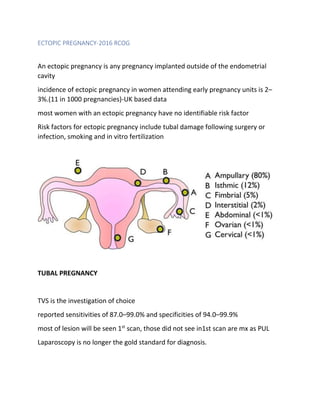
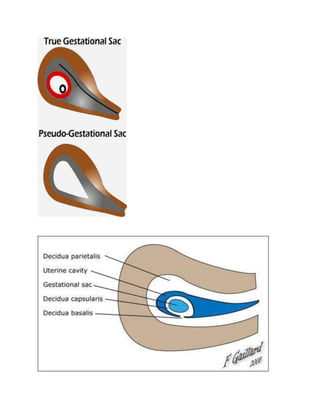
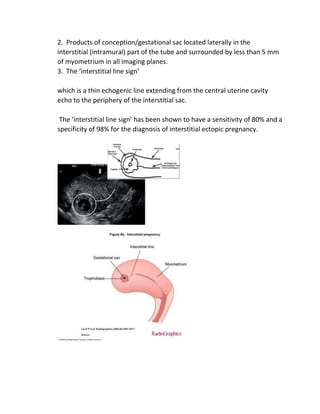
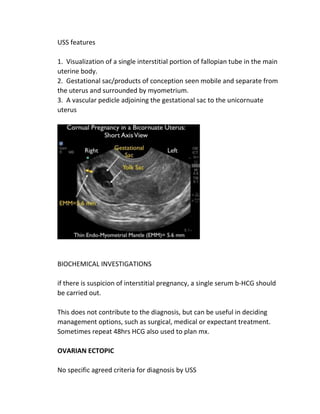
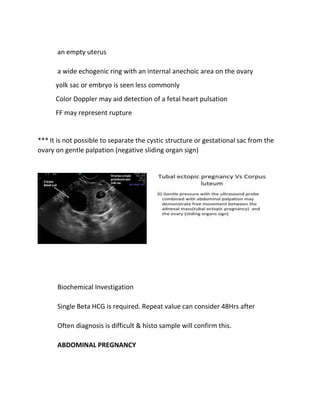
An ectopic pregnancy occurs when a fertilized egg implants outside of the uterus, most commonly in the fallopian tubes. Transvaginal ultrasound is the primary investigation to diagnose ectopic pregnancies. On ultrasound, ectopic pregnancies may appear as an inhomogeneous adnexal mass, empty extrauterine sac, yolk sac, or pseudosac. Serum hCG levels and ultrasound findings are used to determine management, whether surgical, medical, or expectant. Rare sites of ectopic implantation include the cervix, caesarean scar, interstitial portion of the fallopian tube, and ovaries.