The document provides information on how the internet works including:
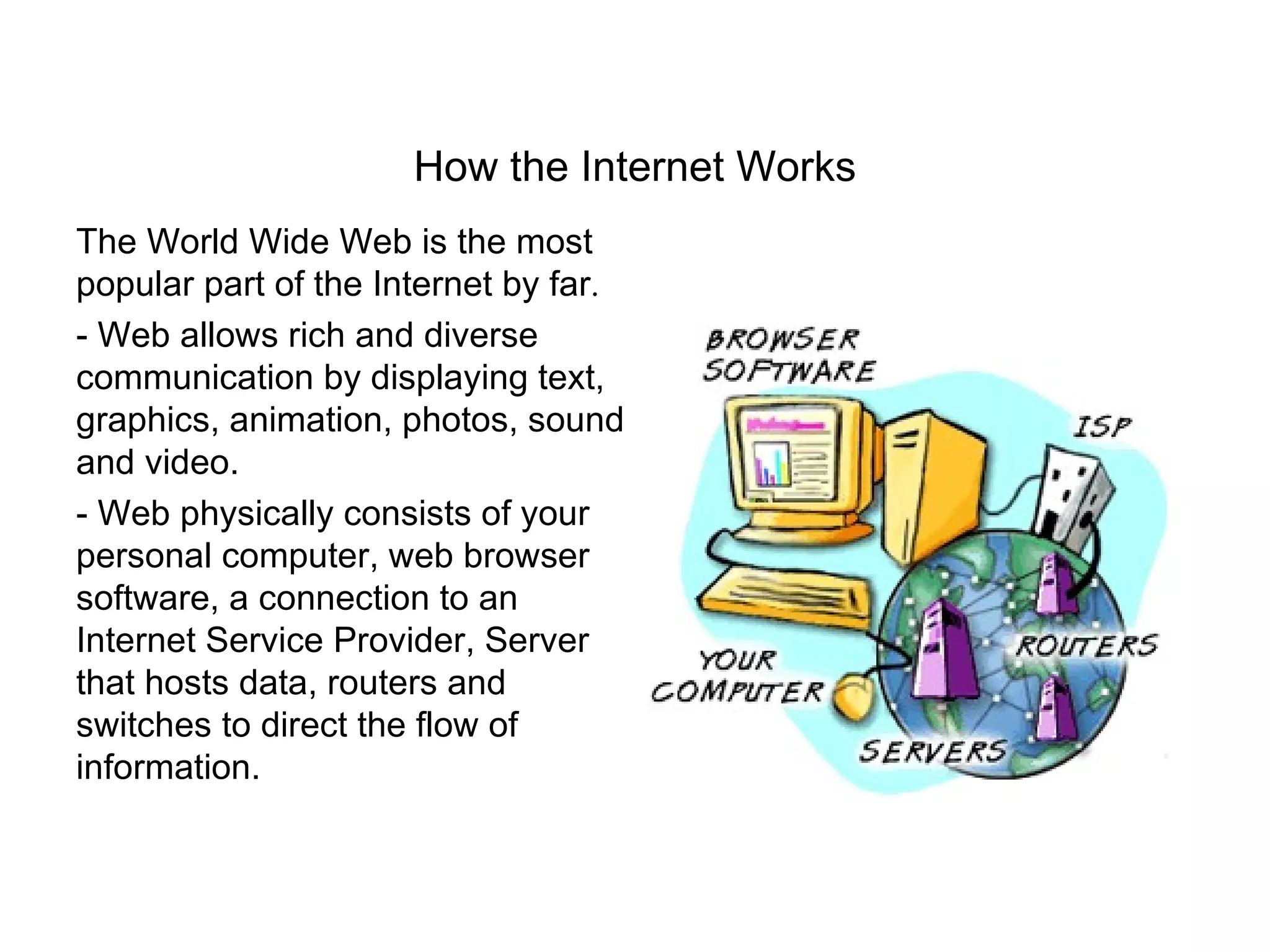
- The World Wide Web is one component of the internet that allows for rich communication through text, graphics, sound and video. It consists of computers, browsers, internet connections, servers, and routers.
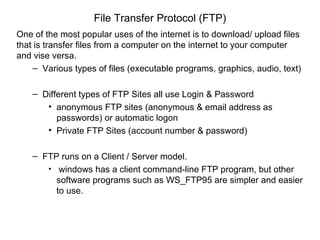
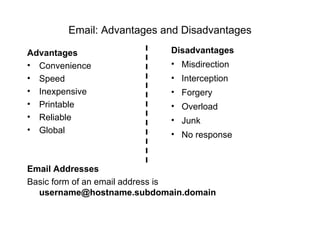
- Other internet components include email, FTP, Usenet news, telnet, chat/instant messaging, and HTTP.
- The World Wide Web uses hypertext and hyperlinks to provide non-linear browsing of graphical and interactive web pages through browsers and servers.