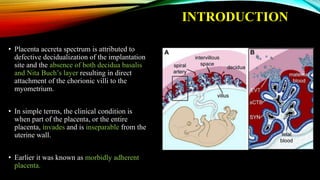
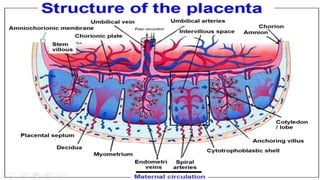
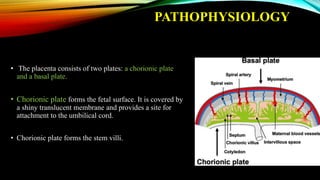
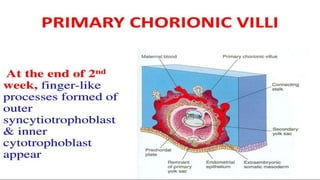
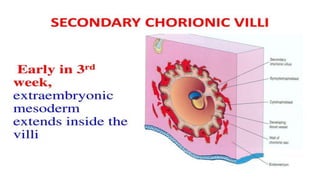
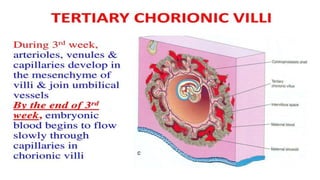
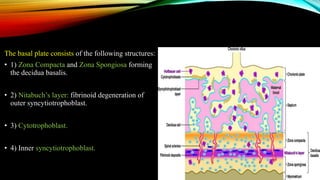
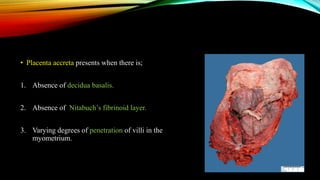
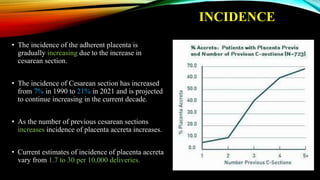
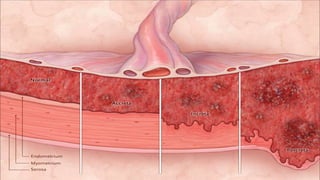
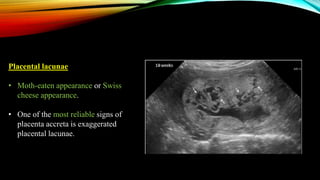
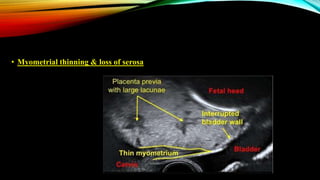
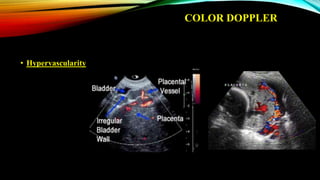
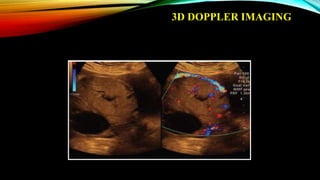
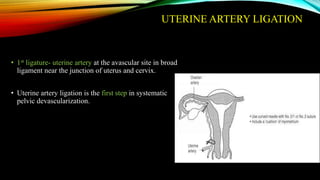
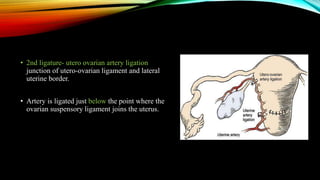
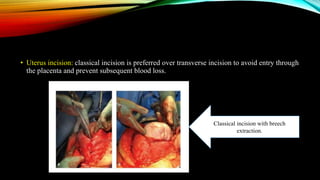
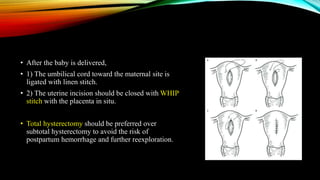
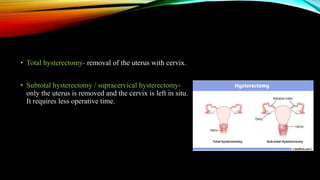
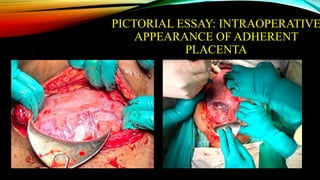
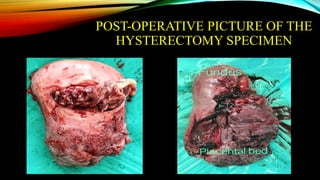
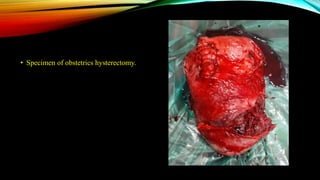
1) Placenta accreta spectrum disorders occur when the placenta invades and is inseparable from the uterine wall, posing risks of heavy bleeding. The incidence has increased 10-fold in recent decades due to rising c-sections.
