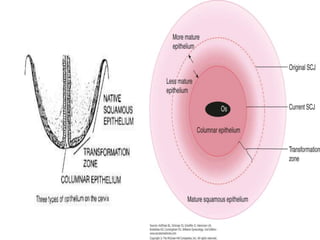
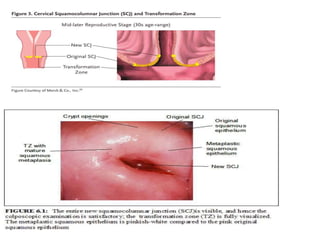
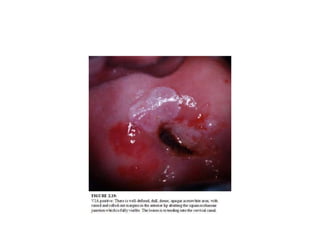
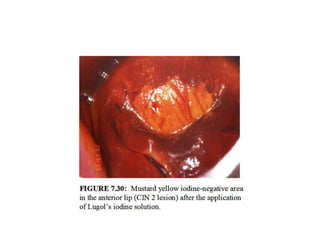
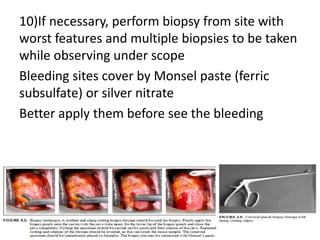
Colposcopy is a procedure that uses magnification and acetic acid/Lugol's iodine to examine the cervix. It can detect precancerous lesions and cancers. The key steps are applying acetic acid and iodine to visualize lesions, which appear white or yellow. Biopsies are taken from abnormal areas. For pregnant patients, extra care must be taken to avoid bleeding and injury during the procedure. Lesions suspicious for cancer must still be biopsied.