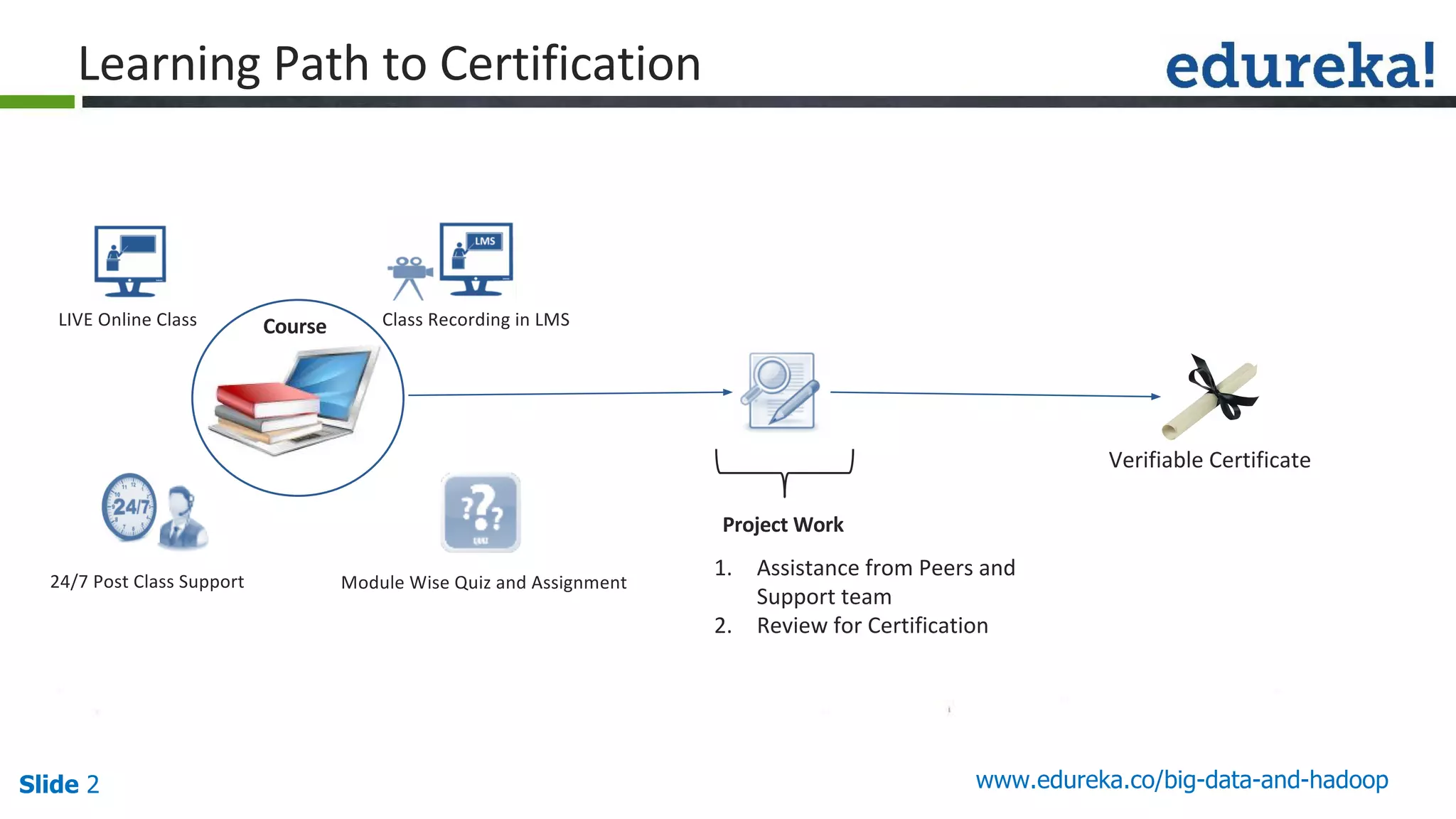
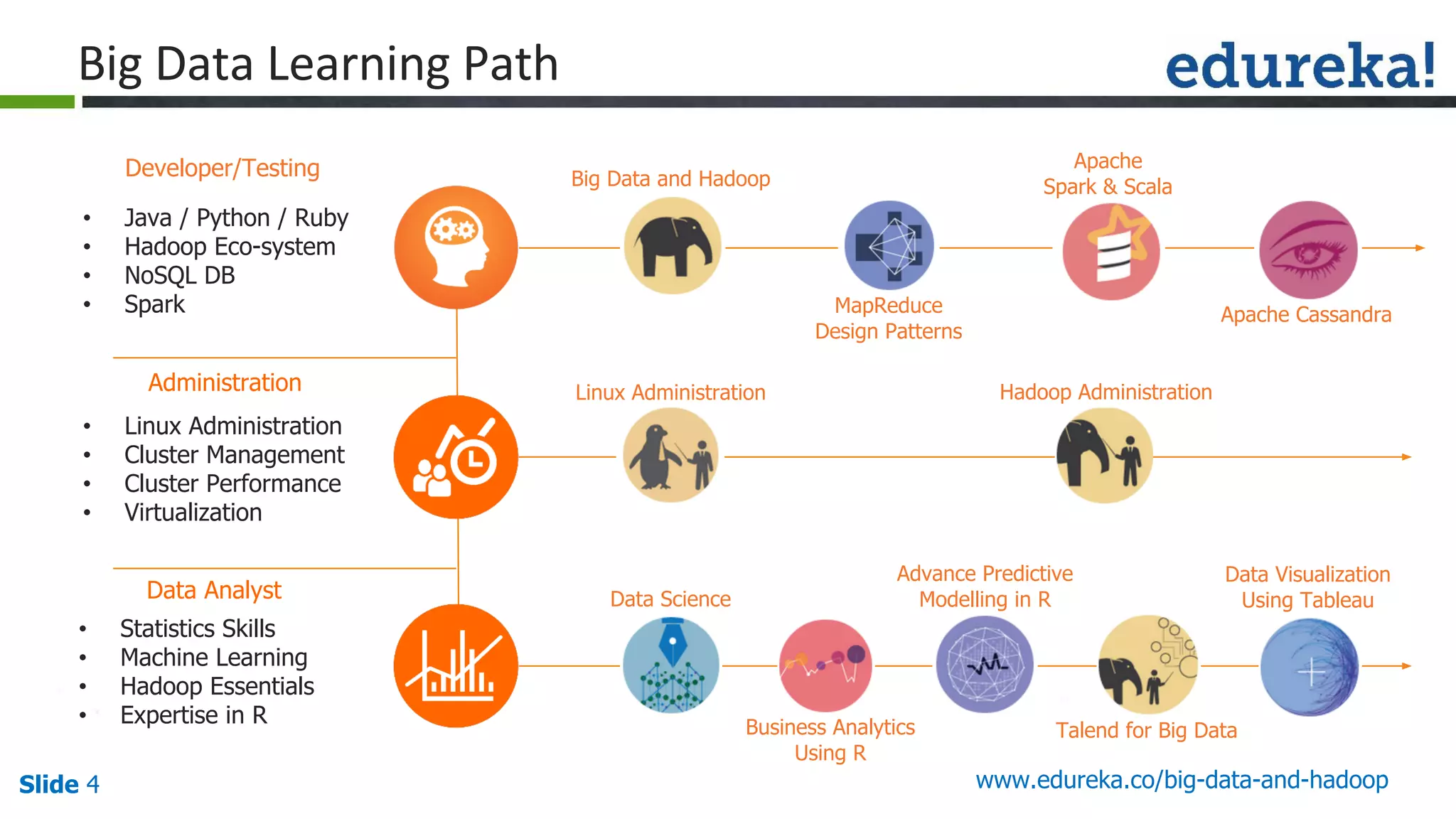
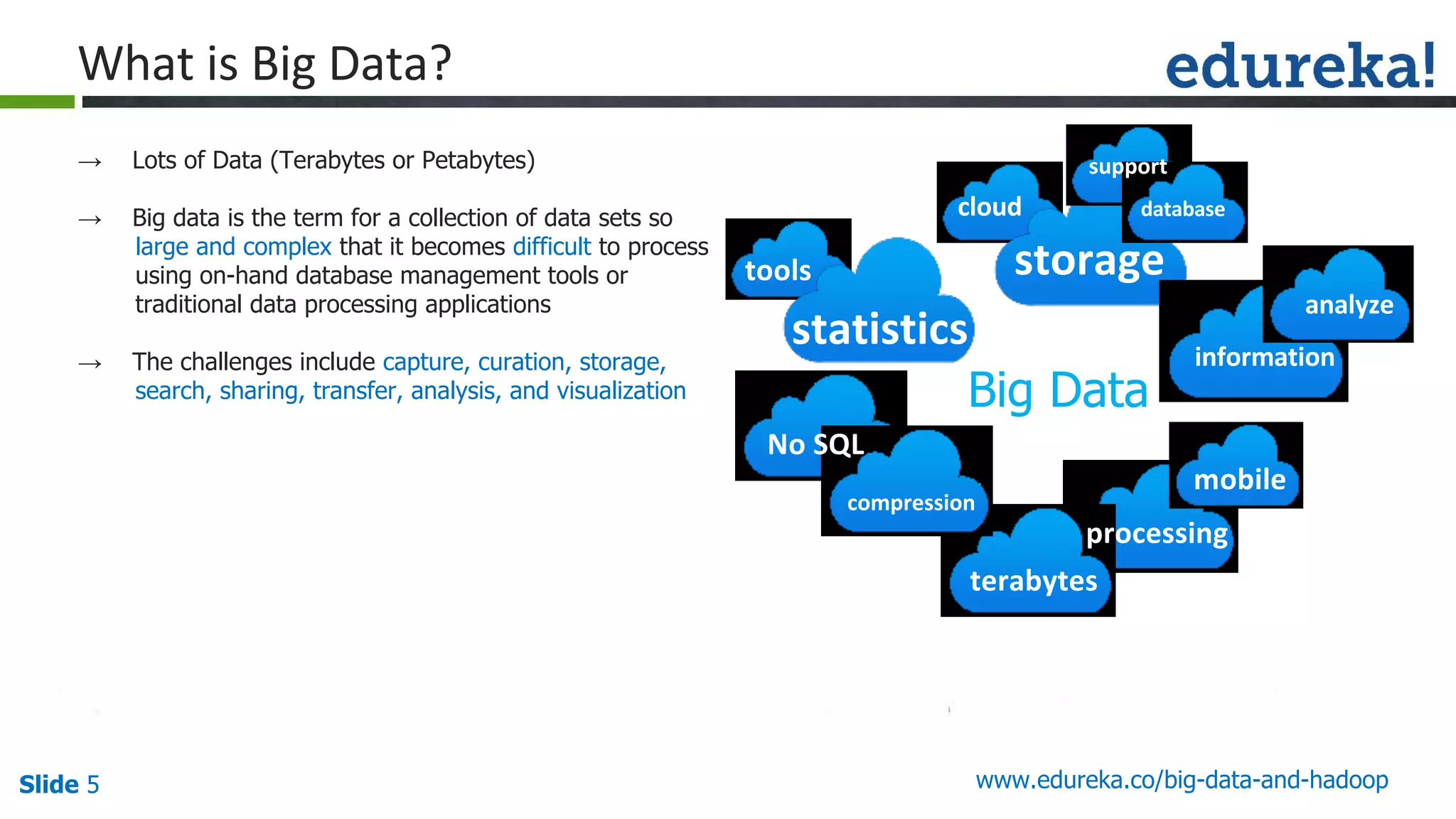
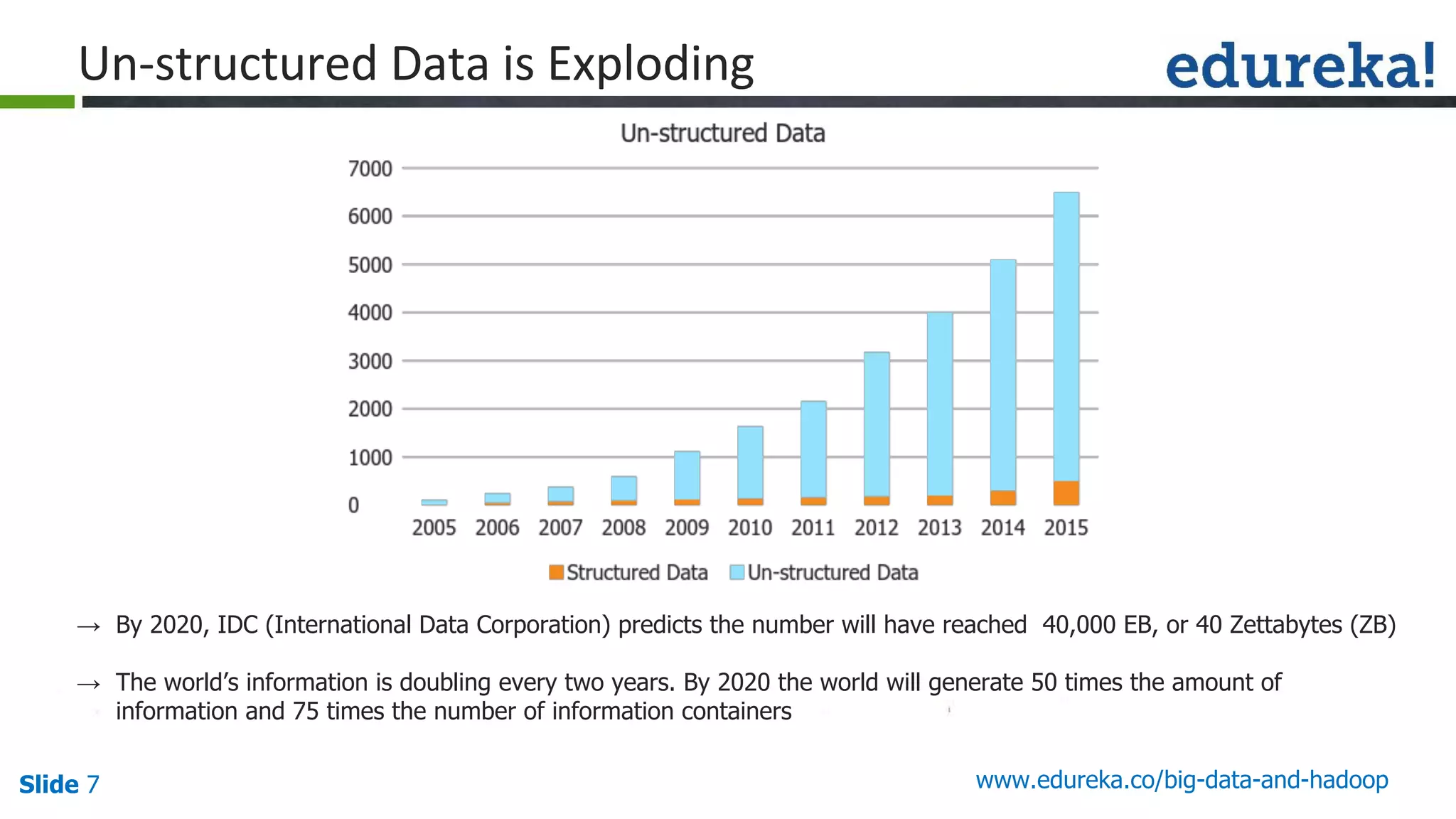
