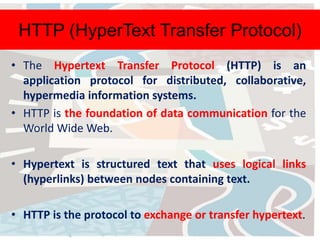
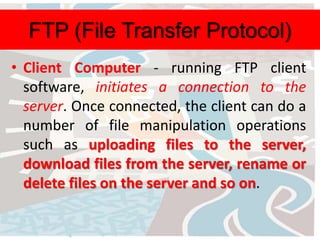
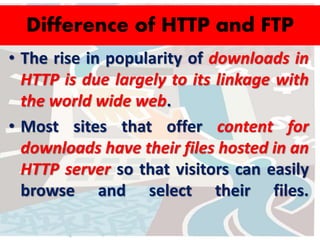
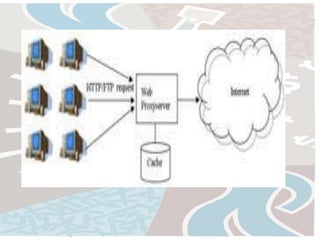
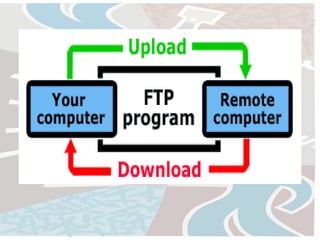
The document discusses several key concepts related to the internet and web technologies. It defines the internet as a worldwide collection of interconnected networks and devices that use common communication protocols. It describes the World Wide Web as the most well-known feature of the internet, allowing users to view rich multimedia content through web pages accessed via web browsers. Various internet protocols are also outlined, including HTTP, FTP, email, internet relay chat, Gopher, and WAIS.



















![Internet Relay Chat
• It is mainly designed for group
communication in discussion forums,
called channels, but also allows one-to-
one communication via private
message as well as chat and data
transfer, ]including file sharing.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/internettoolsandservices-141010234341-conversion-gate01/85/Internet-tools-and-services-27-320.jpg)