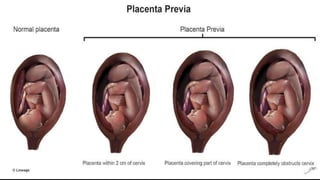
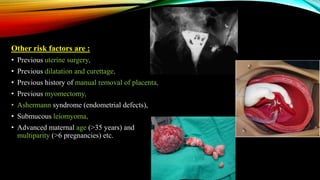
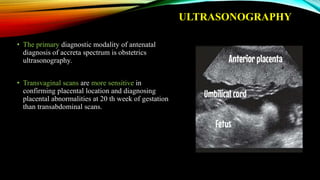
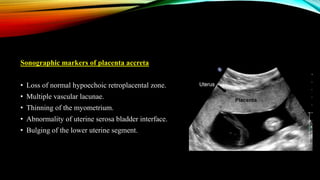
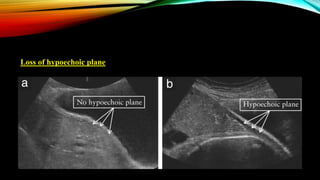
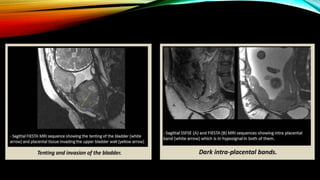
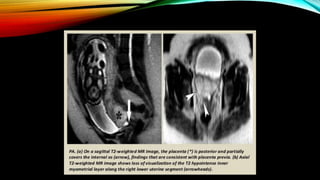
2) Risk factors include placenta previa, prior c-sections, and other uterine surgeries. Early diagnosis using ultrasound and MRI is important for management planning.
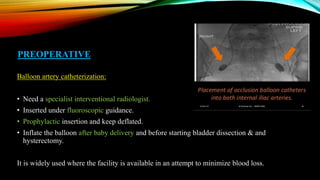
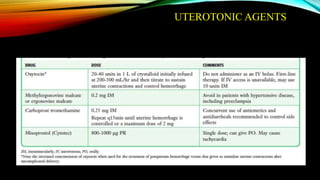
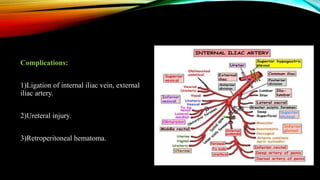
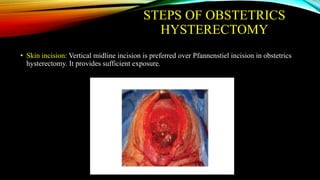
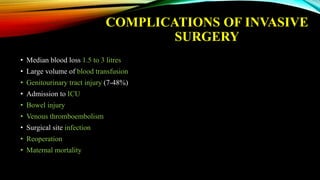
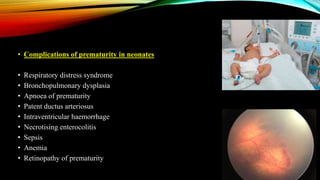
3) Management involves a multidisciplinary approach, with the goal of minimizing blood loss through techniques like arterial embolization and hysterectomy if needed. Conservative management is sometimes attempted but carries risks if failed.