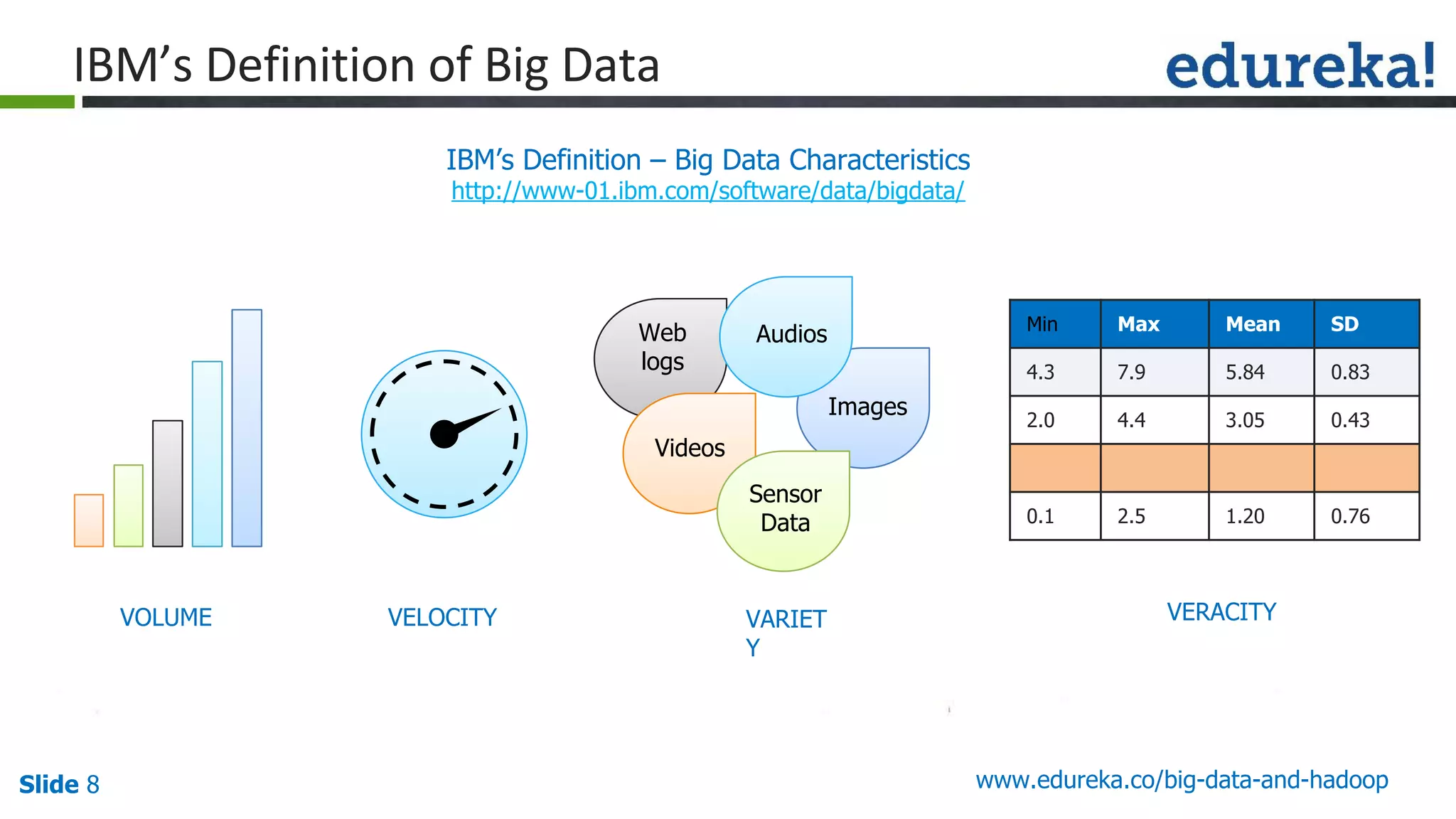
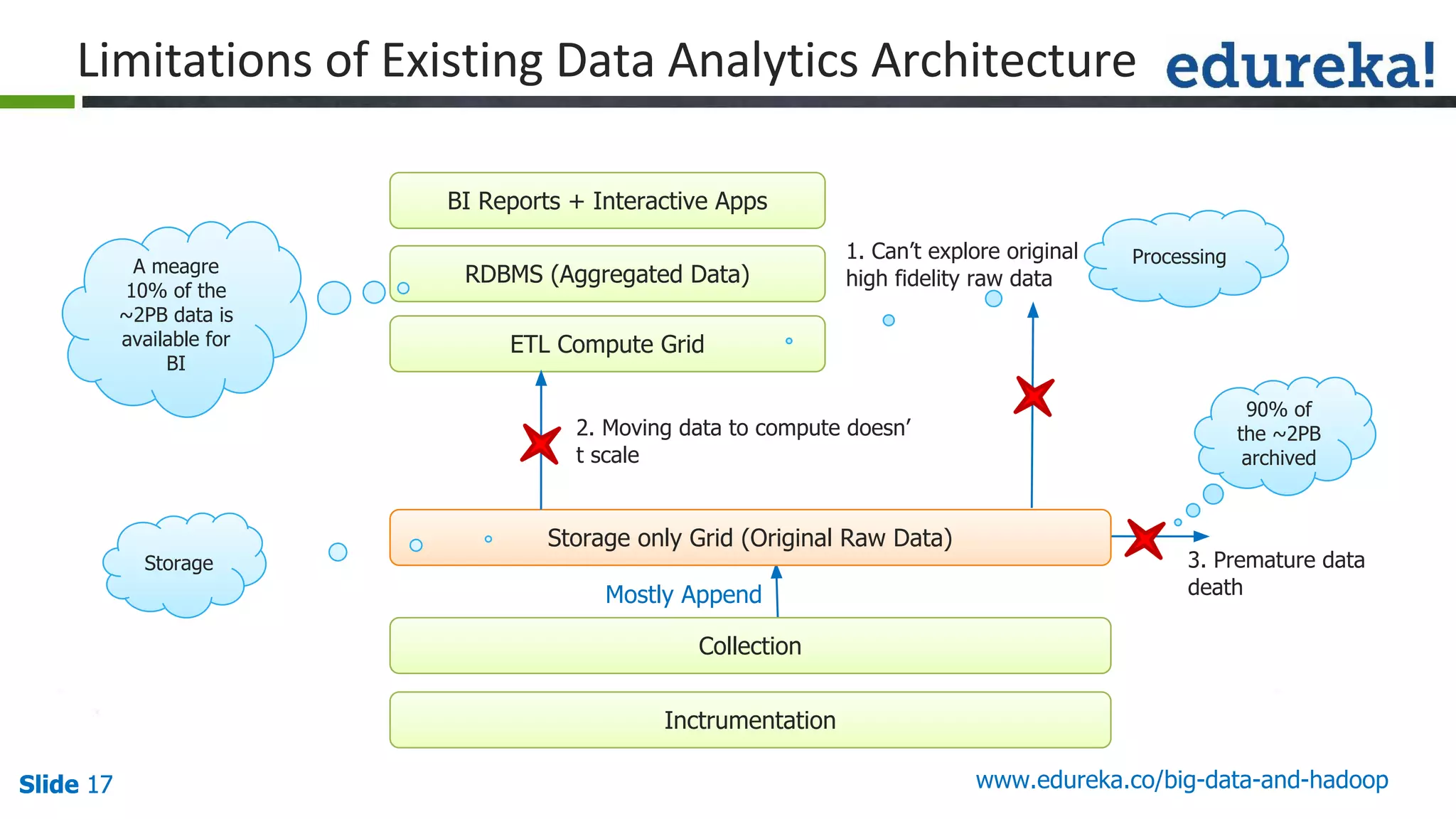
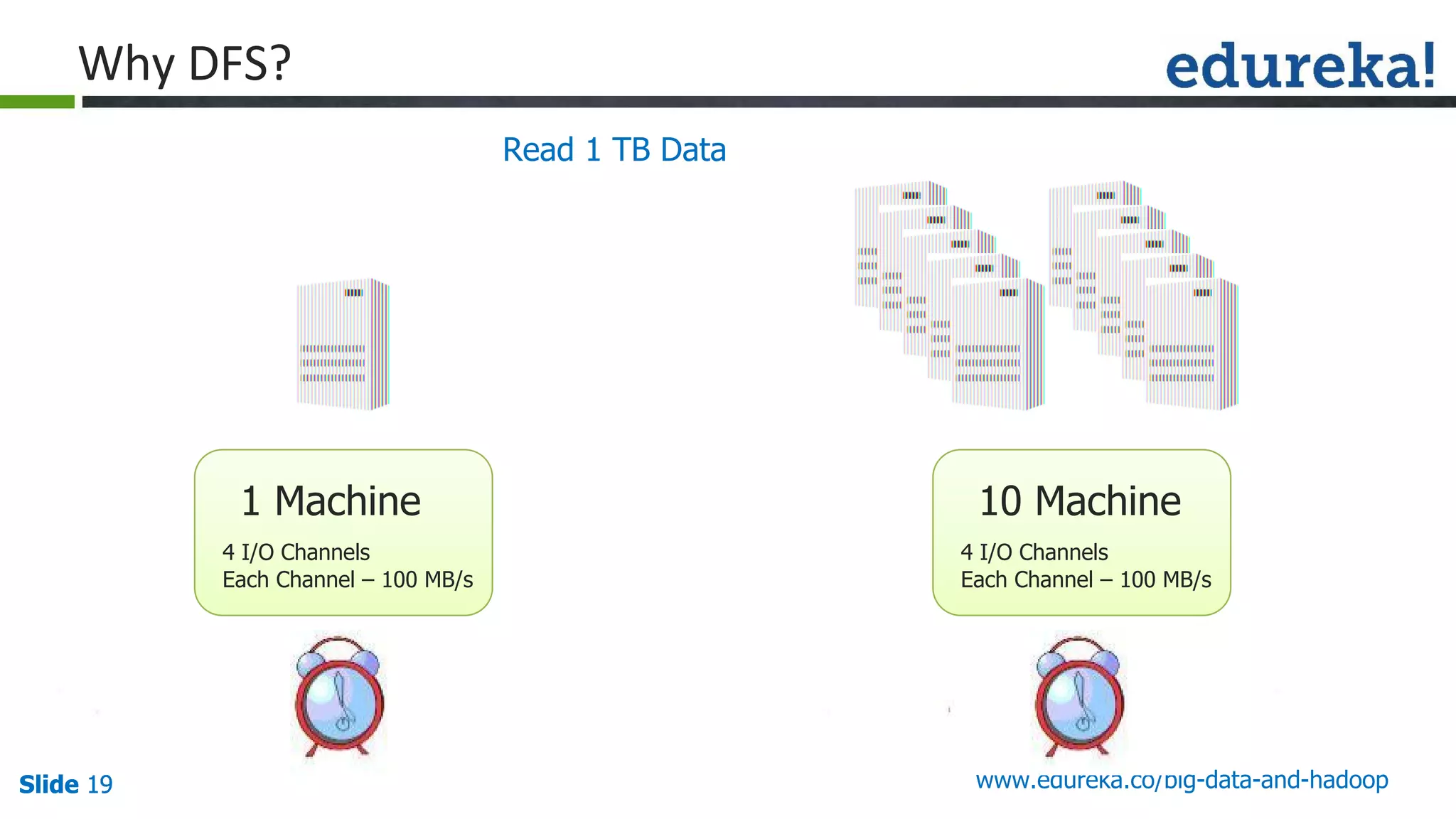
