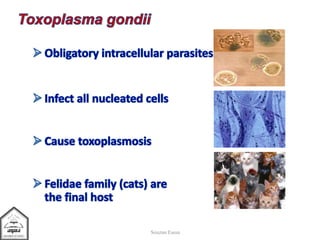
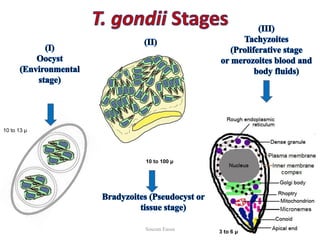
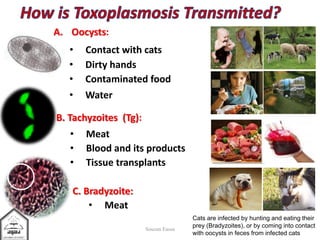
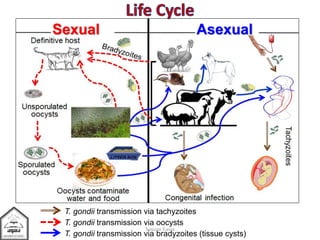
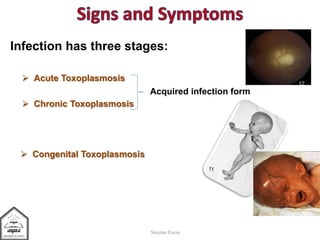
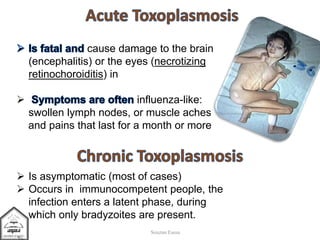
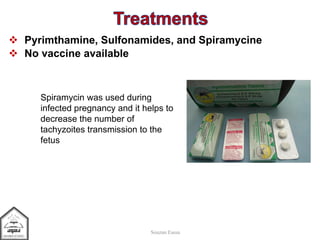
Toxoplasma gondii is an intestinal coccidian parasite that can infect humans and cause toxoplasmosis. It has three infectious stages: oocysts found in cat feces, tachyzoites that actively replicate causing acute infection, and bradyzoites that form cysts in tissues and cause chronic infection. Infection occurs through contact with cat feces, contaminated food or water, or consumption of undercooked meat containing cysts. While most infections are asymptomatic, it can cause flu-like symptoms during acute phase or eye and brain damage in immunocompromised individuals. Treatment involves pyrimethamine, sulfonamides and spiramycine during pregnancy to reduce transmission to fetus. Prevention