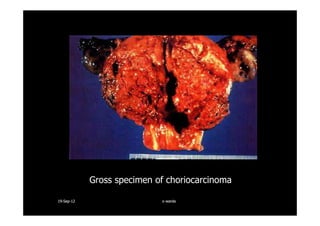
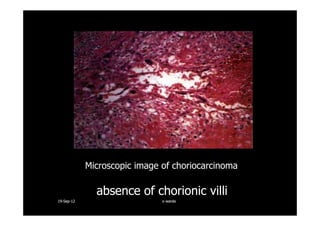
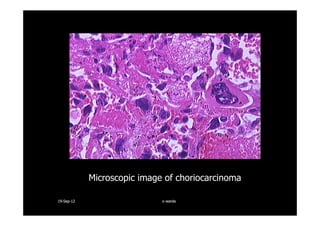
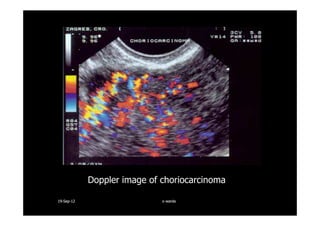
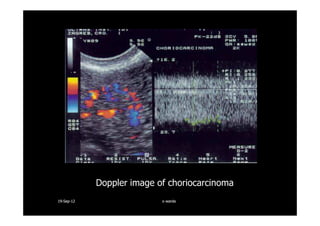
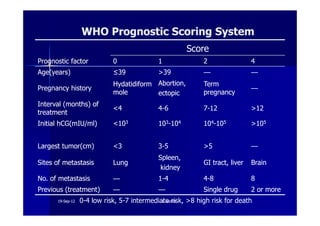
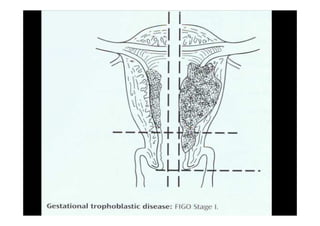
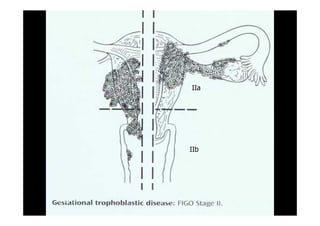
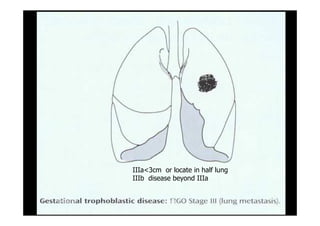
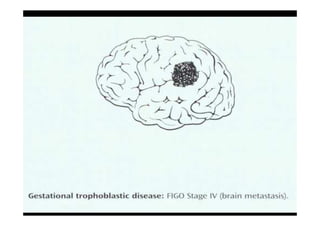
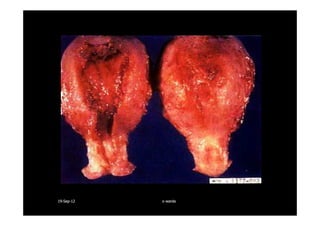
This document discusses gestational trophoblastic disease (GTD), specifically hydatidiform moles. It defines a hydatidiform mole as a pregnancy characterized by vesicular swelling of placental villi, usually with the absence of an intact fetus. Molar pregnancies can be complete or partial based on whether there is a fetus present. Complete moles have no fetus and are diploid, while partial moles may contain defective fetuses and are usually triploid. Symptoms include vaginal bleeding and an enlarged uterus. Diagnosis involves beta-hCG levels and ultrasound showing a "snowstorm" pattern. Treatment is surgical evacuation followed by chemotherapy for high-risk cases to prevent invasive tumors.