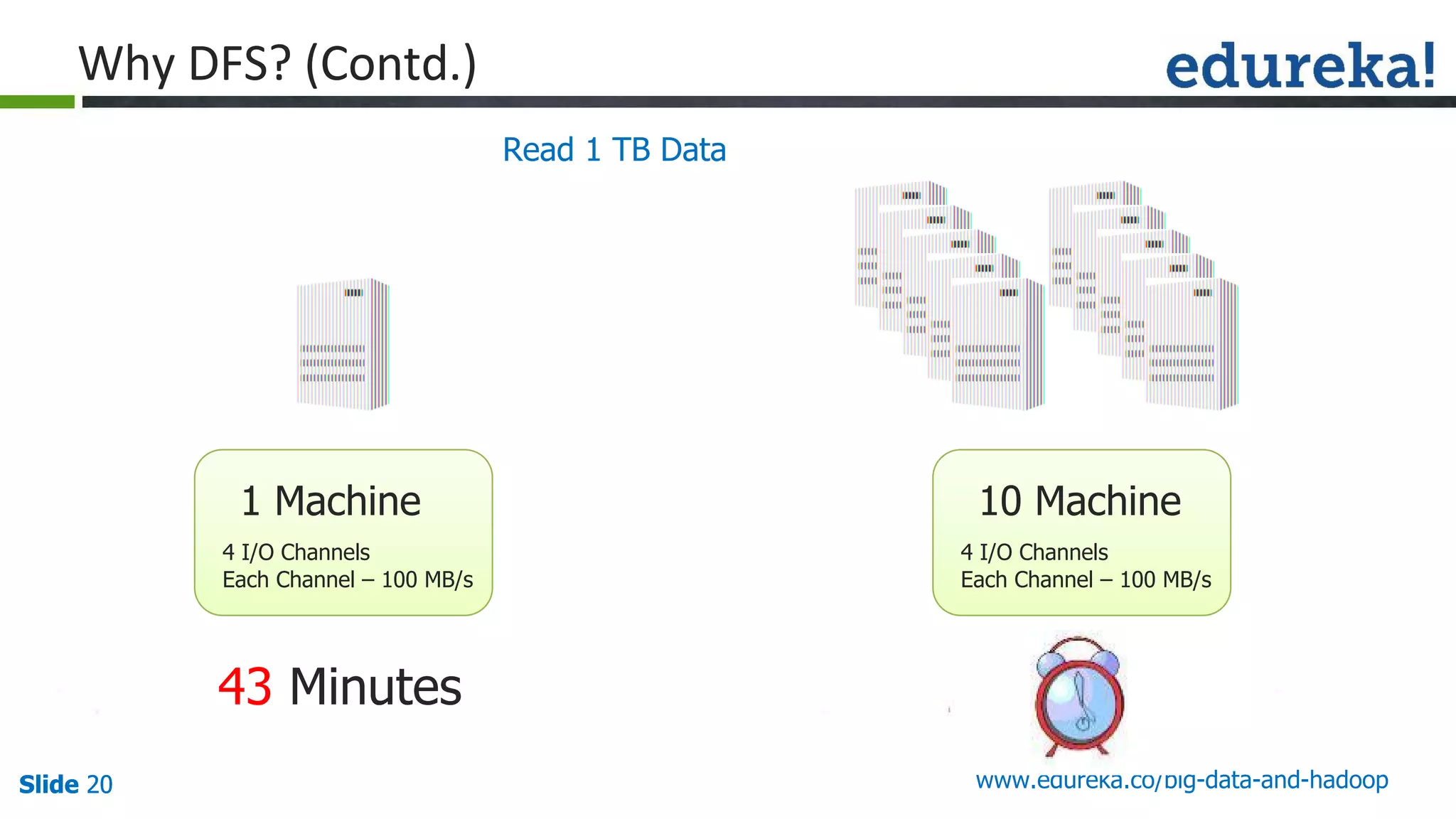
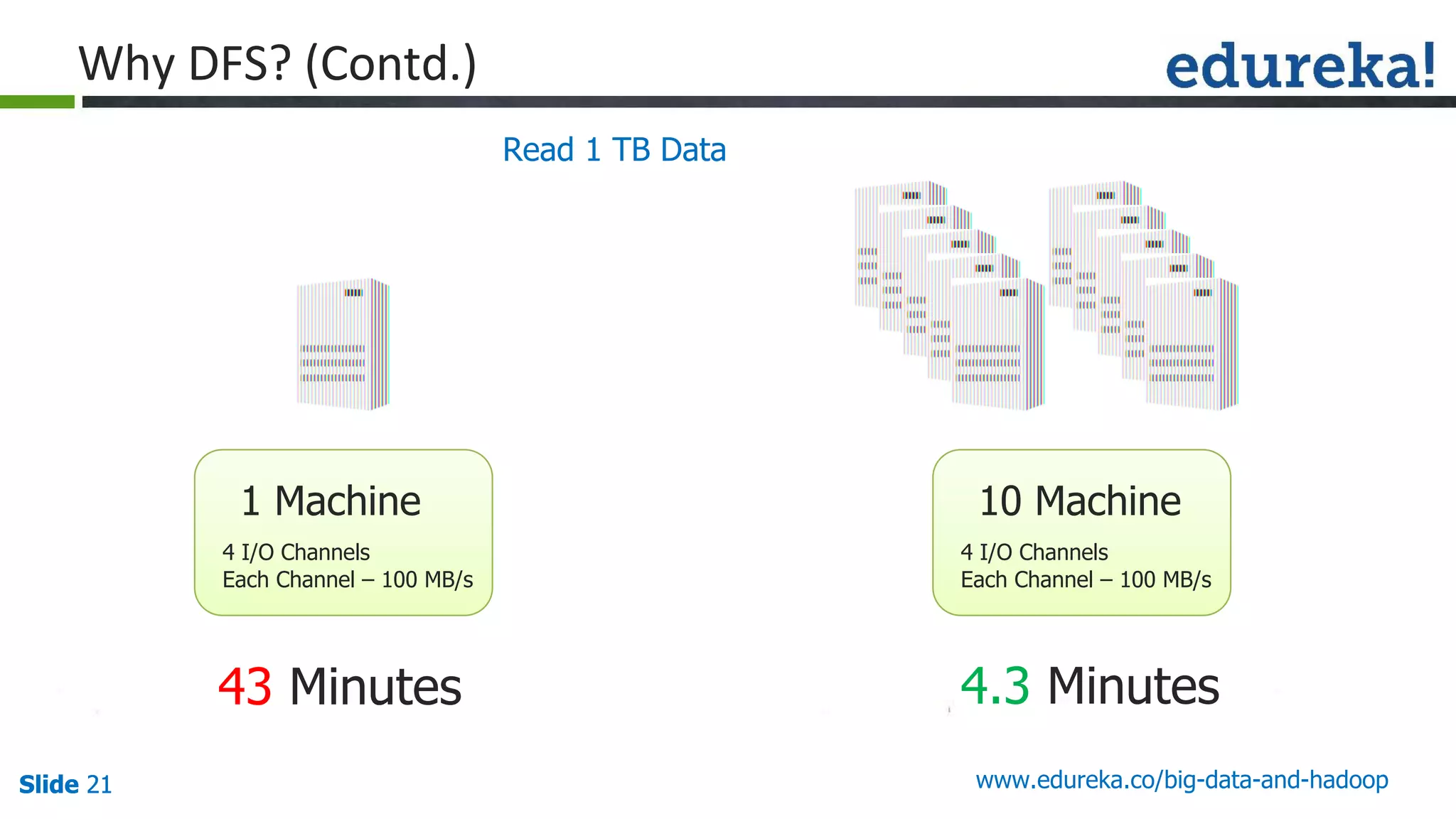
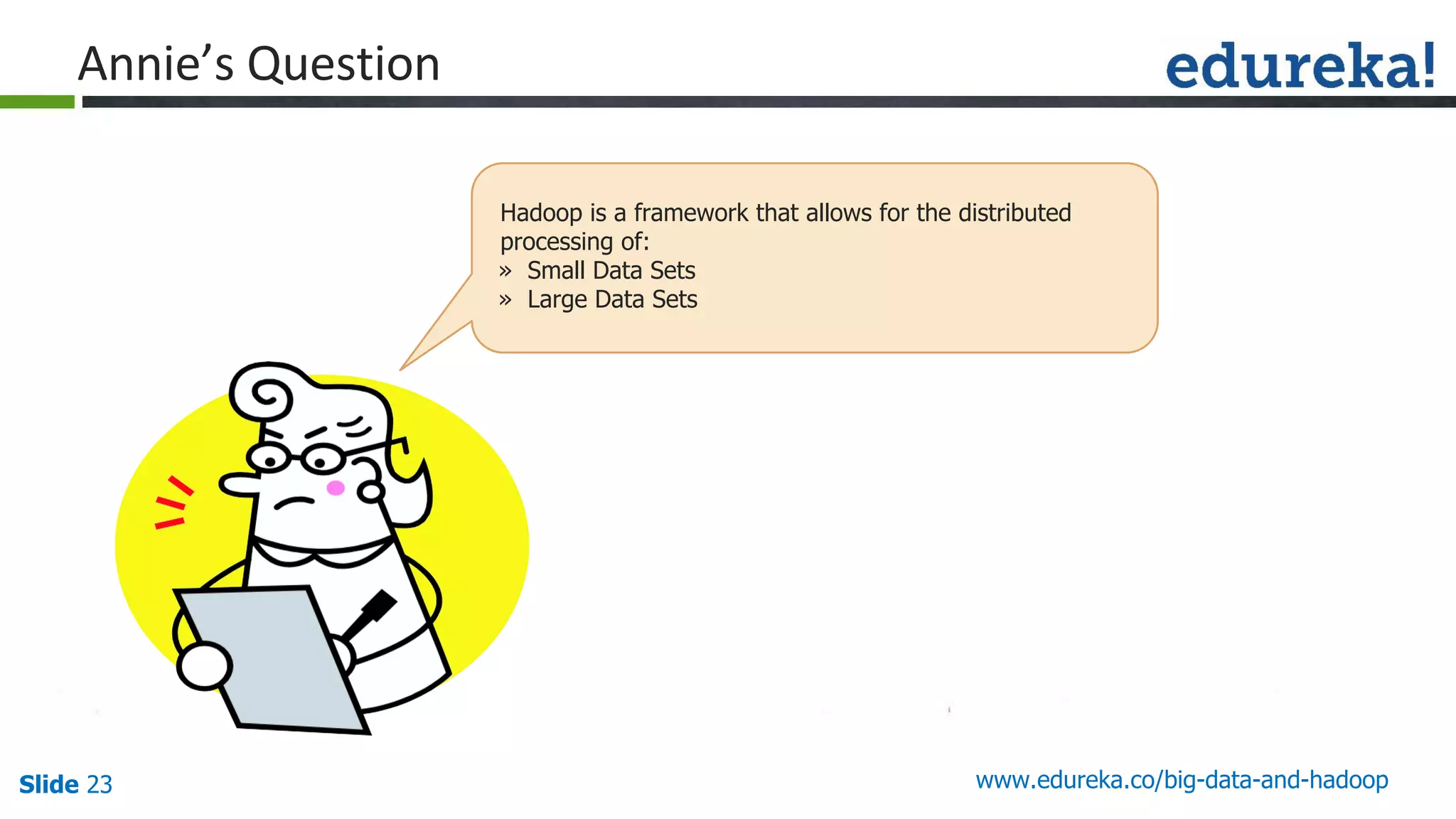
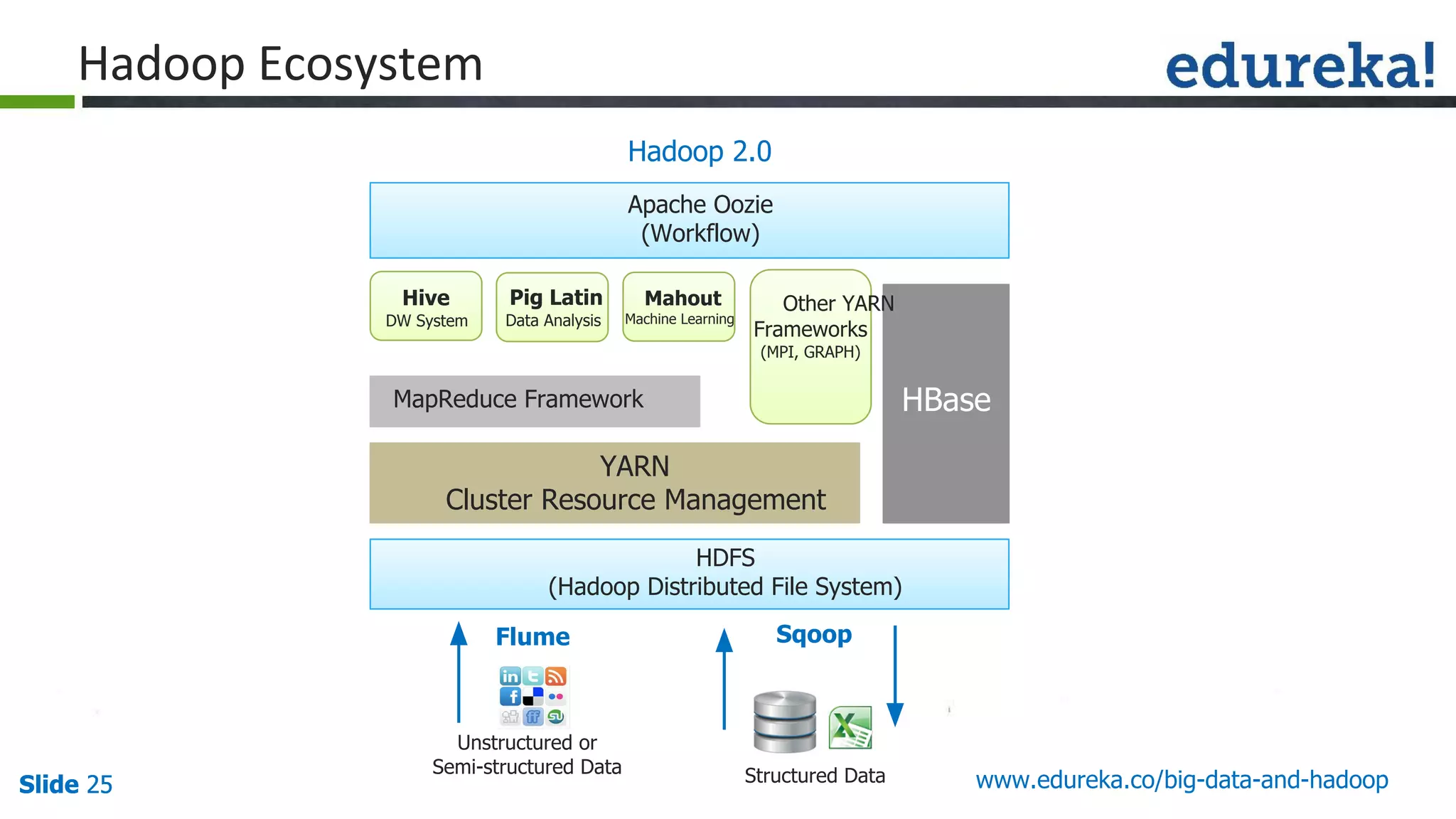
