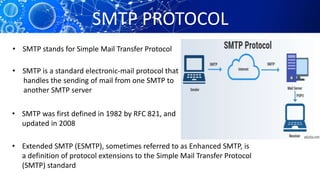
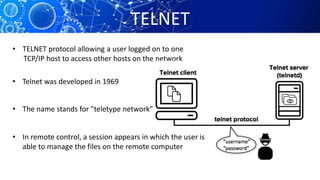
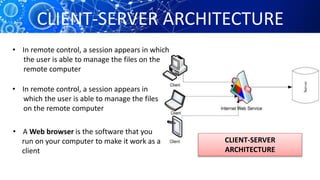
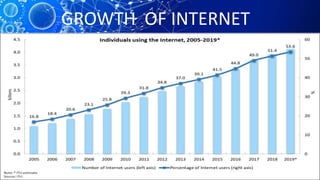
The document provides an overview of the history and workings of the internet. It discusses how ARPAnet was developed in the 1960s as a military network which later became the foundation for the commercial internet. It describes important internet protocols like TCP/IP, HTTP, and DNS. It also explains client-server architecture, IP addressing, URLs, web browsers, search engines, and common uses of the internet like email, e-commerce, and social media.