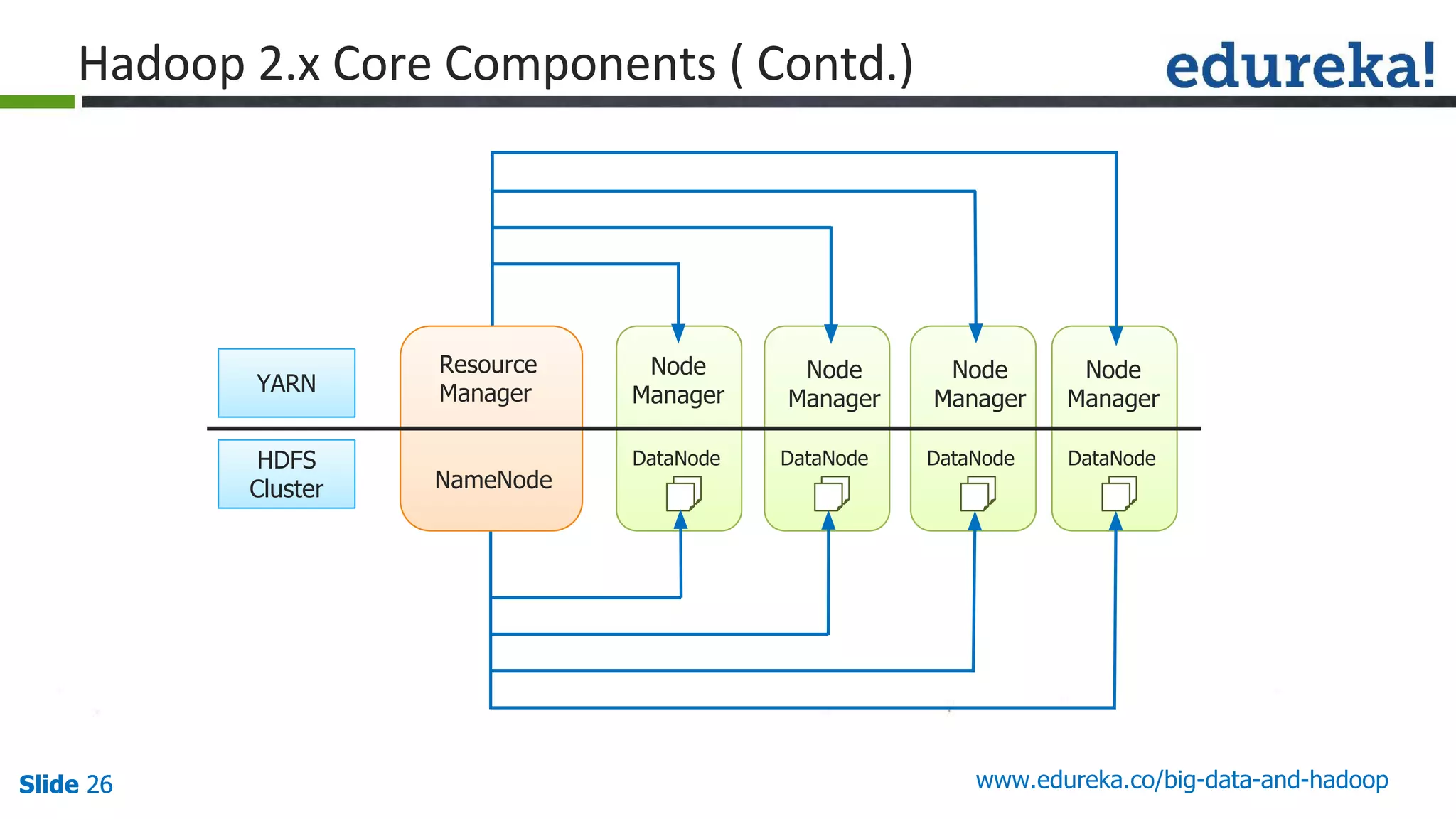
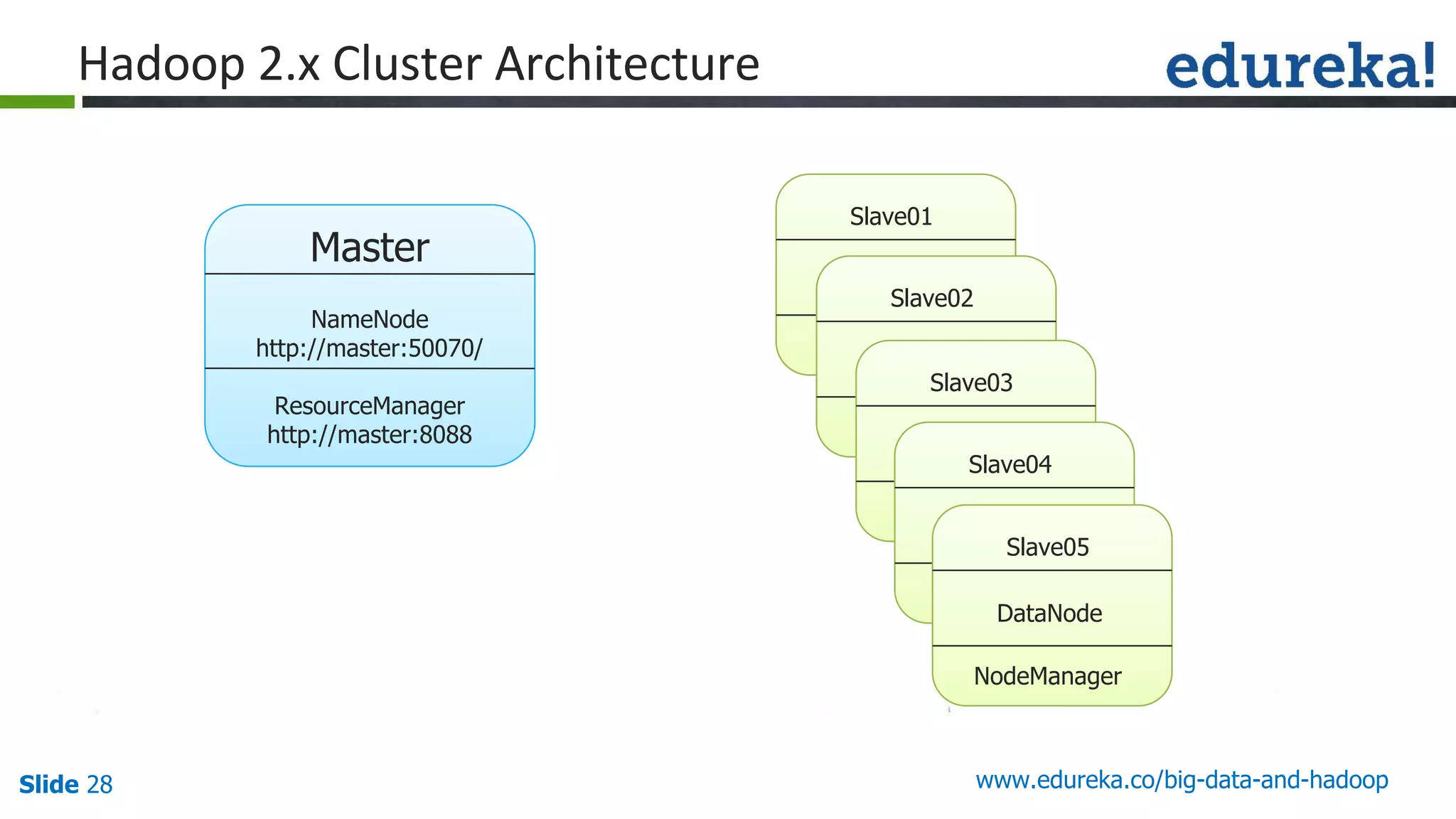
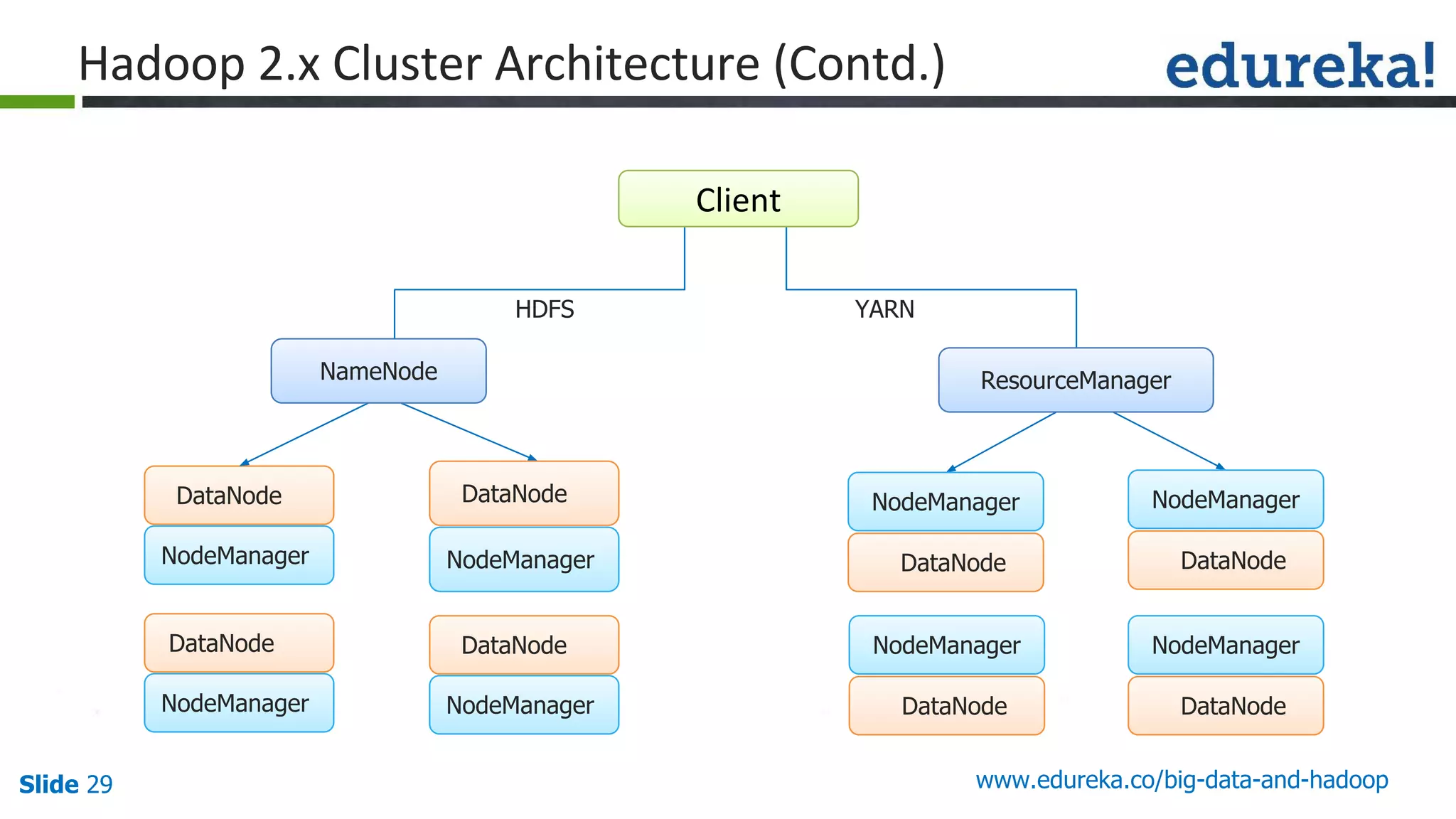
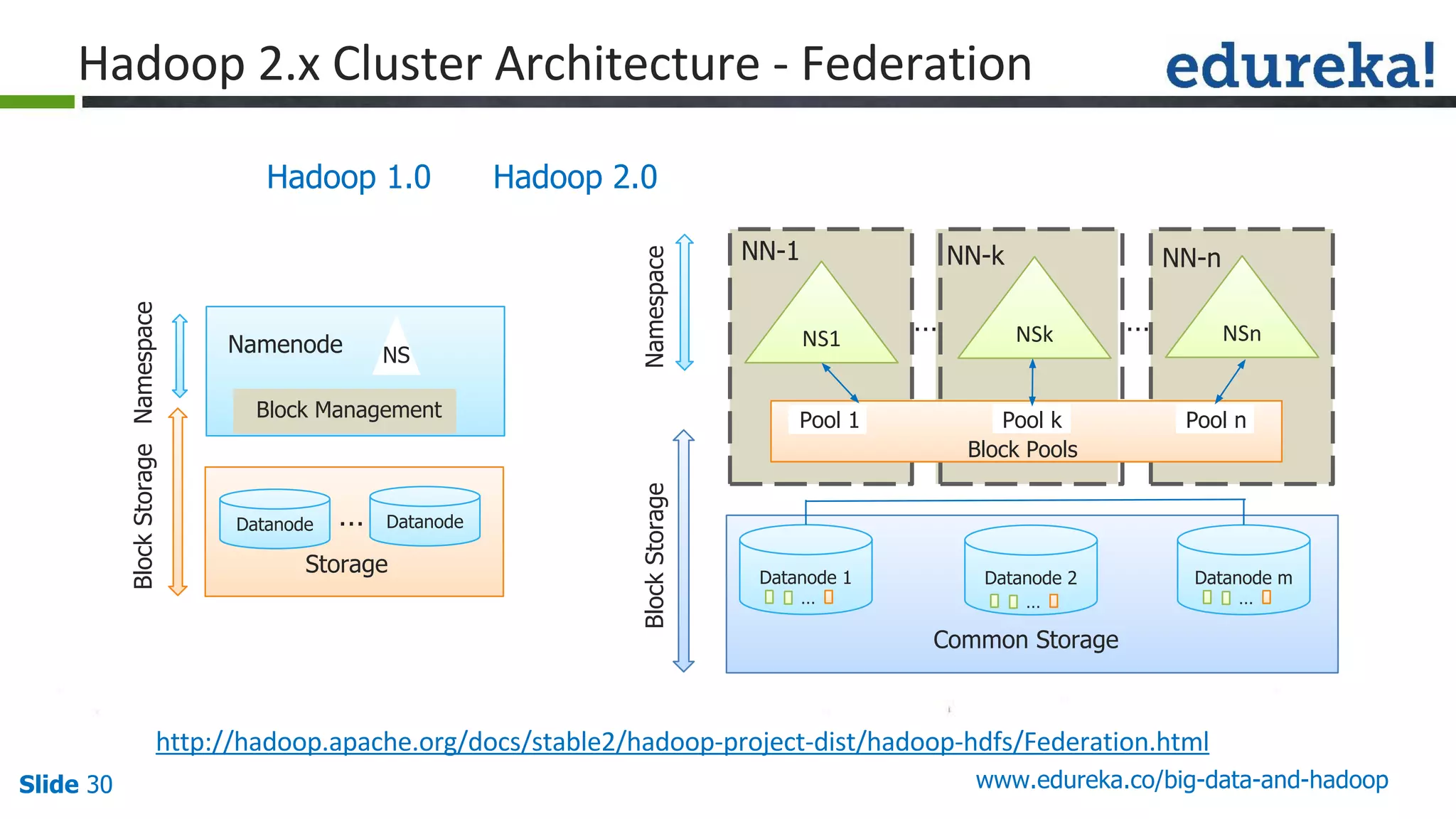
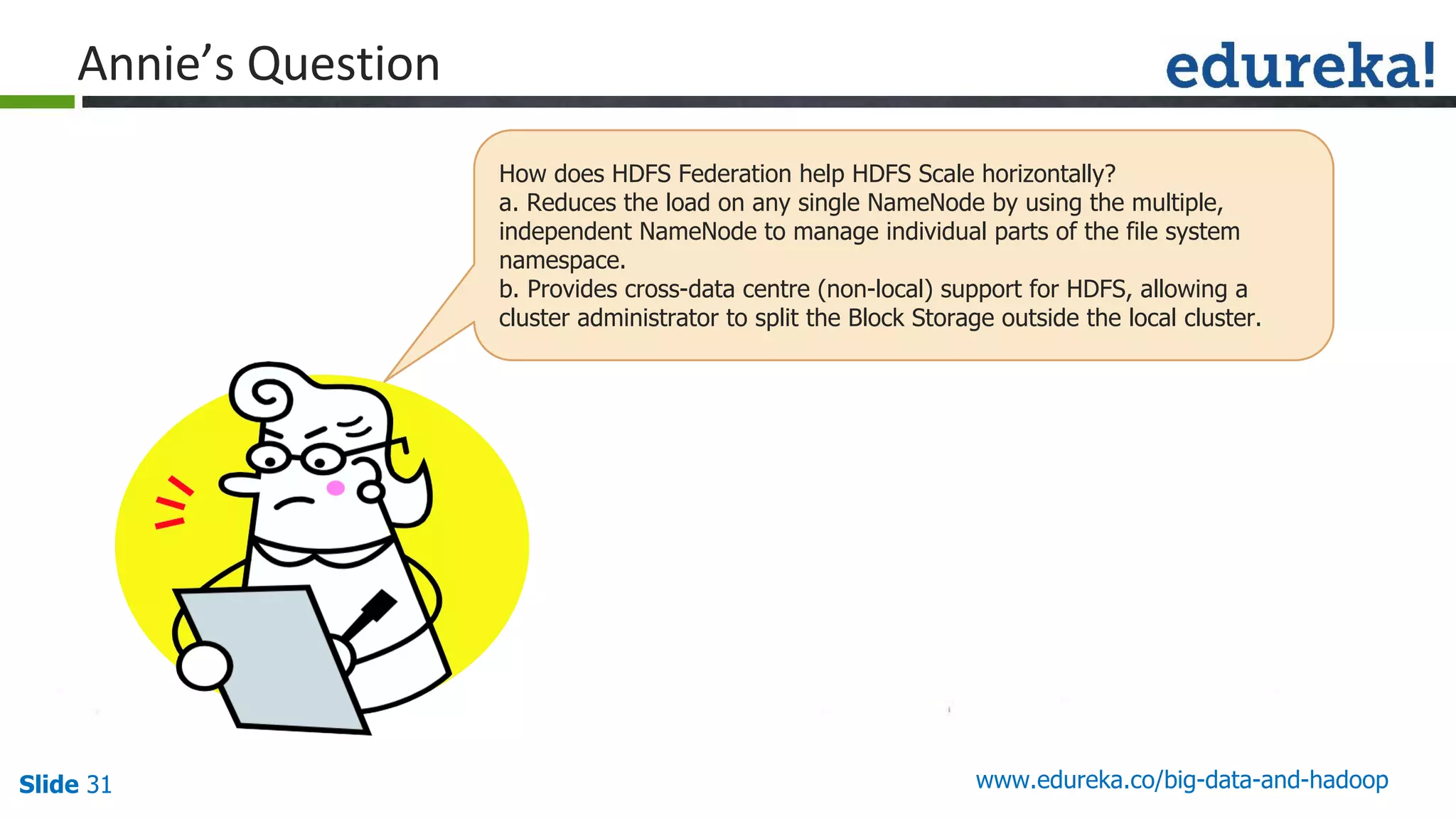
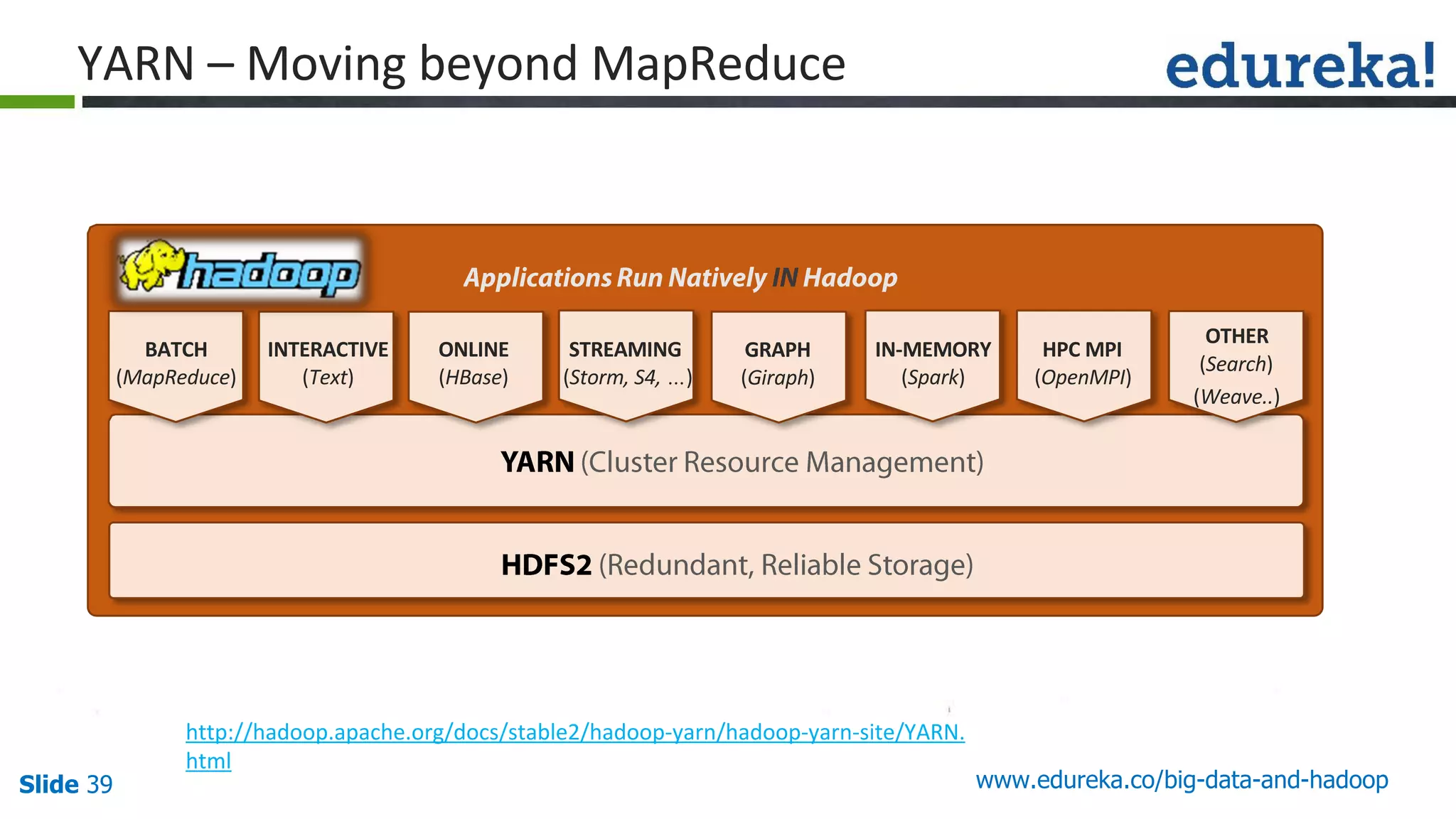
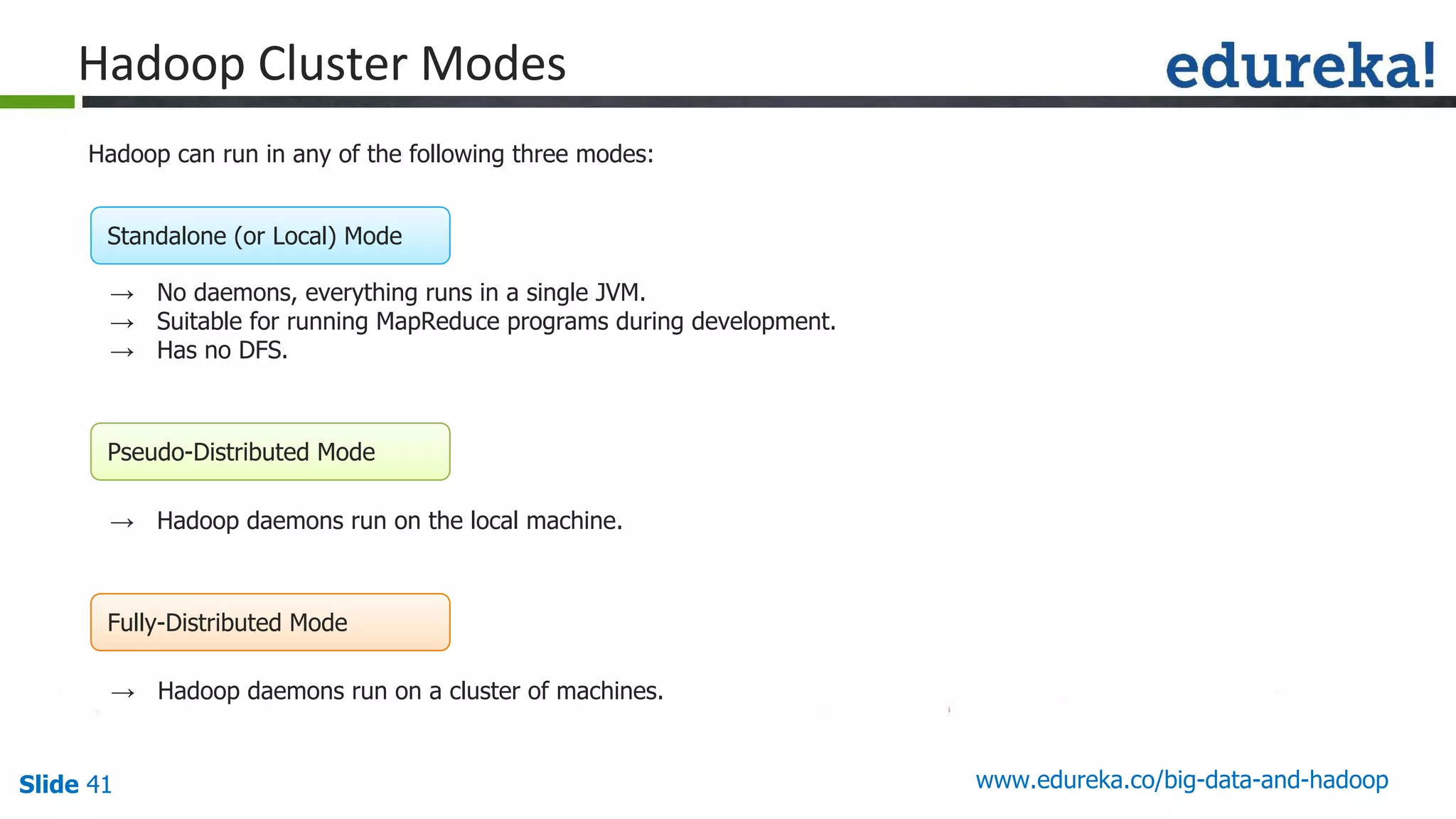
The document provides an introduction to big data and Hadoop, detailing its ecosystem, architecture, and the skills required to work with it. It explains the challenges of big data, including its volume, variety, and velocity, and highlights its applications across various sectors like banking, healthcare, and telecommunications. Additionally, it discusses Hadoop's framework for distributed processing of large datasets and its advantages over traditional data processing systems.